Social distance refers to the perceived or actual space between individuals or groups in social interactions. It encompasses factors such as cultural differences, socioeconomic status, and personal relationships that influence how people connect or separate in society. For example, social distance can be observed in workplace hierarchies, where employees maintain formal communication and distinct boundaries with supervisors. Another example of social distance is seen in urban communities where residents of different ethnic backgrounds may interact minimally due to cultural or language barriers. This separation affects social cohesion and can impact access to resources and opportunities. Measuring social distance helps sociologists understand patterns of inclusion, exclusion, and integration within diverse populations.
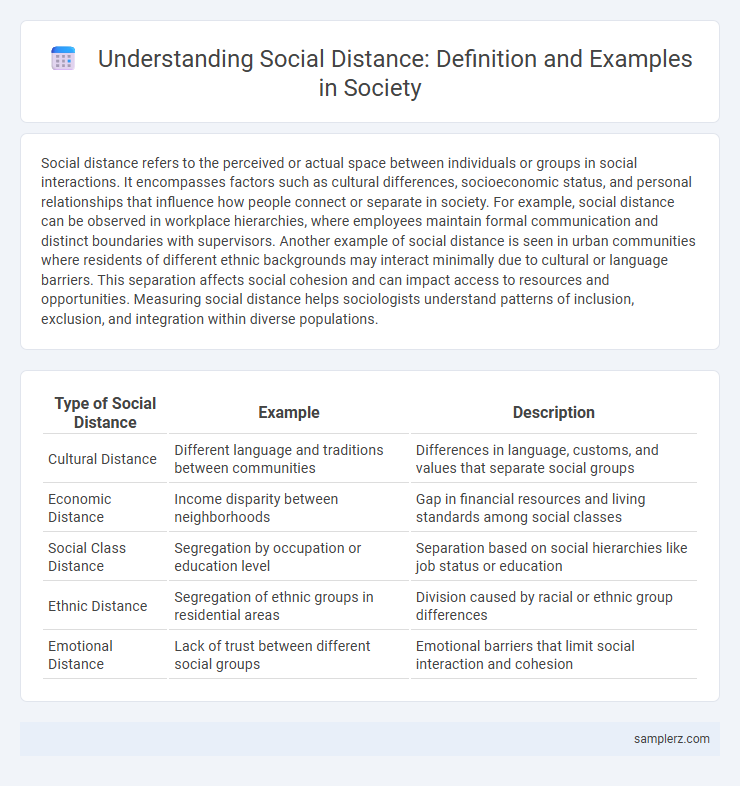
Table of Comparison
| Type of Social Distance | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cultural Distance | Different language and traditions between communities | Differences in language, customs, and values that separate social groups |
| Economic Distance | Income disparity between neighborhoods | Gap in financial resources and living standards among social classes |
| Social Class Distance | Segregation by occupation or education level | Separation based on social hierarchies like job status or education |
| Ethnic Distance | Segregation of ethnic groups in residential areas | Division caused by racial or ethnic group differences |
| Emotional Distance | Lack of trust between different social groups | Emotional barriers that limit social interaction and cohesion |
Understanding Social Distance: Key Concepts
Social distance refers to the perceived or actual degree of separation between individuals or groups based on factors such as socioeconomic status, ethnicity, or cultural backgrounds. This concept highlights variations in social interactions, ranging from close personal relationships to distant, impersonal connections. Understanding social distance helps in analyzing social cohesion, inclusion, and barriers within communities.
Manifestations of Social Distance in Everyday Life
Social distance manifests in everyday life through behaviors such as limited eye contact, physical spacing in public settings, and restrained conversation topics to maintain personal boundaries. These actions reflect underlying social hierarchies and group memberships that influence interpersonal interactions. Nonverbal cues like posture and facial expression also signal varying degrees of social closeness or detachment.
Social Distance in Multicultural Societies
Social distance in multicultural societies often manifests through varying degrees of acceptance and interaction among ethnic or cultural groups, impacting social cohesion and inclusion. Differences in language, customs, and socioeconomic status can increase perceived social distance, leading to segregated communities or limited cross-cultural engagement. Reducing social distance requires policies promoting intercultural dialogue, equitable opportunities, and shared social spaces to foster mutual understanding and integration.
Social Distance and Intergroup Relationships
Social distance in social contexts refers to the perceived or actual degree of acceptance and interaction between individuals or groups, often influenced by factors like ethnicity, socioeconomic status, or cultural background. It significantly impacts intergroup relationships by shaping levels of trust, prejudice, and cooperation, which can either hinder or facilitate social cohesion. Studies show that reducing social distance through inclusive policies and intercultural dialogue improves empathy and diminishes stereotyping in diverse communities.
Effects of Social Distance on Community Cohesion
Social distance significantly impacts community cohesion by reducing interpersonal trust and increasing feelings of alienation among group members. High social distance often leads to fragmented social networks, limiting cooperation and collective action within communities. This erosion of social bonds can weaken local support systems and reduce overall community resilience.
Social Distance in Educational Settings
Social distance in educational settings often manifests through unequal access to resources, leading to disparities in learning opportunities among students from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Schools in affluent areas typically provide advanced technology and experienced teachers, whereas underfunded institutions struggle to meet basic educational needs. These gaps reinforce social stratification and affect students' academic achievement and social integration.
The Role of Social Distance in Workplace Dynamics
Social distance in workplace dynamics influences communication patterns, collaboration, and employee engagement by defining the psychological gap between colleagues at different organizational levels. Lower social distance fosters trust, open dialogue, and teamwork, while higher social distance can lead to misunderstandings, reduced cooperation, and decreased productivity. Effective management of social distance enhances leadership effectiveness and promotes a positive organizational culture.
Social Distance and Digital Communication
Social distance shapes interactions by influencing how people maintain personal space and boundaries in digital communication platforms like social media and video calls. Virtual environments often blur physical distance but create new forms of social distance through curated profiles and selective sharing. This digital mediation affects relationship dynamics, trust, and social cohesion in contemporary society.
Reducing Social Distance Through Social Initiatives
Social initiatives such as community volunteer programs, neighborhood events, and inclusive educational workshops effectively reduce social distance by fostering direct interaction and mutual understanding among diverse groups. These efforts promote empathy, break down stereotypes, and create a sense of belonging, which strengthens social cohesion. Data shows that areas with active social programs report higher levels of trust and cooperation among residents, highlighting the impact of intentional engagement on bridging social divides.
Measuring Social Distance: Tools and Approaches
Measuring social distance involves quantitative tools like the Bogardus Social Distance Scale, which assesses people's willingness to engage with diverse social groups. Surveys and psychometric assessments analyze attitudes and biases, enabling researchers to map social closeness or alienation across communities. Advanced approaches include network analysis and social media data mining to capture real-time social interactions and perceived group boundaries.
example of social distance in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com