Keyloggers are software or hardware tools used in surveillance to monitor and record keystrokes typed on a computer. These devices capture sensitive data such as passwords, emails, and instant messages, enabling organizations or individuals to track user activity discreetly. In corporate environments, keyloggers help ensure compliance with security policies by detecting unauthorized access or data breaches. A common example of a keylogger in surveillance is the use of hardware keyloggers attached between a keyboard and computer, which silently record all typed inputs. Software-based keyloggers operate invisibly in the background, often employed by cybersecurity teams to analyze potential insider threats. Both types generate detailed reports that provide comprehensive insight into user behavior and information flow during surveillance operations.
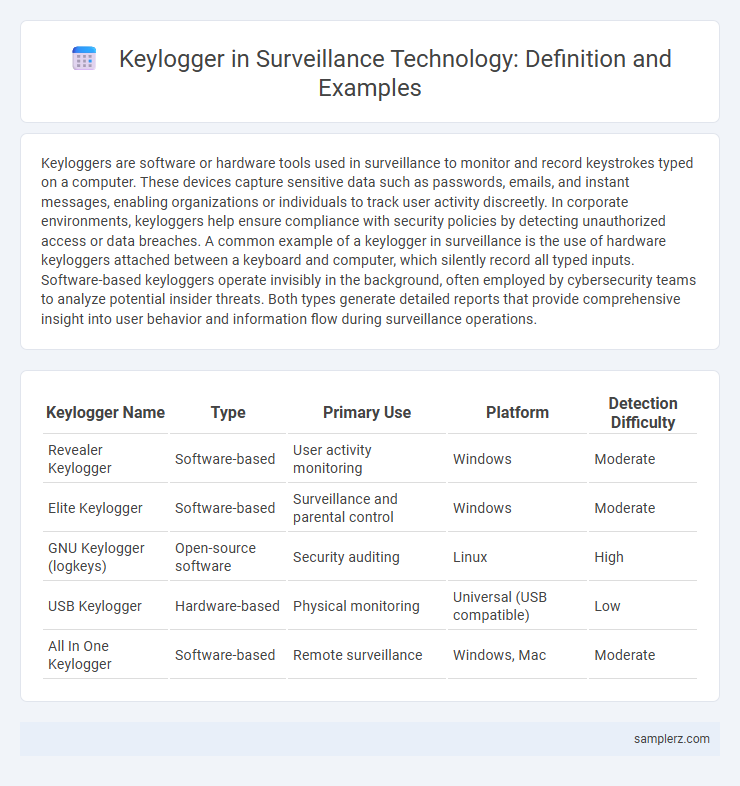
Table of Comparison
| Keylogger Name | Type | Primary Use | Platform | Detection Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revealer Keylogger | Software-based | User activity monitoring | Windows | Moderate |
| Elite Keylogger | Software-based | Surveillance and parental control | Windows | Moderate |
| GNU Keylogger (logkeys) | Open-source software | Security auditing | Linux | High |
| USB Keylogger | Hardware-based | Physical monitoring | Universal (USB compatible) | Low |
| All In One Keylogger | Software-based | Remote surveillance | Windows, Mac | Moderate |
Understanding Keyloggers in Digital Surveillance
Keyloggers, a type of surveillance software, covertly record keystrokes on devices, enabling the capture of passwords, messages, and sensitive data. Widely used in cybersecurity monitoring and employee supervision, keyloggers can operate at the hardware or software level, often evading detection by antivirus programs. Understanding keylogger mechanisms is essential for developing effective countermeasures against unauthorized digital surveillance.
Notable Keylogger Tools Used in Surveillance
Notable keylogger tools used in surveillance include software like Refog Keylogger, known for extensive monitoring capabilities across Windows and macOS platforms, and Spyrix Keylogger, which offers features such as screenshot capturing and remote monitoring. Another prominent tool is Ardamax Keylogger, favored for its stealth operation and detailed keystroke logging, making it valuable for both parental and employee surveillance. These keyloggers integrate advanced data encryption and reporting features, ensuring comprehensive tracking of user activity without detection.
