A primary group in social contexts is characterized by close, personal, and enduring relationships. An example of a primary group is a family, where members share emotional bonds, face-to-face interactions, and long-term commitments. This group plays a crucial role in shaping individual identity and social development. Friendship circles also represent primary groups, with members engaging in regular, intimate communication and mutual support. These groups influence social norms, values, and behaviors through direct interaction and emotional connections. The primary group differs from secondary groups by its depth of personal involvement and emotional intensity.
Table of Comparison
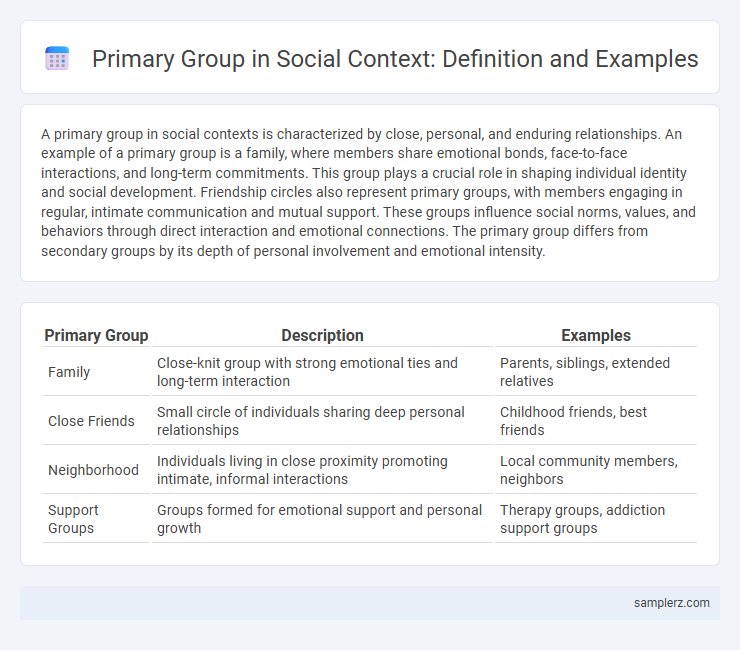
| Primary Group | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Family | Close-knit group with strong emotional ties and long-term interaction | Parents, siblings, extended relatives |
| Close Friends | Small circle of individuals sharing deep personal relationships | Childhood friends, best friends |
| Neighborhood | Individuals living in close proximity promoting intimate, informal interactions | Local community members, neighbors |
| Support Groups | Groups formed for emotional support and personal growth | Therapy groups, addiction support groups |
Understanding Primary Groups in Social Contexts
Primary groups in social contexts consist of close-knit, intimate relationships such as family and close friends, where members share strong emotional bonds and face-to-face interactions. These groups significantly influence individuals' socialization, identity formation, and support systems, providing a sense of belonging and security. Understanding primary groups is essential for analyzing social cohesion and interpersonal dynamics within communities.
Family: The Fundamental Primary Group
The family serves as the fundamental primary group in social structures, providing emotional support, socialization, and a sense of identity. It establishes the earliest and most influential social bonds that shape individual behaviors, values, and norms. Strong family ties contribute to social stability and personal development throughout life.
Close Friendships as Primary Groups
Close friendships serve as quintessential primary groups, characterized by intimate, enduring bonds and direct interactions that foster personal growth and emotional support. These relationships provide a fundamental platform for socialization, shaping values, attitudes, and identity through shared experiences and mutual trust. The unique dynamics of close friendships contribute to psychological well-being, highlighting their critical role within social structures as essential sources of belonging and self-expression.
Peer Groups: Building Social Foundations
Peer groups, consisting of friends and close acquaintances, are prime examples of primary groups in social contexts, shaping individuals' attitudes and behaviors through direct, personal interaction. These groups provide essential emotional support and a sense of belonging, influencing social development from childhood through adolescence. The dynamics within peer groups foster communication skills, norms, and identity formation critical for navigating broader social environments.
Childhood Playgroups: Early Social Ties
Childhood playgroups serve as a primary group where early social ties form through regular, face-to-face interactions among peers. These intimate groups foster emotional support, trust, and the development of social skills essential for future relationships. The shared experiences within playgroups create a foundation for identity and belonging during formative years.
Intimate Relationships and Bonded Groups
Primary groups in social contexts consist of intimate relationships characterized by close, enduring bonds, such as family members and close friends. These bonded groups provide emotional support, socialization, and a sense of belonging integral to individual identity formation. The dynamics within these groups influence personal values, behavior patterns, and social development.
Neighborhood Circles: Proximity and Connection
Neighborhood circles exemplify primary groups through close-knit relationships formed by geographic proximity and frequent interactions. These groups foster trust, emotional support, and shared norms essential for social cohesion within communities. The constant face-to-face contact in neighborhood circles strengthens bonds, creating a reliable support network reflective of primary group dynamics.
Study Groups: Academic Support Networks
Study groups function as primary groups in social contexts by fostering close-knit academic support networks where members collaborate to enhance learning outcomes and share resources. These groups create a sense of belonging and mutual accountability, which strengthens interpersonal bonds and motivates consistent study habits. By engaging regularly in shared goals, study groups promote effective communication and collective problem-solving skills among students.
Support Groups: Shared Experiences and Trust
Support groups exemplify primary groups by fostering deep emotional bonds through shared experiences and mutual trust. Members openly share personal challenges, creating a safe environment that nurtures empathy and strong interpersonal connections. This trust and support system enhances individuals' coping mechanisms and social well-being.
Workplace Teams as Emerging Primary Groups
Workplace teams exemplify emerging primary groups through close-knit interactions and shared goals that foster strong emotional bonds among members. These teams often develop trust, mutual support, and a sense of belonging, characteristics traditionally attributed to primary groups like family or close friends. The dynamic nature of workplace collaboration enhances social cohesion and personal commitment, reinforcing the primary group framework in professional settings.
example of primary group in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com