A sole proprietorship is a common business structure where an individual owns and operates the business independently. An example of a sole proprietorship is a local bakery owned and managed by one person, responsible for all decisions and profits. This structure allows for easy setup with minimal regulatory requirements and direct control over business operations. In a sole proprietorship, the owner assumes all liabilities and financial risks associated with the business. Data shows that sole proprietorships make up a significant portion of small businesses due to their simplicity and tax advantages. Common industries for sole proprietorships include retail, service-based businesses, and freelance professions, highlighting their flexibility in various sectors.
Table of Comparison
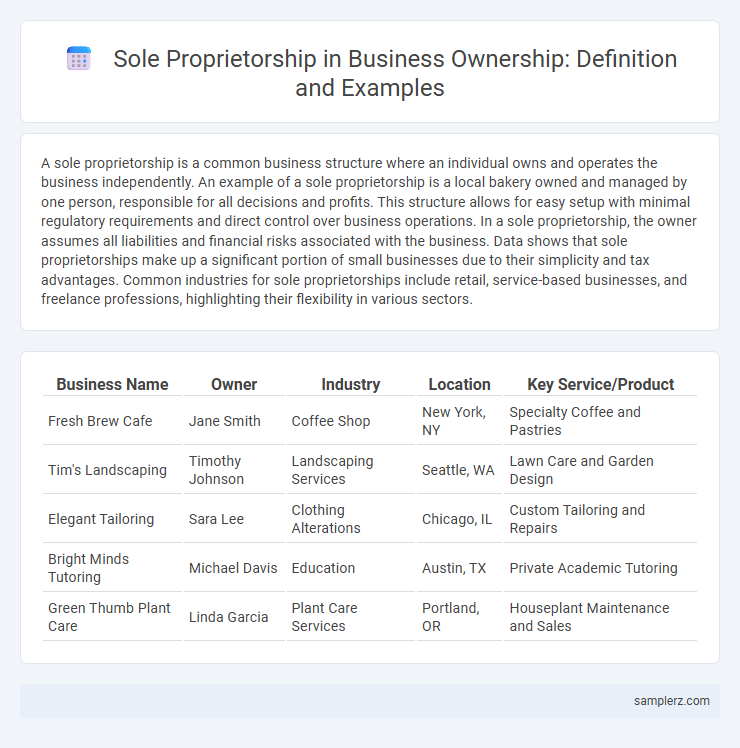
| Business Name | Owner | Industry | Location | Key Service/Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Brew Cafe | Jane Smith | Coffee Shop | New York, NY | Specialty Coffee and Pastries |
| Tim's Landscaping | Timothy Johnson | Landscaping Services | Seattle, WA | Lawn Care and Garden Design |
| Elegant Tailoring | Sara Lee | Clothing Alterations | Chicago, IL | Custom Tailoring and Repairs |
| Bright Minds Tutoring | Michael Davis | Education | Austin, TX | Private Academic Tutoring |
| Green Thumb Plant Care | Linda Garcia | Plant Care Services | Portland, OR | Houseplant Maintenance and Sales |
Overview of Sole Proprietorship Ownership
Sole proprietorship ownership is the simplest business structure, where a single individual owns and operates the business, bearing full responsibility for liabilities and profits. This model offers complete control and easy decision-making but exposes the owner to unlimited personal liability. Common examples include freelance consultants, independent retailers, and small service providers such as local plumbers or graphic designers.
Key Characteristics of Sole Proprietorships
A sole proprietorship is owned and operated by a single individual who assumes full responsibility for the business's debts and liabilities. Key characteristics include unlimited liability, direct control over decision-making, and simplicity in establishment and dissolution. This form of ownership allows for straightforward tax filing since profits and losses are reported on the owner's personal tax return.
Famous Examples of Sole Proprietorship Businesses
Famous examples of sole proprietorship businesses include small local retailers, independent consultants, and freelance graphic designers who operate under their own name without forming a separate legal entity. Entrepreneurs like Richard Branson initially started as sole proprietors before expanding into larger business structures. These sole proprietorships benefit from simplified tax reporting and complete managerial control, making them popular among individual business owners.
Case Study: Local Retail Store Ownership
A local retail store owned by a single entrepreneur exemplifies sole proprietorship, where the owner assumes full control and liability for business operations. This structure enables streamlined decision-making processes and direct management of inventory, customer relations, and finances. Profit retention and personal responsibility for debts highlight the trade-offs unique to sole proprietorship ownership in small-scale retail businesses.
Real-World Examples in the Service Industry
Jane's freelance graphic design business exemplifies a sole proprietorship in the service industry, where she retains full control and ownership while managing client projects independently. Many consultants, personal trainers, and tutors operate as sole proprietors, leveraging their specialized skills to attract clients without forming a formal business entity. This structure offers simplicity in tax filing and operational flexibility, appealing to professionals providing individualized services.
Sole Proprietorships in Freelancing and Consulting
Sole proprietorships are common among freelancers and consultants who operate independently without forming a separate legal entity. Examples include freelance graphic designers, independent marketing consultants, and self-employed IT specialists who manage their business finances and client contracts personally. This ownership structure offers simplicity and full control but exposes the owner to unlimited personal liability.
Examples of Sole Proprietorships in E-Commerce
Many sole proprietorships in e-commerce include independent online retailers selling handmade crafts on platforms like Etsy, freelance digital marketers managing client campaigns through personal websites, and individual dropshipping entrepreneurs operating small-scale online stores without holding inventory. These businesses benefit from simple tax filings and complete managerial control, making them attractive for start-ups with limited capital. The ease of setting up a sole proprietorship encourages innovation and agility in the competitive e-commerce sector.
Comparison: Sole Proprietorship vs Other Ownership Structures
A sole proprietorship offers simplicity and full control, unlike corporations that require complex regulations and shared decision-making. Compared to partnerships, sole proprietorships have fewer legal formalities and allow the owner to retain all profits but carry unlimited personal liability. Small retail shops and freelance businesses often prefer sole proprietorships for their tax advantages and straightforward setup.
Legal and Financial Implications in Sole Proprietorship Ownership
A sole proprietorship offers full legal control to the owner, who assumes unlimited personal liability for business debts and obligations, risking personal assets in case of lawsuits or financial losses. Financially, this structure simplifies tax filing as business income is reported on the owner's personal tax return, but it limits access to capital sources compared to corporations. Legal compliance is minimal, yet owners must ensure proper licensing and permits to avoid penalties and maintain business legitimacy.
How to Register Your Sole Proprietorship Business
Registering a sole proprietorship involves selecting a unique business name and filing a Doing Business As (DBA) registration with the local government or county clerk's office to ensure legal operation under that name. Entrepreneurs must obtain necessary licenses and permits specific to their industry and location, such as health permits or sales tax licenses. Lastly, securing an Employer Identification Number (EIN) from the IRS is essential for tax reporting and hiring employees, even though sole proprietors can often use their Social Security Number for tax purposes.
example of sole proprietorship in ownership Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com