A sandbox in code isolation is a secure environment that restricts the execution of untrusted code to prevent harmful effects on the host system. Developers use sandboxes to test new software, ensuring that any malicious or faulty operations do not affect the overall system integrity. Common examples include browser sandboxes that isolate web page scripts and mobile app sandboxes restricting app permissions on smartphones. In software development, container technologies like Docker serve as advanced sandboxes, isolating applications and their dependencies from the host operating system. Virtual machines also provide sandboxing by creating separate environments that mimic hardware, safeguarding the main system from potential security threats. These sandboxing methods help organizations improve security and maintain stable development workflows by containing code within controlled boundaries.
Table of Comparison
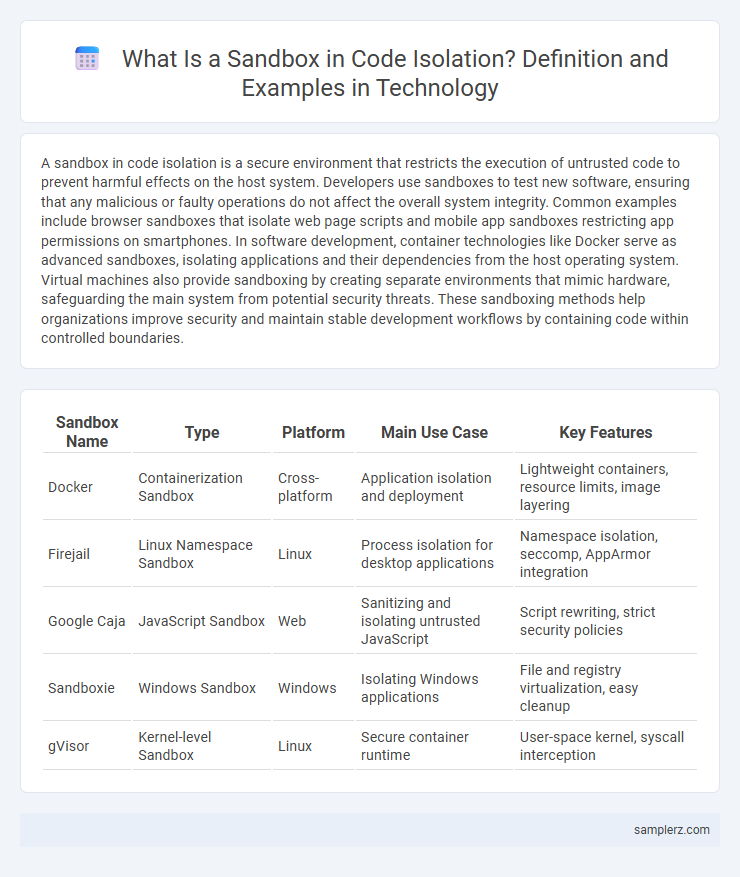
| Sandbox Name | Type | Platform | Main Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Docker | Containerization Sandbox | Cross-platform | Application isolation and deployment | Lightweight containers, resource limits, image layering |
| Firejail | Linux Namespace Sandbox | Linux | Process isolation for desktop applications | Namespace isolation, seccomp, AppArmor integration |
| Google Caja | JavaScript Sandbox | Web | Sanitizing and isolating untrusted JavaScript | Script rewriting, strict security policies |
| Sandboxie | Windows Sandbox | Windows | Isolating Windows applications | File and registry virtualization, easy cleanup |
| gVisor | Kernel-level Sandbox | Linux | Secure container runtime | User-space kernel, syscall interception |
Introduction to Sandbox Environments in Code Isolation
Sandbox environments in code isolation provide a secure space for developers to execute and test code safely, preventing potential harm to the host system. These isolated environments replicate real-world conditions, allowing thorough debugging and experimentation without risking the integrity of production systems. Popular sandbox technologies include Docker containers, virtual machines, and specialized frameworks like Google's Native Client, which enforce strict resource controls and limit access to critical system components.
