The darknet is a specialized segment of the internet that focuses on privacy and anonymity by utilizing encrypted networks such as Tor and I2P. This hidden part of the internet hosts various marketplaces, forums, and communication platforms that are not indexed by traditional search engines. Entities involved in the darknet include both legitimate users seeking privacy and malicious actors engaging in illegal activities such as drug trafficking, cybercrime, and data breaches. Data from cybersecurity firms reveal that darknet marketplaces have experienced fluctuating activity, with notable platforms like AlphaBay and Silk Road being shut down by law enforcement. Studies indicate that the volume of transactions on darknet markets often involves cryptocurrencies to maintain anonymity and evade tracking. Security professionals emphasize monitoring darknet channels to detect emerging threats, data leaks, and hacktivist campaigns that impact both corporate and government infrastructures.
Table of Comparison
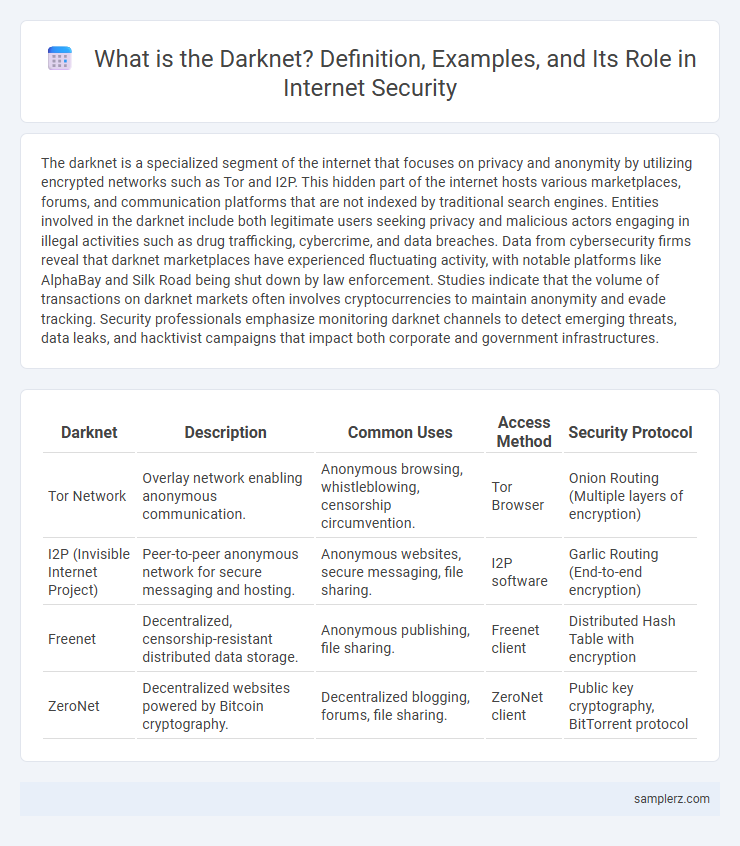
| Darknet | Description | Common Uses | Access Method | Security Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tor Network | Overlay network enabling anonymous communication. | Anonymous browsing, whistleblowing, censorship circumvention. | Tor Browser | Onion Routing (Multiple layers of encryption) |
| I2P (Invisible Internet Project) | Peer-to-peer anonymous network for secure messaging and hosting. | Anonymous websites, secure messaging, file sharing. | I2P software | Garlic Routing (End-to-end encryption) |
| Freenet | Decentralized, censorship-resistant distributed data storage. | Anonymous publishing, file sharing. | Freenet client | Distributed Hash Table with encryption |
| ZeroNet | Decentralized websites powered by Bitcoin cryptography. | Decentralized blogging, forums, file sharing. | ZeroNet client | Public key cryptography, BitTorrent protocol |
Introduction to the Darknet: Unveiling Hidden Networks
The Darknet represents a subset of the internet accessible only through specialized software such as Tor, designed to ensure anonymity and privacy for users. It hosts hidden networks where encrypted communication and untraceable transactions occur, often utilized for both legitimate privacy purposes and illicit activities. Understanding the architecture of the Darknet is crucial for cybersecurity professionals aiming to monitor threats and protect digital infrastructure effectively.
