An air gap in network security refers to the physical isolation of a computer or network from unsecured networks, such as the public internet. This technique ensures that sensitive data and critical systems remain disconnected to prevent unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Air-gapped systems are commonly used in military, financial, and industrial control environments where data confidentiality and integrity are paramount. Data transfer in an air-gapped environment often relies on removable media like USB drives, which are strictly controlled and scanned for malware. This isolation enhances security by minimizing attack vectors, effectively stopping remote hacking attempts. Organizations that implement air gaps significantly reduce the risk of network infiltration and data breaches.
Table of Comparison
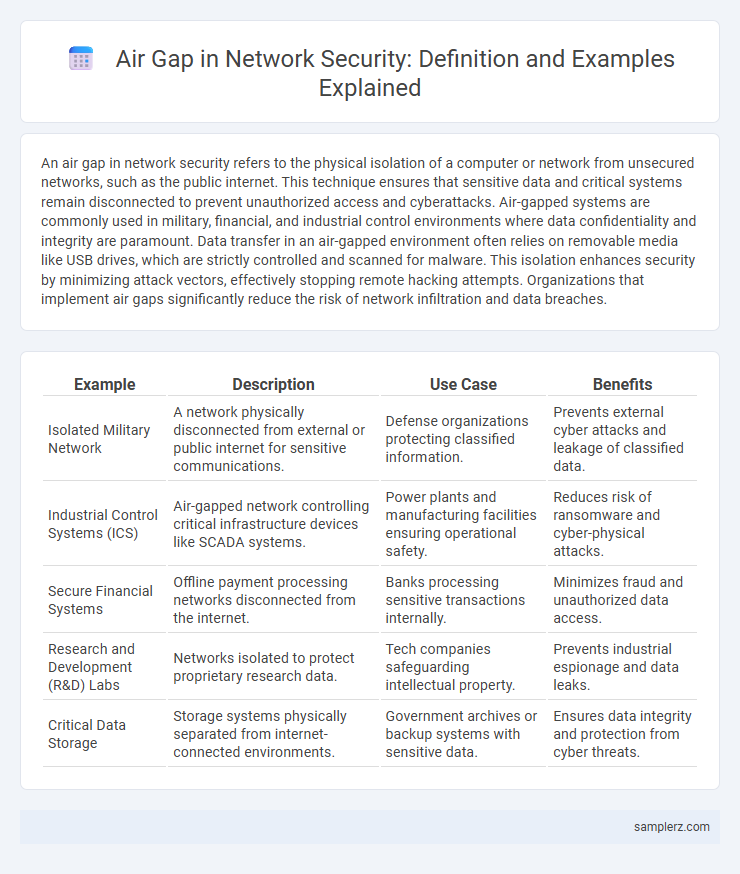
| Example | Description | Use Case | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isolated Military Network | A network physically disconnected from external or public internet for sensitive communications. | Defense organizations protecting classified information. | Prevents external cyber attacks and leakage of classified data. |
| Industrial Control Systems (ICS) | Air-gapped network controlling critical infrastructure devices like SCADA systems. | Power plants and manufacturing facilities ensuring operational safety. | Reduces risk of ransomware and cyber-physical attacks. |
| Secure Financial Systems | Offline payment processing networks disconnected from the internet. | Banks processing sensitive transactions internally. | Minimizes fraud and unauthorized data access. |
| Research and Development (R&D) Labs | Networks isolated to protect proprietary research data. | Tech companies safeguarding intellectual property. | Prevents industrial espionage and data leaks. |
| Critical Data Storage | Storage systems physically separated from internet-connected environments. | Government archives or backup systems with sensitive data. | Ensures data integrity and protection from cyber threats. |
Introduction to Air Gap in Network Security
Air gap in network security refers to a physical isolation method where a secure computer or network is completely disconnected from unsecured networks like the internet, preventing any form of digital communication or data transfer. Common examples include military systems, critical infrastructure controls, and financial institutions that use air-gapped networks to protect sensitive information from cyber threats and unauthorized access. This approach significantly reduces vulnerability to remote hacking by eliminating network connectivity pathways, ensuring robust protection for highly classified data.
