Groupthink is a psychological phenomenon that occurs within social groups when the desire for harmony and conformity results in irrational or dysfunctional decision-making. An example of groupthink can be seen in social movements where members suppress dissenting opinions to maintain consensus, leading to poor judgment or misguided actions. For instance, during certain political protests, individuals may ignore valid concerns or alternative strategies to align with the dominant group narrative. This suppression of critical thinking diminishes the group's ability to evaluate risks and consider diverse perspectives. The social dynamics involved often include pressure to conform, self-censorship, and the belief that dissent harms group cohesion. Data from social psychology studies show that groups experiencing groupthink tend to make more errors compared to those encouraging open debate and dissent.
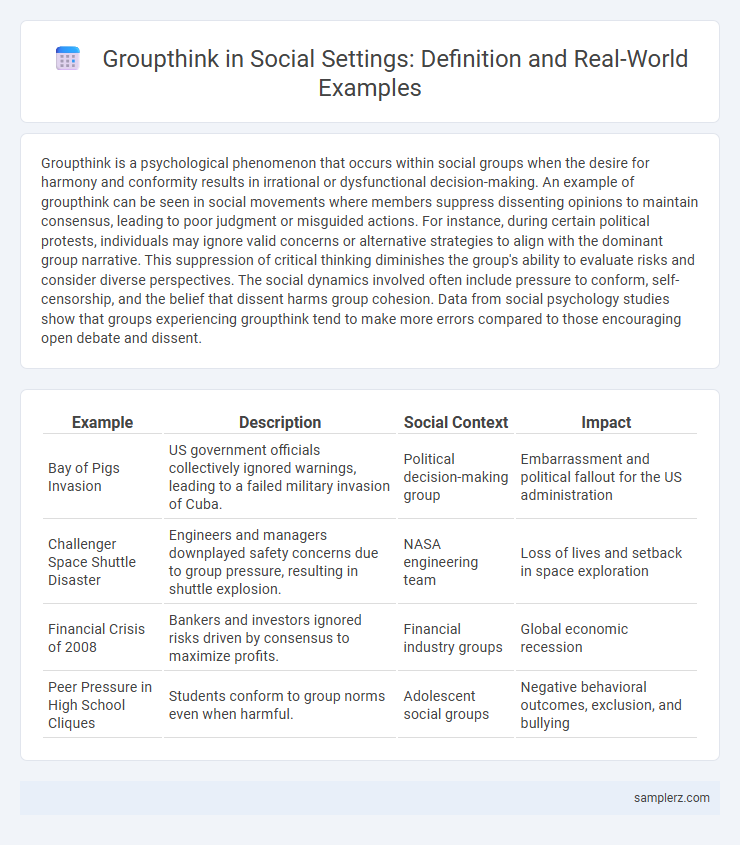
Table of Comparison
| Example | Description | Social Context | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bay of Pigs Invasion | US government officials collectively ignored warnings, leading to a failed military invasion of Cuba. | Political decision-making group | Embarrassment and political fallout for the US administration |
| Challenger Space Shuttle Disaster | Engineers and managers downplayed safety concerns due to group pressure, resulting in shuttle explosion. | NASA engineering team | Loss of lives and setback in space exploration |
| Financial Crisis of 2008 | Bankers and investors ignored risks driven by consensus to maximize profits. | Financial industry groups | Global economic recession |
| Peer Pressure in High School Cliques | Students conform to group norms even when harmful. | Adolescent social groups | Negative behavioral outcomes, exclusion, and bullying |
Classic Cases of Groupthink in Social Settings
The Bay of Pigs invasion exemplifies classic groupthink in social settings, where cohesive decision-making led to ignoring critical warnings and fostering overconfidence. Social groups involved in the Challenger Space Shuttle disaster also demonstrated groupthink by suppressing dissenting opinions and underestimating risks. These cases highlight the dangers of conformity and poor critical evaluation within social groups, resulting in flawed decisions.
Famous Social Movements Impacted by Groupthink
The Bay of Pigs invasion in 1961 exemplifies groupthink, where U.S. government officials ignored realistic critiques leading to a disastrous outcome. The Challenger Space Shuttle disaster also highlights groupthink, as engineers' concerns were suppressed to maintain consensus. These cases demonstrate how social movements or decisions can falter when dissenting opinions are undervalued.
Groupthink in Online Communities and Social Media
Groupthink in online communities and social media manifests when users prioritize consensus over critical thinking, leading to the spread of misinformation and echo chambers. Platforms like Facebook and Twitter amplify group polarization by encouraging homogenous viewpoints, often suppressing dissenting opinions through algorithm-driven content curation. This phenomenon undermines constructive dialogue and fosters environments where conformity overrides individual judgment.
Peer Pressure as a Catalyst for Social Groupthink
Peer pressure significantly accelerates social groupthink by compelling individuals to conform to the prevailing opinions and behaviors within a community, often at the expense of personal beliefs. This dynamic suppresses dissent and critical thinking, leading to homogenous decision-making and reinforcing collective biases. Social psychologists identify peer pressure as a primary catalyst that intensifies group cohesion and conformity, ultimately shaping group consensus and social norms.
Groupthink in High School and College Social Circles
Groupthink in high school and college social circles often manifests when students prioritize conformity over individual opinions, leading to poor decision-making and suppression of dissenting views. Peer pressure within these environments encourages unanimous agreement, resulting in exclusion of alternative perspectives and reinforcing stereotypes or risky behaviors. Such dynamics hinder critical thinking and foster an environment where controversial or unethical actions go unchallenged.
Groupthink Among Friends: Real-Life Social Examples
Groupthink often occurs in close-knit friend groups where the desire for harmony suppresses dissenting opinions, such as when a group unanimously agrees to exclude a member despite underlying conflicts. In social settings, friends might collectively make poor decisions like peer pressure to engage in risky behaviors, ignoring individual doubts to maintain group cohesion. Real-life examples highlight how the fear of social rejection within friend circles can lead to conformity, hindering honest communication and critical thinking.
Groupthink in Activist Groups and Social Causes
Groupthink in activist groups often manifests when members suppress dissenting opinions to maintain unity, leading to poor decision-making and unchallenged assumptions. For example, during the planning of large-scale protests, activists may overlook potential risks and alternative strategies due to pressure for consensus. This phenomenon can result in ineffective campaigns and reduced long-term impact on social causes.
How Social Gatherings Foster Groupthink
Social gatherings create environments where conformity pressures increase, prompting individuals to align their opinions with the dominant group mindset and suppress dissenting views. This dynamic often leads to groupthink, characterized by reduced critical evaluation and an inflated sense of consensus. Research shows that factors like cohesive social bonds, shared goals, and the desire for harmony in gatherings amplify the risk of collective decision-making errors.
The Role of Groupthink in Viral Social Trends
Groupthink plays a pivotal role in viral social trends by facilitating rapid consensus around ideas or behaviors, often without critical evaluation. When individuals prioritize harmony and conformity within a social group, they tend to adopt popular memes, challenges, or opinions that spread widely across platforms like TikTok and Instagram. This collective mindset accelerates trend propagation but can also limit diversity of thought and reinforce superficial engagement.
Preventing Groupthink in Social Group Dynamics
Preventing groupthink in social group dynamics involves encouraging open dialogue, promoting diverse perspectives, and establishing a culture where members feel safe to express dissenting opinions. Techniques such as assigning a devil's advocate and conducting anonymous surveys help safeguard against conformity pressures. Effective leadership that values critical thinking and actively seeks feedback enhances decision-making quality and reduces the risks of groupthink.
example of groupthink in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com