Socialization in childhood is a crucial process where children learn to interact with others and develop essential communication skills. Through playdates and group activities, children acquire the ability to share, cooperate, and resolve conflicts. These early interactions shape their understanding of social norms and emotional regulation. Family dynamics and school environments serve as primary contexts for socialization during childhood. Parents and teachers model appropriate behaviors, while peers provide opportunities for practicing social roles. Exposure to diverse social settings enhances children's adaptability and fosters empathy, critical for healthy social development.
Table of Comparison
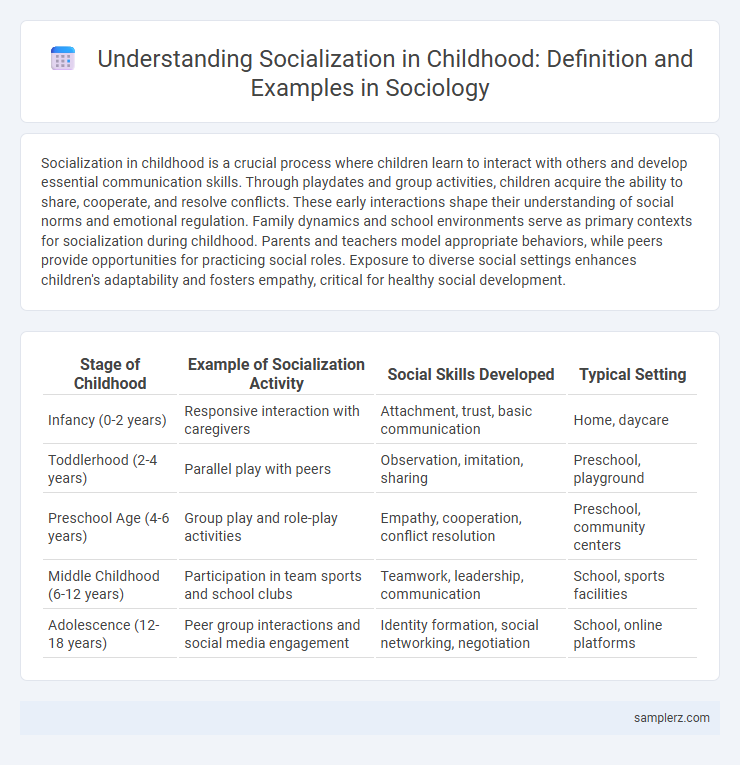
| Stage of Childhood | Example of Socialization Activity | Social Skills Developed | Typical Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infancy (0-2 years) | Responsive interaction with caregivers | Attachment, trust, basic communication | Home, daycare |
| Toddlerhood (2-4 years) | Parallel play with peers | Observation, imitation, sharing | Preschool, playground |
| Preschool Age (4-6 years) | Group play and role-play activities | Empathy, cooperation, conflict resolution | Preschool, community centers |
| Middle Childhood (6-12 years) | Participation in team sports and school clubs | Teamwork, leadership, communication | School, sports facilities |
| Adolescence (12-18 years) | Peer group interactions and social media engagement | Identity formation, social networking, negotiation | School, online platforms |
Family Influence: Primary Agents of Childhood Socialization
Family serves as the primary agent of childhood socialization, shaping early habits, values, and social norms through daily interactions and emotional bonding. Parents and siblings provide foundational role models that influence communication styles, conflict resolution, and cultural traditions. These family dynamics establish the framework for children's social identity and interpersonal skills development.
Peer Interactions: Building Social Skills in Early Years
Peer interactions during early childhood play a crucial role in developing communication, empathy, and conflict resolution skills. Children learn to share, cooperate, and understand social cues through group play, fostering emotional intelligence and self-regulation. Engaging with peers helps establish foundational social competencies essential for lifelong relationships and community participation.
School Environment: Learning Social Norms and Values
School environments play a critical role in childhood socialization by providing structured opportunities to learn social norms and values. Children adapt to rules, develop communication skills, and understand cooperation through classroom interactions, group projects, and peer relationships. These experiences foster empathy, respect, and a sense of community essential for societal integration.
Playtime: Development of Cooperation and Sharing
Playtime in childhood serves as a crucial platform for developing cooperation and sharing skills, fostering early social interaction and emotional growth. Engaging in group activities like building blocks or team games teaches children negotiation, turn-taking, and empathy, essential components of socialization. These experiences lay the groundwork for effective communication and relationship-building throughout life.
Cultural Traditions: Shaping Identity Through Socialization
Cultural traditions play a crucial role in childhood socialization by embedding values, customs, and language that shape a child's identity and worldview. Participating in rituals such as festivals, family gatherings, and storytelling helps children internalize social norms and develop a sense of belonging within their community. This process fosters emotional connections and cultural continuity, reinforcing shared heritage and collective identity from an early age.
Media Exposure: Impact on Childhood Social Learning
Media exposure significantly shapes childhood social learning by providing models for behavior, language use, and social norms that children mimic and internalize. Television programs, digital games, and online platforms contribute to the development of empathy, communication skills, and understanding of diverse cultures. Excessive or unsupervised exposure, however, can lead to skewed perceptions of reality and hinder face-to-face social interactions necessary for healthy social development.
Role of Teachers: Guiding Social Behaviors in Classrooms
Teachers play a crucial role in guiding social behaviors in classrooms by modeling positive interactions and setting clear expectations for respectful communication. Structured group activities and collaborative projects encourage children to develop empathy, cooperation, and conflict resolution skills. Through consistent reinforcement and feedback, educators help shape children's social competencies essential for successful peer relationships.
Community Events: Fostering Social Bonds Among Children
Community events such as local fairs, school festivals, and neighborhood sports games serve as prime opportunities for childhood socialization, enabling children to develop essential social skills and build meaningful relationships. Participation in these events encourages cooperation, empathy, and communication, which are critical for emotional intelligence and peer interaction. Research indicates that children involved in community activities demonstrate higher levels of social competence and a stronger sense of belonging within their communities.
Sibling Relationships: Early Lessons in Conflict Resolution
Sibling relationships serve as a primary context for childhood socialization, providing practical lessons in conflict resolution through everyday interactions and disagreements. Children learn to negotiate boundaries, share resources, and develop empathy by navigating disputes and reconciling differences with their brothers and sisters. These early experiences in conflict management contribute to essential social skills that influence future interpersonal relationships.
Sports and Group Activities: Encouraging Teamwork and Communication
Participating in sports and group activities during childhood fosters essential social skills such as teamwork, communication, and cooperation. These experiences promote empathy and conflict resolution by encouraging children to work together toward common goals. Early involvement in team settings builds a foundation for positive peer relationships and effective interpersonal interactions.
example of socialization in childhood Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com