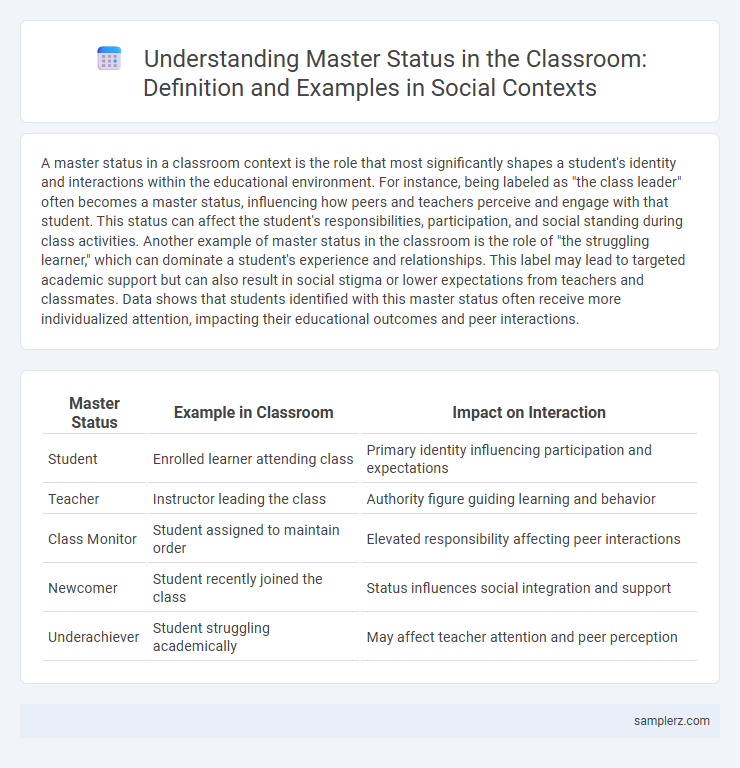
A master status in a classroom context is the role that most significantly shapes a student's identity and interactions within the educational environment. For instance, being labeled as "the class leader" often becomes a master status, influencing how peers and teachers perceive and engage with that student. This status can affect the student's responsibilities, participation, and social standing during class activities. Another example of master status in the classroom is the role of "the struggling learner," which can dominate a student's experience and relationships. This label may lead to targeted academic support but can also result in social stigma or lower expectations from teachers and classmates. Data shows that students identified with this master status often receive more individualized attention, impacting their educational outcomes and peer interactions.
Table of Comparison
| Master Status | Example in Classroom | Impact on Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Student | Enrolled learner attending class | Primary identity influencing participation and expectations |
| Teacher | Instructor leading the class | Authority figure guiding learning and behavior |
| Class Monitor | Student assigned to maintain order | Elevated responsibility affecting peer interactions |
| Newcomer | Student recently joined the class | Status influences social integration and support |
| Underachiever | Student struggling academically | May affect teacher attention and peer perception |
Student Leadership Roles as Master Status
Student leadership roles in the classroom serve as a master status by defining students' identities and shaping peer interactions. Positions such as class president, group leader, or peer mentor carry expectations that influence behavior and social recognition within the educational environment. These roles often overshadow other social statuses, directing attention toward leadership qualities and responsibilities.
Academic Achievement as a Dominant Identity
Master status in the classroom often manifests through academic achievement, where a student's high grades and academic awards become their dominant identity among peers and teachers. This status shapes social interactions, influencing peer recognition and teacher expectations, reinforcing the student's role as an academic leader. Academic success, therefore, serves as a key indicator of social position within educational settings.
Teacher’s Perception and Labeling in Classrooms
Master status profoundly shapes teacher's perception and labeling in classrooms, often leading educators to ascribe disproportionate importance to a single identity trait, such as special needs or giftedness. This dominant label influences instructional expectations and peer interactions, reinforcing social hierarchies and potentially limiting student opportunities. Research highlights that teachers' reliance on master status can perpetuate bias, affecting academic evaluations and classroom dynamics.
Socioeconomic Background and Classroom Status
In a classroom setting, a student's socioeconomic background often serves as a master status that influences peer interactions and teacher expectations, shaping their overall classroom status. Wealthier students may receive more positive attention and resources, while those from lower socioeconomic backgrounds might face stigmatization or limited opportunities. This entrenched master status impacts academic performance, social inclusion, and long-term educational outcomes.
Influence of Popularity on Student Identity
In a classroom setting, a student's master status often revolves around their popularity, which significantly shapes their social identity and peer interactions. Popular students typically experience greater social influence, often becoming leaders or trendsetters within the group, which reinforces their dominant identity. This master status of popularity affects both self-perception and how others assign roles, impacting academic participation and social opportunities.
Gender as a Master Status Among Peers
Gender often serves as a master status in classroom settings, influencing peer interactions and social grouping significantly. Female and male students frequently experience different expectations and roles assigned by teachers and classmates, affecting participation and leadership opportunities. These gender-based perceptions shape social dynamics and peer relationships, reinforcing traditional gender norms within the school environment.
Special Education Labels and Social Hierarchy
In a classroom setting, a master status often emerges through special education labels such as "learning-disabled" or "gifted," which dominate how peers and teachers perceive a student's identity and abilities. These labels can create distinct social hierarchies, where students with special education designations may experience stigmatization or elevated expectations influencing their social interactions and academic opportunities. Understanding the impact of master status helps educators create inclusive environments that challenge hierarchical divisions based on special education classifications.
Ethnicity and Cultural Identity in Classroom Dynamics
Master status in a classroom setting often revolves around ethnicity and cultural identity, profoundly influencing student interactions and teacher expectations. For instance, a student from a minority ethnic background may be perceived primarily through the lens of their cultural identity, affecting peer relationships and academic opportunities. This dominant social identity can shape classroom dynamics by reinforcing stereotypes or fostering cultural awareness and inclusivity.
Sports Participation as a Defining Role
Sports participation often becomes a master status for students in the classroom, shaping their identity and influencing peer interactions. Athletes frequently receive social recognition and leadership opportunities that overshadow other roles, such as academic or extracurricular achievements. This dominant role can affect teacher expectations and peer group dynamics, reinforcing the athlete's primary social position.
Effects of Master Status on Classroom Inclusion
A student's master status, such as being identified as "gifted" or having a disability, significantly shapes their experiences of classroom inclusion. This dominant social identity influences peer interactions, teacher expectations, and the availability of learning resources, often leading to either enhanced support or social isolation. Understanding the effects of master status helps educators create more equitable and inclusive learning environments that accommodate diverse student needs.
example of master status in classroom Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com