In automotive suspension systems, a jounce occurs when the vehicle's strut compresses due to an upward road force, such as hitting a bump or pothole. The strut, which combines a shock absorber with a coil spring, helps absorb this impact by compressing the spring and damping the motion. This jounce movement is essential for maintaining tire contact with the road and improving ride comfort. Strut jounce is measured by the distance the suspension travels upward before the spring fully compresses or the bump stop is engaged. Sensors often monitor jounce displacement to adjust electronic suspension systems in real time, enhancing vehicle stability and handling. Accurate detection of jounce also aids in diagnosing suspension wear or damage, ensuring optimal automotive performance.
Table of Comparison
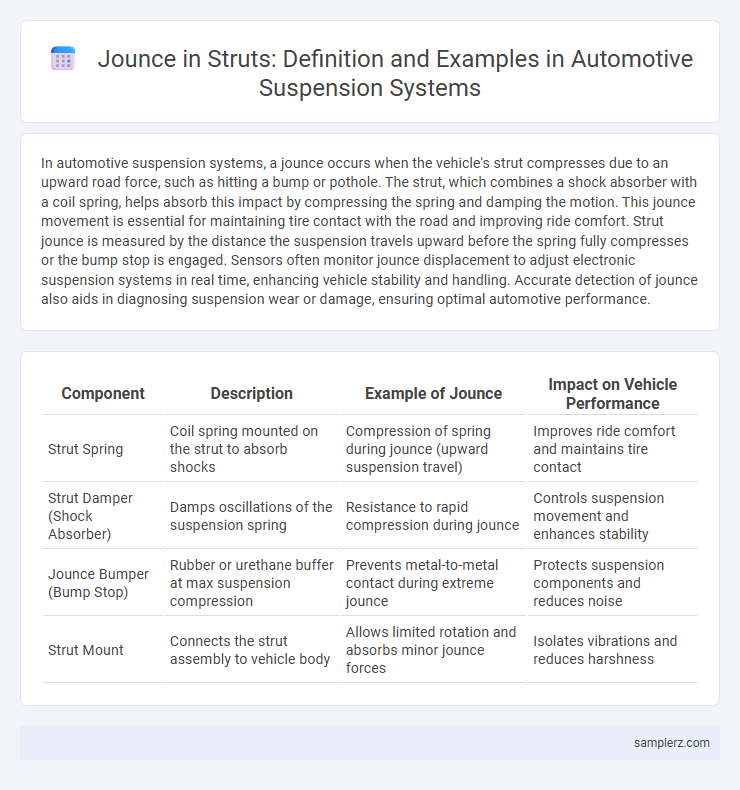
| Component | Description | Example of Jounce | Impact on Vehicle Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strut Spring | Coil spring mounted on the strut to absorb shocks | Compression of spring during jounce (upward suspension travel) | Improves ride comfort and maintains tire contact |
| Strut Damper (Shock Absorber) | Damps oscillations of the suspension spring | Resistance to rapid compression during jounce | Controls suspension movement and enhances stability |
| Jounce Bumper (Bump Stop) | Rubber or urethane buffer at max suspension compression | Prevents metal-to-metal contact during extreme jounce | Protects suspension components and reduces noise |
| Strut Mount | Connects the strut assembly to vehicle body | Allows limited rotation and absorbs minor jounce forces | Isolates vibrations and reduces harshness |
Understanding Jounce in Automotive Strut Systems
Jounce in automotive strut systems refers to the compression phase of the suspension when the wheel moves upward relative to the vehicle body, absorbing shocks from road irregularities. It plays a critical role in maintaining tire contact with the road, enhancing vehicle stability and ride comfort. Understanding jounce dynamics helps engineers optimize strut design for improved handling, vibration reduction, and overall suspension performance.
Key Symptoms of Jounce in Strut Assemblies
Key symptoms of jounce in strut assemblies include unusual clunking noises when driving over bumps, indicating excessive play or worn components. Drivers may experience reduced ride comfort and increased vibration, signaling compromised damping performance. Visible signs such as uneven tire wear and fluid leaks from the strut also suggest jounce-related damage requiring immediate inspection.
How Jounce Affects Ride Comfort and Handling
Jounce in a strut refers to the upward suspension travel when the vehicle wheel moves over a bump, influencing how the suspension absorbs shocks. Excessive jounce can lead to stiffness, reducing ride comfort by transmitting harsh impacts to the cabin while also affecting handling stability through compromised tire contact. Optimizing jounce travel in struts enhances both ride smoothness and precise vehicle control during dynamic driving conditions.
Real-World Scenarios: Jounce in Action
Jounce in a strut occurs when a vehicle encounters a pothole or speed bump, causing the suspension to compress sharply under the load. This rapid compression absorbs impact energy, preventing damage to the chassis and improving ride comfort. In real-world scenarios, precise jounce control enhances vehicle stability and handling during sudden road irregularities.
Differences Between Jounce and Rebound in Struts
Jounce in struts refers to the compression phase where the suspension absorbs impact by compressing the spring and shock absorber, while rebound is the extension phase allowing the suspension to return to its original length. The key difference lies in their motion direction: jounce deals with downward forces and compression, whereas rebound manages upward motion and extension. Understanding these phases is critical for optimizing vehicle handling, ride comfort, and suspension durability.
Common Causes of Excessive Strut Jounce
Excessive strut jounce often results from worn or damaged components such as coil springs, strut mounts, or bushings that fail to absorb shocks efficiently. Corrosion and inadequate lubrication can exacerbate wear, leading to reduced suspension travel and compromised ride quality. Regular inspection of these parts ensures optimal strut performance and prevents premature suspension failure.
Preventing Jounce-related Strut Damage
Jounce in a strut occurs when excessive suspension travel causes the coil spring or damper to compress fully, leading to metal-to-metal contact and potential damage. Preventing jounce-related strut damage involves installing high-quality bump stops and ensuring proper suspension tuning to limit bottoming out during harsh impacts. Regular inspection of strut mounts, bushings, and bump stops helps maintain optimal suspension performance and extends the lifespan of strut components.
Diagnostics: Identifying Jounce Problems in Struts
Diagnosing jounce issues in struts involves inspecting the suspension system for abnormal noise, uneven tire wear, and poor handling characteristics. Technicians utilize vibration analysis and physical compression tests to detect degraded bushings or worn-out shock absorbers causing excessive jounce. Early identification of jounce failures enhances vehicle stability and prevents further suspension damage.
Maintenance Tips to Reduce Jounce Issues
Regular inspection of strut jounce bumpers and replacing worn components can prevent excessive suspension noise and improve ride comfort. Applying lubricant to the jounce bumper contact areas minimizes friction and reduces premature wear. Maintaining proper strut alignment and checking for damaged seals helps to avoid jounce-related damage and extend the lifespan of suspension parts.
Advances in Strut Design to Manage Jounce
Advances in strut design have significantly improved the management of jounce by integrating progressive-rate springs and hydraulic bump stops that absorb impact forces during suspension compression. Modern struts utilize dual-tube constructions and adaptive damping technologies to modulate jounce responses, enhancing ride comfort and vehicle stability. Innovations like electronically controlled struts dynamically adjust stiffness to optimize jounce behavior based on driving conditions and road surfaces.
example of jounce in strut Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com