Key Principles of Air Gapped Networks
Air-gapped networks physically isolate critical systems from unsecured networks, preventing unauthorized access and cyber threats by eliminating direct digital communication channels. Key principles include strict physical separation, no wireless connectivity, and controlled data transfer through secure, manual methods such as removable media under rigorous protocols. This isolation ensures enhanced protection for sensitive information in environments like military, financial institutions, and critical infrastructure operations.
Real-World Examples of Air Gapped Systems
Air gapped systems isolate critical infrastructure by physically separating them from unsecured networks to prevent cyberattacks, commonly seen in nuclear power plants and military command centers. Financial institutions often use air gaps to protect sensitive data in offline storage devices, ensuring no direct connection to the internet. Industrial control systems in manufacturing also employ air gaps to safeguard against ransomware and remote intrusion attempts.
Air Gap Implementations in Government Agencies
Government agencies often implement air gaps by physically isolating sensitive networks from external internet connections to prevent cyber threats and unauthorized access. Military and intelligence organizations use air-gapped systems for classified information processing, ensuring data remains secure in offline environments. Critical infrastructure sectors employ air gaps for control systems, protecting vital operations from external attacks and malware infiltration.
Industrial Control Systems Utilizing Air Gaps
Industrial Control Systems (ICS) utilize air gaps to isolate critical operational technology networks from external internet connections, effectively preventing cyber threats from infiltrating sensitive infrastructure. In oil refineries and power plants, air-gapped networks ensure that control systems operate independently, reducing risks of ransomware attacks and unauthorized remote access. This physical separation enhances security by restricting data flow and limiting attack vectors, making air gaps a vital defense mechanism in industrial cybersecurity strategies.
Air Gap Use Cases in Financial Institutions
Air gaps in financial institutions are crucial for isolating sensitive systems such as transaction processing servers and customer data repositories from external networks, preventing cyberattacks and data breaches. These air gap use cases often include safeguarding critical infrastructure like ATMs, payment processing terminals, and internal audit systems by physically separating them from unsecured networks. Implementing air gaps ensures enhanced protection against ransomware, insider threats, and advanced persistent threats targeting financial organizations.
Military and Defense: Air Gapped Infrastructure
Military and defense networks employ air-gapped infrastructure to isolate critical systems from external internet access, preventing cyber intrusions and data breaches. This physical separation ensures sensitive operations, such as command and control systems or weapons deployment platforms, remain secure from remote hacking attempts. Air-gapped environments are integral to securing classified information and maintaining operational integrity in defense technology.
Air Gap Strategies in Healthcare Networks
Air gap strategies in healthcare networks involve physically isolating critical medical devices and patient data storage from external internet connections to prevent cyberattacks. Hospitals implement dedicated offline systems for imaging equipment and electronic health records, ensuring sensitive information remains inaccessible to hackers. This method significantly reduces risks of ransomware and data breaches, enhancing the overall cybersecurity posture of healthcare facilities.
Challenges in Maintaining Air Gapped Security
Air gap security faces significant challenges such as difficulty in securely transferring data between isolated and connected networks without introducing vulnerabilities. Physical media like USB drives pose risks of malware infiltration, requiring strict protocols and personnel training to prevent breaches. Maintaining up-to-date threat detection and response capabilities in an air gapped environment often demands specialized solutions due to lack of direct network connectivity.
Future Trends in Air Gap Technology
Future trends in air gap technology emphasize integrating advanced machine learning algorithms to detect physical breaches and unauthorized access in real-time. Innovations in quantum encryption techniques will enhance data isolation, making air gaps more impenetrable against evolving cyber threats. The adoption of autonomous robotic systems for continuous physical monitoring promises to significantly reduce human error in maintaining network security.
example of air gap in network security Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com