A swashplate in an automotive compressor functions as a crucial mechanical component that converts rotary motion into linear motion. This component is typically found in axial piston compressors, where the swashplate's angled surface drives the pistons to compress air or refrigerant. Its efficiency directly impacts the performance and reliability of air conditioning systems in vehicles. The swashplate mechanism is composed of a tilted disc connected to the drive shaft, which rotates to move piston rods attached at various points. Precise engineering of the swashplate ensures smooth piston movement and optimal compression cycles within the automotive compressor. Data from automotive manufacturers highlight that swashplate compressors offer compact design and enhanced energy efficiency for modern vehicle HVAC systems.
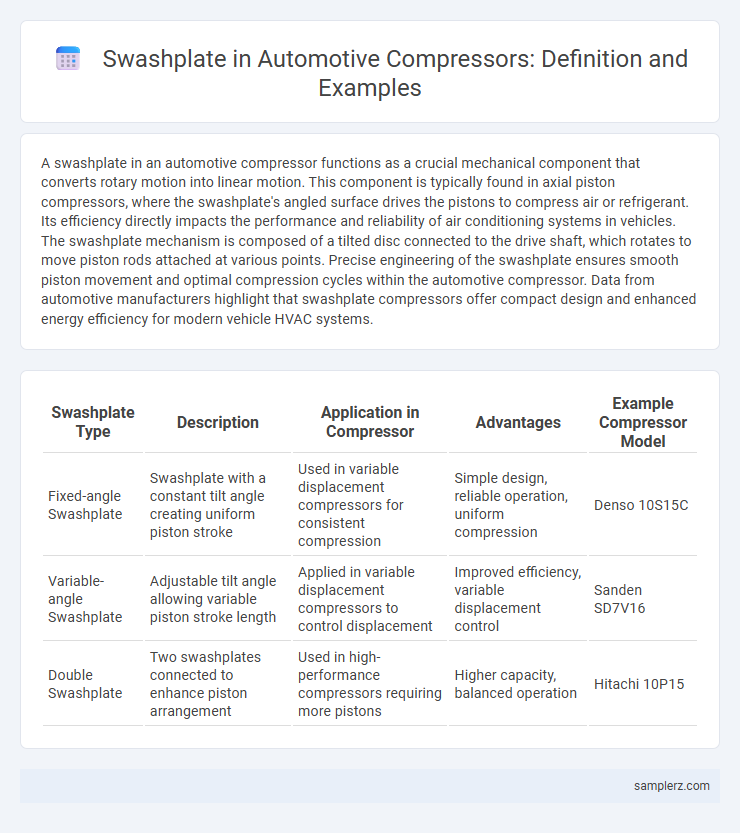
Table of Comparison
| Swashplate Type | Description | Application in Compressor | Advantages | Example Compressor Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed-angle Swashplate | Swashplate with a constant tilt angle creating uniform piston stroke | Used in variable displacement compressors for consistent compression | Simple design, reliable operation, uniform compression | Denso 10S15C |
| Variable-angle Swashplate | Adjustable tilt angle allowing variable piston stroke length | Applied in variable displacement compressors to control displacement | Improved efficiency, variable displacement control | Sanden SD7V16 |
| Double Swashplate | Two swashplates connected to enhance piston arrangement | Used in high-performance compressors requiring more pistons | Higher capacity, balanced operation | Hitachi 10P15 |
Introduction to Swashplate Mechanisms in Compressors
Swashplate mechanisms in compressors convert rotational motion into reciprocating motion by tilting a disc called the swashplate, which drives the pistons in automotive air conditioning systems. This design enhances efficiency by providing smooth, continuous piston movement and variable displacement control, optimizing engine load and fuel consumption. Swashplate compressors are widely used in automotive applications due to their compact size, reliability, and ability to maintain consistent refrigerant flow under varying operating conditions.
