Haptic technology in interfaces involves the use of tactile feedback to enhance user interaction by simulating the sense of touch. Devices such as smartphones and gaming controllers utilize haptic feedback through vibrations or force sensations, providing users with physical responses to touch inputs. This technology improves accessibility and immersion by conveying information through texture, pressure, or movement cues. Touchscreen interfaces equipped with haptic feedback often deliver subtle vibrations when typing or selecting options, creating a more intuitive user experience. In virtual reality systems, haptic gloves enable users to feel virtual objects, enhancing realism and engagement. The integration of haptic feedback data into user interface design plays a crucial role in increasing the effectiveness of digital interactions across multiple applications.
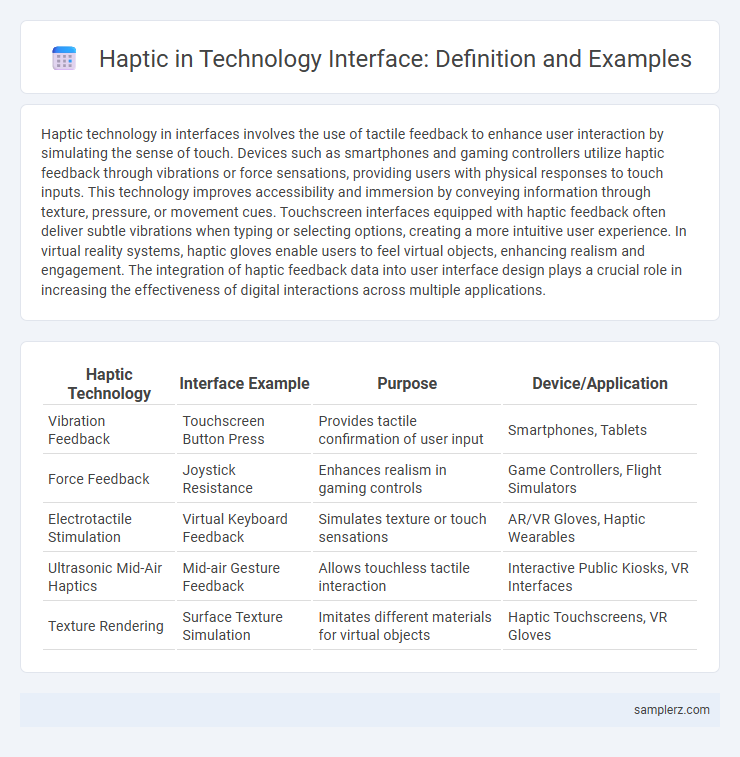
Table of Comparison
| Haptic Technology | Interface Example | Purpose | Device/Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibration Feedback | Touchscreen Button Press | Provides tactile confirmation of user input | Smartphones, Tablets |
| Force Feedback | Joystick Resistance | Enhances realism in gaming controls | Game Controllers, Flight Simulators |
| Electrotactile Stimulation | Virtual Keyboard Feedback | Simulates texture or touch sensations | AR/VR Gloves, Haptic Wearables |
| Ultrasonic Mid-Air Haptics | Mid-air Gesture Feedback | Allows touchless tactile interaction | Interactive Public Kiosks, VR Interfaces |
| Texture Rendering | Surface Texture Simulation | Imitates different materials for virtual objects | Haptic Touchscreens, VR Gloves |
Introduction to Haptic Feedback in Interfaces
Haptic feedback in interfaces uses tactile sensations to enhance user interaction, replicating the sense of touch through vibrations or forces. Common examples include smartphone vibrations for notifications and force feedback in gaming controllers, which simulate real-world textures and movements. This technology improves accessibility and immersion, making digital experiences more intuitive and responsive.
Touchscreens with Vibrational Response
Touchscreens with vibrational response utilize advanced haptic technology to simulate realistic tactile feedback, improving user interaction and device usability. This technology integrates precision actuators, such as linear resonant actuators (LRAs) or piezoelectric motors, to create nuanced vibrations that replicate textures and button presses. Popular applications include smartphones and automotive interfaces, where haptic feedback enhances accessibility and user experience.
Haptic Technology in Gaming Controllers
Haptic technology in gaming controllers enhances user experience by providing precise tactile feedback through vibrations, textures, and force sensations, simulating real-world interactions. Advanced systems like the Sony DualSense controller utilize adaptive triggers and dynamic haptic responses to increase immersion and realism during gameplay. These innovations improve player engagement by delivering nuanced sensory information directly through the controller.
Wearable Devices with Haptic Alerts
Wearable devices with haptic alerts provide tactile feedback through vibrations or pulses to notify users of incoming calls, messages, or health-related updates without relying on visual or auditory signals. Smartwatches and fitness trackers employ haptic motors to deliver discrete, customizable alerts that enhance user experience and accessibility in various environments. Advanced haptic technology in wearables supports precise and context-aware notifications, improving real-time interaction and response efficiency.
Haptic Feedback in Virtual Reality Systems
Haptic feedback in virtual reality systems enhances immersion by providing tactile sensations that simulate real-world interactions, such as vibrations, forces, and textures. Advanced VR controllers and gloves use precise actuators and sensors to deliver these haptic cues, enabling users to feel virtual objects and environments with high fidelity. This technology improves user experience in applications ranging from gaming and training simulations to medical and industrial design.
Mobile Device Interfaces Using Haptics
Mobile device interfaces employing haptic technology enhance user experience by providing tactile feedback through vibrations or pulses, simulating physical touch sensations. Advanced smartphones utilize haptic actuators like linear resonant actuators (LRAs) to deliver precise and varied vibrations, improving interaction in gaming, typing, and notifications. This sensory feedback increases accessibility and engagement by making digital interactions more intuitive and immersive.
Automotive Touch Controls with Haptic Sensations
Automotive touch controls with haptic sensations enhance driver interaction by providing tactile feedback through vibrations or pulses on touchscreens and control panels. This technology improves safety by allowing users to operate functions like climate control and navigation without diverting their gaze from the road. Major automotive brands integrate haptic feedback to create intuitive, responsive interfaces that reduce driver distraction and increase overall vehicle usability.
Medical Interfaces Enhanced by Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback in medical interfaces enables surgeons to feel virtual tissues during robotic-assisted surgeries, improving precision and reducing errors. Devices like the Da Vinci Surgical System integrate advanced haptic technology to simulate tactile sensations, enhancing real-time decision-making. This sensory input helps practitioners perform minimally invasive procedures with greater confidence and patient safety.
Haptic Integration in Consumer Electronics
Haptic integration in consumer electronics enhances user experience by providing tactile feedback through devices such as smartphones, wearables, and gaming controllers. Technologies like piezoelectric actuators and electroactive polymers enable precise vibration patterns and force feedback, improving navigation and interaction. Leading brands like Apple and Sony incorporate advanced haptic engines to simulate realistic touch sensations, increasing device immersion and usability.
Future Trends in Haptic Interface Design
Future trends in haptic interface design include the integration of ultrathin, flexible piezoelectric materials that provide highly localized tactile feedback for enhanced user immersion. Advanced machine learning algorithms enable adaptive haptic responses tailored to individual user preferences and real-time context. Research into mid-air haptics using focused ultrasound promises touchless feedback experiences, transforming interfaces in virtual reality and wearable devices.
example of haptic in interface Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com