Keylogger Hardware Devices in Security Monitoring
Keylogger hardware devices are crucial in security monitoring, capturing keystrokes directly from keyboards to track user activity without detection. These devices, often connected between the keyboard and computer, provide reliable data access for forensic investigations and insider threat prevention. Their discrete design enables continuous surveillance in high-security environments, enhancing overall cybersecurity measures.
Popular Software-Based Keyloggers in Surveillance Operations
Popular software-based keyloggers used in surveillance operations include tools like Actual Keylogger, Refog Keylogger, and KidLogger, each offering comprehensive monitoring features such as keystroke capturing, screenshot recording, and application tracking. These keyloggers enable organizations and security professionals to covertly track user activity on computers and mobile devices, enhancing insider threat detection and data loss prevention. Their integration with remote monitoring systems ensures real-time data collection and seamless analysis for effective surveillance management.
Keylogger Integration in Commercial Surveillance Systems
Keylogger integration in commercial surveillance systems enhances monitoring capabilities by capturing detailed keystroke data alongside video feeds, enabling comprehensive user activity tracking. These systems often utilize advanced software-based keyloggers compatible with various operating systems to ensure seamless embedding into existing security infrastructures. Real-time alerts and encrypted data storage improve both the efficiency and security of surveillance operations in corporate environments.
Legal and Ethical Aspects of Surveillance Keyloggers
Surveillance keyloggers like Spyrix and Refog are often employed for monitoring employee activities, raising significant legal and ethical considerations regarding consent and privacy rights. In many jurisdictions, explicit consent is required before installation, and unauthorized use can lead to severe legal penalties including invasion of privacy lawsuits. Ethical guidelines emphasize transparency and proportionality, ensuring keylogger use respects individual freedoms while supporting legitimate security needs.
Real-World Case Studies: Keyloggers in Surveillance
One prominent real-world case involving keyloggers in surveillance is the 2013 Target data breach, where attackers used keylogging malware to capture employee credentials, resulting in the theft of 40 million credit and debit card records. Another example includes government surveillance programs utilizing specialized keylogger tools to monitor suspects' keystrokes to gather intelligence during counterterrorism operations. Corporate espionage cases also reveal keyloggers deployed to track competitor activities, demonstrating the tool's extensive application in unauthorized digital surveillance.
Detecting Keyloggers in Surveillance Environments
Detecting keyloggers in surveillance environments involves analyzing system behavior for unusual keystroke logging activities and monitoring network traffic for unauthorized data transmission. Advanced techniques include using heuristic-based antivirus software and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to identify suspicious processes that mimic legitimate surveillance operations. Regular audits and real-time monitoring enhance the ability to uncover hardware or software keyloggers deployed to capture sensitive information covertly.
Advanced Keylogging Techniques in Modern Surveillance
Advanced keylogging techniques in modern surveillance employ sophisticated methods such as kernel-based keyloggers, which operate at the system core to evade detection by antivirus software. These keyloggers capture keystrokes with high accuracy and can intercept encrypted inputs by integrating with system drivers or using hardware devices placed between the keyboard and computer. Integration with remote monitoring tools and AI-driven analytics enhances the ability to analyze captured data in real-time, making keylogging a critical component in comprehensive surveillance frameworks.
Countermeasures Against Keylogger-Based Surveillance
Effective countermeasures against keylogger-based surveillance include deploying reputable anti-malware software that detects and removes keylogging programs, and enabling multi-factor authentication to reduce the risk posed by compromised credentials. Regularly updating operating systems and applications patches vulnerabilities exploited by keyloggers, while using virtual keyboards or password managers can limit keystroke capture. Network monitoring tools also help identify unusual data transmissions indicative of keylogger activity, strengthening overall surveillance defense.
example of keylogger in surveillance Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com