Distinguishing the Darknet from the Surface Web
The darknet operates on encrypted networks requiring specialized software like Tor for access, contrasting sharply with the surface web which is accessible through standard browsers and indexed by search engines such as Google. Unlike the surface web, where websites have public domain names and are easily searchable, darknet sites use non-standard URLs ending in ".onion" that remain hidden and untraceable by traditional means. This distinction in accessibility and anonymity highlights the darknet's role in hosting sensitive or illicit content, necessitating heightened security measures and awareness.
Popular Darknet Marketplaces and Their Functions
Popular darknet marketplaces like AlphaBay, Dream Market, and Empire Market primarily facilitate anonymous trading of illicit goods, including drugs, counterfeit currencies, and hacking tools, using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for payment. These platforms employ advanced encryption techniques and run on the Tor network to ensure user anonymity and evade law enforcement detection. Their functions extend to offering vendor reviews, escrow services, and encrypted communication channels, enhancing trust and security among users conducting illegal transactions.
Tools and Technologies Enabling Darknet Access
Darknet access relies heavily on technologies like Tor (The Onion Router), which utilizes layered encryption to anonymize user identity and location. Distributed networks such as I2P (Invisible Internet Project) and Freenet provide decentralized platforms for private communication and data sharing, enhancing resistance to surveillance and censorship. Advanced encryption protocols, including AES and RSA, underpin secure transactions and interactions within these hidden services, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
Notorious Case Studies: Real-World Darknet Examples
Silk Road, one of the most infamous darknet marketplaces, facilitated illegal drug trade and was shut down by the FBI in 2013, leading to the arrest of its founder Ross Ulbricht. Another notorious case involves the AlphaBay marketplace, which was seized in 2017 for hosting illegal firearms, stolen data, and counterfeit goods, significantly disrupting darknet criminal operations. These real-world examples highlight the complexity and scale of illegal activities enabled by darknet platforms despite law enforcement efforts.
Security Challenges Posed by the Darknet
The darknet presents significant security challenges, including the facilitation of illicit activities such as drug trafficking, weapons trade, and cybercrime operations. Its encrypted and anonymous environment complicates law enforcement efforts to track and apprehend cybercriminals, increasing the risk of ransomware attacks and data breaches. Darknet marketplaces also enable the distribution of malware and stolen data, posing ongoing threats to individual and organizational cybersecurity.
How Cybercriminals Exploit Darknet Platforms
Cybercriminals exploit darknet platforms by utilizing encrypted networks like Tor to anonymously buy and sell illegal goods, such as stolen data, malware, and counterfeit documents. These hidden marketplaces facilitate transactions using cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, ensuring both parties remain untraceable. Darknet forums also enable the sharing of hacking tools, exploits, and instructions, accelerating cybercrime activities globally.
Law Enforcement Strategies in Tracking Darknet Activities
Law enforcement agencies employ advanced data analytics and blockchain forensics to trace cryptocurrency transactions linked to darknet marketplaces. Utilizing undercover operations and digital infiltration, they identify key operators and disrupt illicit networks. Cross-border collaboration enhances intelligence sharing, enabling the dismantling of complex darknet infrastructures.
Ethical and Legal Implications of Darknet Usage
The darknet, often accessed via Tor, hosts anonymous activities that range from privacy protection to illicit trade, raising significant ethical and legal questions. Law enforcement agencies face challenges balancing individual privacy rights with combating illegal activities such as drug trafficking, cybercrime, and human trafficking prevalent on darknet marketplaces. Ethical debates center on whether restricting darknet access impedes freedom of expression or safeguards public safety in cyberspace.
Protecting Yourself from Darknet-Related Risks
The darknet, a hidden part of the internet accessible through specialized networks like Tor, hosts illicit activities ranging from drug trafficking to identity theft, posing significant risks to users. Protecting yourself from darknet-related dangers involves using robust cybersecurity measures, including updated antivirus software, secure VPN connections, and strong, unique passwords. Avoiding suspicious links and practicing cautious online behavior are essential to mitigate exposure to malware, phishing attacks, and data breaches originating from darknet marketplaces.
example of darknet in internet Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com