Key Benefits of Code Sandbox Implementation
Code sandbox implementation enhances security by isolating untrusted code, preventing harmful access to the host system and sensitive data. It improves debugging efficiency as developers can test snippets in a controlled environment without affecting the main application. This isolation also facilitates safe experimentation with new features, accelerating innovation while minimizing production risks.
Classic Examples of Sandboxing in Programming Languages
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) exemplifies sandboxing by isolating Java bytecode execution, preventing unauthorized access to system resources. WebAssembly's sandbox enforces strict memory safety and execution limits, enabling secure run of untrusted code in web browsers. Python's use of restricted execution environments, though limited, demonstrates sandboxing attempts through modules like RestrictedPython to control code behavior.
Virtual Machines vs. Containers: Sandbox Comparison
Virtual Machines (VMs) provide a robust sandbox environment by isolating code within separate operating systems, ensuring strong security boundaries but requiring more resources and slower startup times. Containers offer lightweight sandboxing by sharing the host OS kernel while isolating applications at the process level, enabling faster deployment and efficient resource utilization but with a smaller security boundary compared to VMs. Choosing between VMs and containers depends on the required balance between isolation strength, performance, and resource constraints in the code isolation strategy.
Using Docker as a Sandbox for Application Testing
Docker provides an efficient sandbox environment for application testing by isolating code within lightweight, containerized instances that replicate production settings. This containerization ensures consistent test results and prevents dependencies from interfering with local systems or other applications. Utilizing Docker as a sandbox streamlines continuous integration and deployment workflows by enabling rapid environment setup and teardown.
Browser-Based Code Sandboxes for Web Development
Browser-based code sandboxes like CodeSandbox and StackBlitz provide secure environments for web development by isolating code execution within virtual containers. These platforms enable real-time collaboration, instant preview, and support for JavaScript frameworks such as React, Vue, and Angular, enhancing developer productivity. By running code in isolated browser iframes or Web Workers, they prevent system-level access and protect against malicious code execution during testing and debugging.
JavaScript Sandbox Engines: Safe Script Execution
JavaScript sandbox engines, such as Google Caja and SES (Secure EcmaScript), enable safe script execution by isolating untrusted code within controlled environments that prevent access to the global scope and sensitive APIs. These sandboxes enforce strict security policies and utilize realm-based isolation to mitigate risks like cross-site scripting (XSS) and data leakage. By leveraging techniques such as membrane proxies and capability-based security, JavaScript sandbox engines ensure safe execution without compromising application integrity or performance.
Secure Mobile App Development with Sandboxed Environments
Sandboxed environments in secure mobile app development create isolated containers where code executes independently, preventing unauthorized access to the device's operating system and user data. Technologies like Android's Work Profiles and iOS App Sandbox enforce strict boundaries, minimizing risks from malicious code or vulnerabilities during runtime. Leveraging sandboxing enhances app security by containing potential threats, ensuring data integrity, and complying with privacy standards such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Code Isolation Strategies in Cloud Sandboxes
Cloud sandboxes employ code isolation strategies such as namespace isolation, containerization with Docker, and virtual machines to securely separate execution environments. These methods prevent unauthorized access and mitigate risks by restricting resource sharing and enforcing strict boundaries between user code and host systems. Leveraging Kubernetes namespaces and seccomp profiles further enhances sandbox security by controlling system calls and network access.
Real-world Use Cases of Sandboxes in Cybersecurity
Sandboxes in cybersecurity isolate code execution to prevent malicious software from affecting the host system, commonly used in antivirus testing environments where suspicious files run safely without risking network integrity. Financial institutions deploy sandboxing techniques to analyze potentially harmful email attachments, ensuring malware cannot breach secure systems. Cloud service providers implement sandboxes to detect zero-day exploits during application development, enhancing threat detection before deployment.
example of sandbox in code isolation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com