Overview of Swashplate Compressor Designs
Swashplate compressors utilize a rotating swashplate to convert rotary motion into reciprocating piston movement, enabling efficient compression in automotive air conditioning systems. Common designs include fixed and variable displacement swashplate compressors, where variable models adjust the swashplate angle to modulate cooling capacity and improve fuel efficiency. These compressors feature compact construction, high reliability, and are integral to modern vehicle HVAC performance.
How Swashplate Compressors Work in Automotive Applications
Swashplate compressors convert rotational motion into linear piston movement using an angled swashplate, enabling efficient compression of refrigerant in automotive air conditioning systems. As the driveshaft spins, the swashplate's tilt forces pistons to reciprocate within cylinders, increasing pressure and circulating the refrigerant cycle. This design offers compact size, smooth operation, and variable displacement capabilities, optimizing performance and fuel efficiency in modern vehicle climate control.
Key Components of a Swashplate Compressor
Key components of a swashplate compressor include the swashplate itself, which converts rotational motion into reciprocating motion, pistons that compress the refrigerant gas, and the crankshaft that drives the swashplate's rotation. The swashplate is mounted at an angle on the crankshaft, causing the pistons to move back and forth within their cylinders. Seals and valves ensure efficient compression and prevent leaks, contributing to the overall performance of the automotive air conditioning system.
Swashplate vs. Other Compressor Types: Comparative Analysis
Swashplate compressors provide precise displacement control through their unique axial piston mechanism, enabling efficient variable output in automotive air conditioning systems. Compared to traditional reciprocating compressors, swashplate designs offer smoother operation and reduced vibration, enhancing vehicle comfort and system durability. Unlike scroll compressors, swashplate types excel in handling high loads and fluctuating pressure conditions, making them suitable for heavy-duty automotive applications.
Real-World Examples: Swashplate Compressors in Popular Automotive Models
Swashplate compressors are commonly found in automotive air conditioning systems, such as those in the Toyota Camry and Honda Accord, where they provide efficient refrigerant compression through their axial piston design. These compressors enhance performance by delivering variable displacement capabilities, allowing optimal cooling efficiency and fuel economy. The swashplate mechanism enables smooth power transfer in compact engine bays, making it a preferred choice for midsize and full-size passenger vehicles.
Advantages of Using Swashplate Compressors in Vehicles
Swashplate compressors in vehicles offer high efficiency by providing smooth and continuous compression, resulting in improved fuel economy and reduced emissions. Their compact design allows for significant space savings in engine compartments, enhancing overall vehicle packaging. Enhanced reliability and lower maintenance requirements further contribute to the popularity of swashplate compressors in automotive air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
Common Issues and Maintenance for Swashplate Compressors
Swashplate compressors commonly face issues such as worn bushings, oil leakage, and loss of compression due to seal failure. Regular maintenance includes inspecting the swashplate angle, checking for abnormal noises, and ensuring proper lubrication to prevent premature wear. Timely replacement of seals and bushings significantly enhances the compressor's lifespan and operational efficiency.
Innovations and Trends in Swashplate Compressor Technology
Innovations in swashplate compressor technology include variable stroke mechanisms, which enhance fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by precisely controlling refrigerant flow. Advanced materials like wear-resistant alloys improve durability and reduce maintenance needs in automotive air conditioning systems. Current trends also involve integrating electronic control units (ECUs) for real-time performance optimization and noise reduction, aligning with the shift toward electrification and sustainability in the automotive industry.
Future Prospects for Swashplate Compressors in the Automotive Industry
Swashplate compressors, integral to variable displacement systems, are poised for significant advancements driven by the automotive industry's shift towards electrification and efficiency. Future prospects include enhanced control precision through integration with electronic control units (ECUs) and the adoption of lightweight materials to reduce overall vehicle weight. Innovations targeting reduced friction and improved durability will support compliance with stringent emissions regulations and contribute to the development of more energy-efficient air conditioning systems in electric and hybrid vehicles.
example of swashplate in compressor Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com