Hypergamy in marriage refers to the practice where an individual marries someone of a higher social or economic status. A common example is when a woman marries a man with significantly greater income or education level, seeking improved financial stability or social prestige. This behavior is often influenced by cultural norms valuing upward mobility through matrimonial alliances. In many societies, hypergamy can impact patterns of social stratification and economic mobility. Studies show that women tend to marry men with higher socioeconomic status more frequently than men marry women of higher status, reflecting traditional gender roles. Data from marriage markets reveal that hypergamic tendencies contribute to the maintenance of social hierarchies.
Table of Comparison
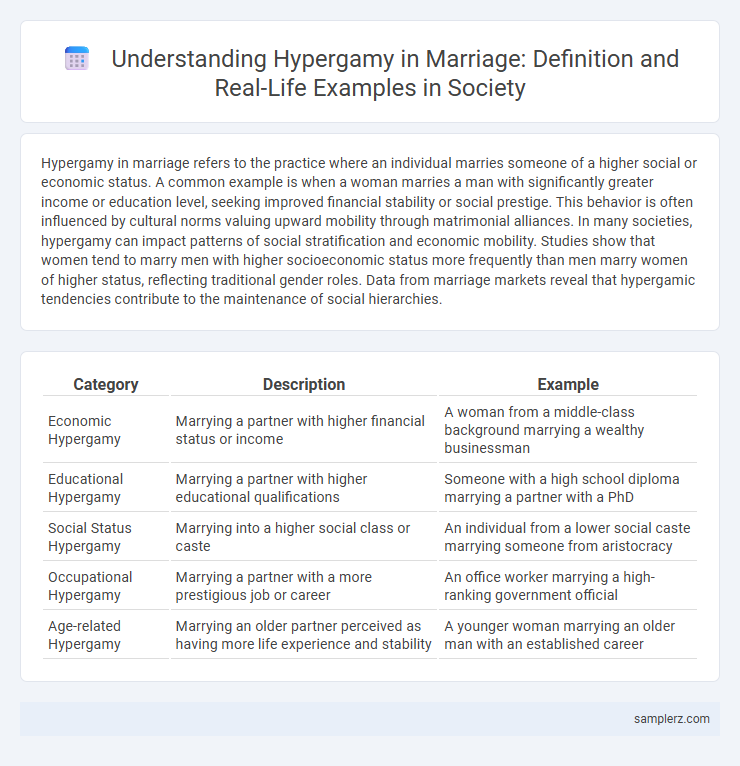
| Category | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Hypergamy | Marrying a partner with higher financial status or income | A woman from a middle-class background marrying a wealthy businessman |
| Educational Hypergamy | Marrying a partner with higher educational qualifications | Someone with a high school diploma marrying a partner with a PhD |
| Social Status Hypergamy | Marrying into a higher social class or caste | An individual from a lower social caste marrying someone from aristocracy |
| Occupational Hypergamy | Marrying a partner with a more prestigious job or career | An office worker marrying a high-ranking government official |
| Age-related Hypergamy | Marrying an older partner perceived as having more life experience and stability | A younger woman marrying an older man with an established career |
Understanding Hypergamy in Modern Marriages
Hypergamy in modern marriages often manifests as individuals marrying partners with higher socioeconomic status, education, or social prestige, reflecting a strategic pursuit of upward social mobility. This trend is notably prevalent in urban settings where economic opportunities and social networks influence mate selection. Studies indicate that hypergamy can impact marital satisfaction, gender roles, and economic dynamics within contemporary households.
Historical Roots of Hypergamous Relationships
Hypergamy in marriage has deep historical roots tied to social and economic stratification, where women traditionally sought partners of higher social status to secure economic stability and elevate family lineage. In many ancient societies, such as those in India and Europe, hypergamous practices were institutionalized through marriage customs and caste systems, reinforcing social hierarchies. These historical patterns reflect the persistent influence of wealth, power, and prestige on partner selection across cultures and eras.
Socioeconomic Factors Driving Hypergamy
Hypergamy in marriage often occurs when individuals seek partners with higher socioeconomic status to improve financial stability and social mobility. Factors such as income disparity, educational attainment, and occupational prestige strongly influence these partner selection patterns. This social behavior reflects the desire for enhanced resources, security, and upward class movement within marital relationships.
Real-Life Stories: Hypergamy in Contemporary Couples
In contemporary couples, hypergamy is exemplified when partners prioritize socioeconomic status and education in matrimonial choices, such as a woman marrying a man with a higher income or advanced degree. Real-life stories frequently highlight scenarios where career achievements and financial stability influence relationship dynamics and long-term commitments. Studies show that hypergamous tendencies remain prevalent despite evolving social norms, impacting marriage patterns across various cultures.
Education and Hypergamy: The Academic Gap
Educational hypergamy in marriage occurs when spouses exhibit a significant disparity in academic attainment, often with one partner holding advanced degrees while the other has comparatively lower educational qualifications. Studies show women increasingly marry men with higher educational levels, reflecting societal shifts and economic incentives tied to academic credentials. This academic gap influences household dynamics, impacting income distribution, career opportunities, and social mobility within families.
Gender Roles and Hypergamy Today
Hypergamy in marriage often reflects traditional gender roles where women seek partners with higher socioeconomic status, reinforcing existing social hierarchies. Contemporary studies show that despite evolving gender norms, many women still prioritize financial stability and social mobility in mate selection. This trend highlights the persistent influence of economic factors and cultural expectations in shaping modern marital choices.
Cultural Perspectives on Hypergamous Marriages
Hypergamous marriages, prevalent in South Asian cultures, often reflect deeply ingrained social hierarchies where women marry into families with higher economic or social status to elevate their familial standing. In Ethiopian societies, hypergamy is linked to traditional dowry practices, emphasizing the groom's superior social position as a means of securing alliance and prestige. These cultural perspectives highlight how hypergamy serves as a mechanism to reinforce existing social stratifications through marital unions.
Financial Stability as a Hypergamous Incentive
Financial stability often serves as a primary hypergamous incentive in marriage, where individuals seek partners with higher income or wealth to enhance their economic security. Research shows that women frequently prioritize financial resources and career prospects when selecting a spouse, aiming to improve their lifestyle and social status. This economic advantage influences marital decisions and reinforces patterns of hypergamy across diverse cultures.
The Impact of Hypergamy on Marital Satisfaction
Hypergamy, where one partner marries into a higher socioeconomic status, often influences marital satisfaction by creating power imbalances and unmet expectations. Studies show couples with significant social or economic disparities experience higher conflict levels and reduced emotional intimacy. Understanding hypergamy's role in expectations and communication can help improve relationship dynamics and overall marital satisfaction.
Hypergamy and Its Influence on Divorce Rates
Hypergamy, the practice of marrying someone of higher socioeconomic status, significantly influences divorce rates by creating imbalances in power and expectations within marriages. Studies indicate that couples with pronounced hypergamous dynamics face higher divorce risks due to conflicting financial goals and social pressures. Research from the American Sociological Association highlights that marriages with unequal educational or income levels often experience increased marital instability and dissolution.
example of hypergamy in marriage Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com