Gesellschaft refers to a social relationship characterized by impersonal, formal, and goal-driven interactions, often found in modern corporations. In corporations, employees and management interact based on roles, responsibilities, and contractual agreements rather than personal bonds. This type of social structure prioritizes efficiency, productivity, and professional objectives over emotional connections. Corporations exemplify Gesellschaft through structured hierarchies and policies that govern workplace behavior and decision-making. Data from organizational studies show that communication in such settings is primarily task-focused, with clearly defined reporting lines and accountability measures. The entity of a corporation operates as a collective with shared economic goals, where individual relationships are secondary to the organization's overarching mission.
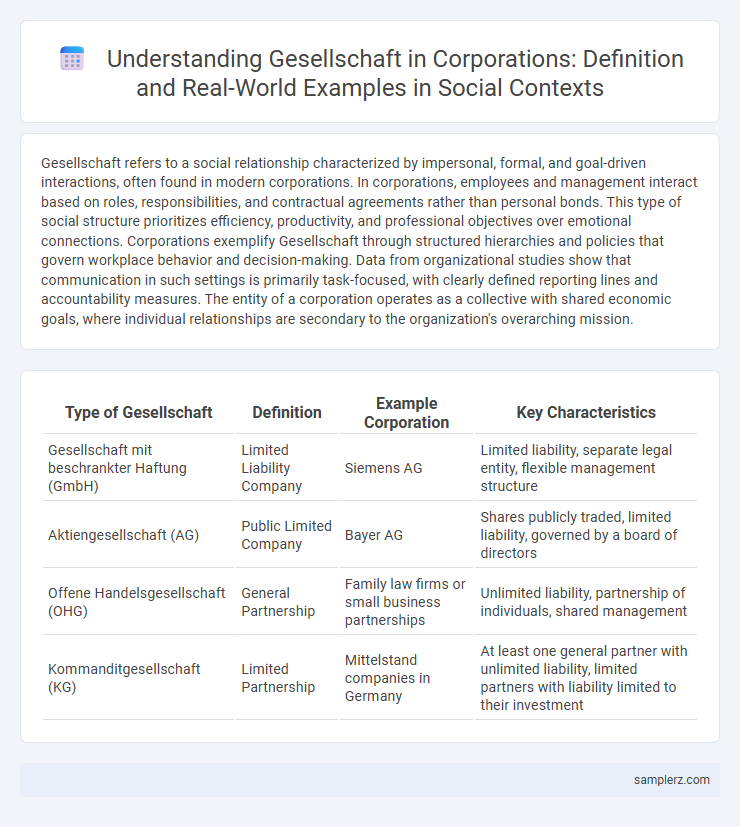
Table of Comparison
| Type of Gesellschaft | Definition | Example Corporation | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gesellschaft mit beschrankter Haftung (GmbH) | Limited Liability Company | Siemens AG | Limited liability, separate legal entity, flexible management structure |
| Aktiengesellschaft (AG) | Public Limited Company | Bayer AG | Shares publicly traded, limited liability, governed by a board of directors |
| Offene Handelsgesellschaft (OHG) | General Partnership | Family law firms or small business partnerships | Unlimited liability, partnership of individuals, shared management |
| Kommanditgesellschaft (KG) | Limited Partnership | Mittelstand companies in Germany | At least one general partner with unlimited liability, limited partners with liability limited to their investment |
Defining Gesellschaft in the Corporate World
Gesellschaft in the corporate world refers to formal, impersonal relationships driven by individual goals and contractual agreements rather than personal bonds. Corporations exemplify Gesellschaft through structured hierarchies, clear roles, and an emphasis on efficiency and productivity. This framework fosters goal-oriented collaboration, prioritizing organizational objectives over emotional or traditional ties.
Key Features of Gesellschaft in Modern Businesses
Gesellschaft in modern businesses is characterized by impersonal relationships, formal contracts, and a focus on individual achievements within corporate structures. Key features include clearly defined roles, hierarchical organization, and explicit rules governing interactions, promoting efficiency and accountability. This model supports large-scale operations where economic goals outweigh personal connections, typified by multinational corporations and publicly traded companies.
Corporate Hierarchies and Gesellschaft Structures
Corporate hierarchies exemplify Gesellschaft structures through their formalized roles, defined responsibilities, and impersonal relationships that prioritize efficiency and goal achievement. In multinational corporations like IBM or General Electric, rigid chains of command and standardized communication protocols reinforce the bureaucratic organization characteristic of Gesellschaft. These structures facilitate coordinated actions across diverse departments and global offices, emphasizing strategic planning and functional specialization over personal connections.
Employee Relationships in Gesellschaft Corporations
In Gesellschaft corporations, employee relationships are typically formal and transactional, emphasizing clearly defined roles, contractual obligations, and performance-based evaluations. Communication tends to be structured and professional, with limited emphasis on personal connections or emotional bonding among coworkers. This framework supports efficiency and goal-oriented collaboration but often lacks the social cohesion found in Gemeinschaft-oriented organizations.
Formal Rules and Regulations in Corporate Settings
Corporations operate under strict formal rules and regulations that define roles, responsibilities, and procedures to ensure accountability and efficiency. These formal structures facilitate coordination among departments and maintain order in decision-making processes. Compliance with corporate governance standards and legal frameworks exemplifies gesellschaft dynamics within business environments.
Decision-Making Processes in Gesellschaft Organizations
In Gesellschaft organizations, decision-making processes are typically formalized and based on rational-legal authority, emphasizing efficiency and clear hierarchical structures. Corporate boards and executive committees use data-driven analysis and strategic planning to guide organizational goals and operations, ensuring accountability and standardized procedures. This approach contrasts with Gemeinschaft models by prioritizing impersonal relationships and objective criteria over personal bonds in organizational governance.
Case Study: Gesellschaft Model in Multinational Companies
The Gesellschaft model in multinational companies emphasizes formal, impersonal relationships characterized by contractual agreements and clear hierarchies. Corporations like Siemens and General Electric illustrate this by structuring global operations with standardized policies and professional management systems across diverse cultural contexts. This approach facilitates efficient coordination, accountability, and scalability in complex international business environments.
Impact of Gesellschaft on Workplace Culture
Gesellschaft relationships in corporations foster formal, goal-oriented interactions that prioritize efficiency and productivity over personal connections. This impersonal dynamic often leads to structured workplace cultures emphasizing roles, rules, and performance metrics. As a result, employees may experience clearer expectations but face challenges in developing deep interpersonal bonds within the company.
Efficiency and Productivity in Gesellschaft Corporations
Gesellschaft corporations prioritize efficiency and productivity through formal structures, defined roles, and clear hierarchies that streamline decision-making processes and reduce ambiguity. These organizations implement standardized procedures and performance metrics to optimize resource allocation and maximize output. The emphasis on goal-oriented collaboration fosters rapid innovation and scalability, distinguishing Gesellschaft models from more community-based social structures.
Challenges of Maintaining Gesellschaft in Large Businesses
Large corporations often struggle to maintain the impersonal and goal-oriented relationships characteristic of Gesellschaft, as hierarchical structures can lead to communication breakdowns and diminished employee engagement. Challenges include balancing formal roles with the need for trust and cooperation, while managing diverse workforces across multiple locations. Navigating these complexities requires strategies that reinforce clear organizational objectives without sacrificing social cohesion and individual motivation.
example of gesellschaft in corporation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com