Adaptive bitrate streaming is a technology used to deliver video content efficiently over varying network conditions. It dynamically adjusts the quality of the video stream by switching between multiple encoded bitrates based on the viewer's current internet speed. Popular platforms like YouTube and Netflix implement this method to provide continuous playback without buffering. This technique relies on encoding the same video in different bitrates and resolutions, creating multiple video files. During playback, the streaming client monitors bandwidth and CPU capacity to select the optimal video quality. MPEG-DASH and HLS are common protocols supporting adaptive bitrate streaming, enabling smooth and responsive user experiences.
Table of Comparison
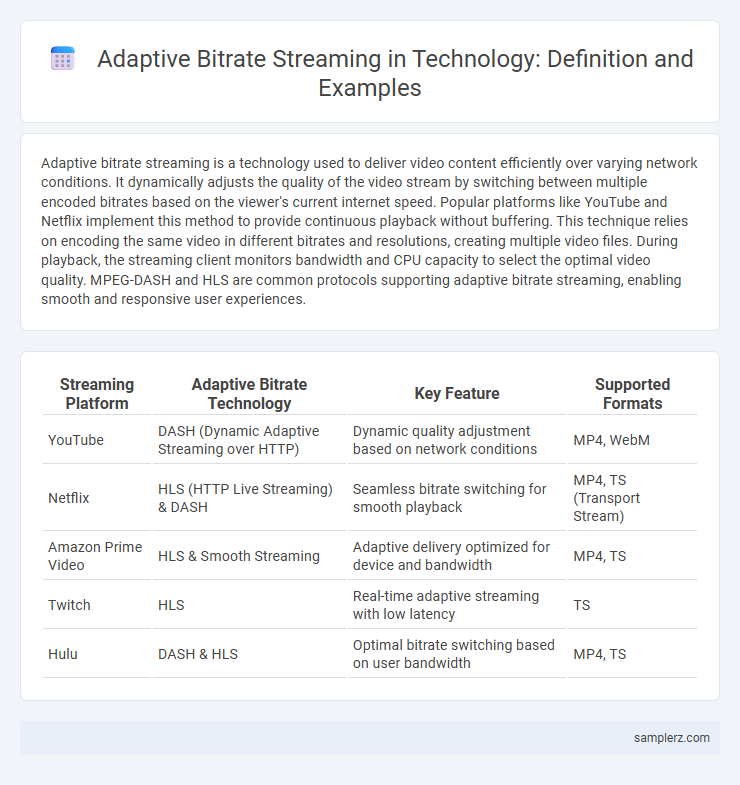
| Streaming Platform | Adaptive Bitrate Technology | Key Feature | Supported Formats |
|---|---|---|---|
| YouTube | DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) | Dynamic quality adjustment based on network conditions | MP4, WebM |
| Netflix | HLS (HTTP Live Streaming) & DASH | Seamless bitrate switching for smooth playback | MP4, TS (Transport Stream) |
| Amazon Prime Video | HLS & Smooth Streaming | Adaptive delivery optimized for device and bandwidth | MP4, TS |
| Twitch | HLS | Real-time adaptive streaming with low latency | TS |
| Hulu | DASH & HLS | Optimal bitrate switching based on user bandwidth | MP4, TS |
Understanding Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts video quality based on the viewer's internet connection to ensure seamless playback without buffering. Popular implementations like HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) segment video files into multiple bitrate versions, allowing real-time switching between them. This technology improves user experience by reducing interruptions and optimizing bandwidth usage across varied network conditions.
Key Benefits of Adaptive Bitrate Technology
Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts video quality based on the user's internet connection and device capabilities, ensuring smooth playback without buffering. This technology enhances user experience by minimizing interruptions and optimizing video resolution for varying network conditions. It also reduces bandwidth consumption, lowering costs for content providers while maintaining high-quality delivery across diverse platforms.
How Adaptive Bitrate Works in Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts video quality in real-time by detecting a user's current network speed and device capabilities. It divides the video file into small segments encoded at multiple bitrates, allowing the player to seamlessly switch between these segments for smooth playback without buffering. This technology enhances user experience by ensuring optimal video quality while minimizing interruptions caused by network fluctuations.
Popular Adaptive Bitrate Protocols
Popular adaptive bitrate protocols such as HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) dynamically adjust video quality based on the viewer's internet speed, ensuring smooth playback with minimal buffering. Apple's HLS segments media into small chunks encoded at various bitrates, enabling seamless transitions between different quality levels during streaming. MPEG-DASH, an open standard, provides flexible content delivery by supporting multiple codecs and resolutions, optimizing streaming experiences across diverse devices and network conditions.
Real-World Examples of Adaptive Bitrate Services
Netflix employs adaptive bitrate streaming to dynamically adjust video quality based on a user's internet speed, ensuring smooth playback across various devices. YouTube uses a similar technology, offering multiple resolution options that automatically shift to prevent buffering during network fluctuations. Amazon Prime Video also leverages adaptive bitrate techniques to provide uninterrupted streaming by adjusting bitrates in real time according to bandwidth changes.
Adaptive Bitrate in Live Sports Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts video quality based on the viewer's internet speed, ensuring uninterrupted playback during live sports events. This technology uses multiple encoded streams at different bitrates, allowing seamless switching to the optimal stream in real-time, which minimizes buffering and latency. Major platforms like ESPN and DAZN implement adaptive bitrate protocols such as HLS and DASH to deliver high-quality live sports streaming experiences worldwide.
Adaptive Bitrate for Mobile Video Delivery
Adaptive bitrate streaming dynamically adjusts video quality based on the viewer's mobile network conditions to ensure smooth playback without buffering. Technologies like Apple's HLS and MPEG-DASH enable seamless bitrate switching by segmenting video into short chunks encoded at multiple bitrates. This approach optimizes user experience on varying mobile connections by prioritizing continuous play and minimizing data consumption.
Adaptive Bitrate in Over-the-Top (OTT) Platforms
Adaptive bitrate streaming on Over-the-Top (OTT) platforms dynamically adjusts video quality based on user bandwidth and device capabilities, ensuring seamless playback without buffering. Services like Netflix and Hulu utilize adaptive bitrate algorithms such as HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) to deliver optimal resolution and bitrate. This technology improves user experience by reducing latency and minimizing interruptions during live broadcasts and on-demand content streaming.
Challenges in Implementing Adaptive Bitrate
Implementing adaptive bitrate streaming faces challenges such as accurately detecting network conditions in real-time to prevent buffering or quality drops. Ensuring seamless transitions between different quality levels requires sophisticated encoding algorithms and consistent client-server communication. Compatibility issues across diverse devices and platforms can also complicate the deployment of adaptive bitrate solutions.
Future Trends in Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Future trends in adaptive bitrate streaming involve the integration of AI-driven algorithms to enhance real-time bitrate selection, improving user experience across diverse network conditions. Edge computing is increasingly utilized to reduce latency and optimize streaming quality by processing data closer to the user. Advances in 5G connectivity will further enable seamless adaptive bitrate streaming with higher resolutions and reduced buffering.
example of adaptive bitrate in streaming Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com