Habitus in a social club refers to the ingrained habits, skills, and dispositions that members develop through their interactions within the club environment. These shared practices influence how individuals behave, speak, and perceive social norms, shaping their identity and sense of belonging. For example, members of a chess club often exhibit strategic thinking and patience as part of their habitus, reflecting the values and culture of the group. The concept of habitus also explains how new members adapt to the club's social structure by internalizing its rules and expectations. In a sports club, habitual gestures, language, and routines create a common framework for cooperation and competition. Data on member participation and communication patterns reveal how habitus reinforces social cohesion and the transmission of club culture over time.
Table of Comparison
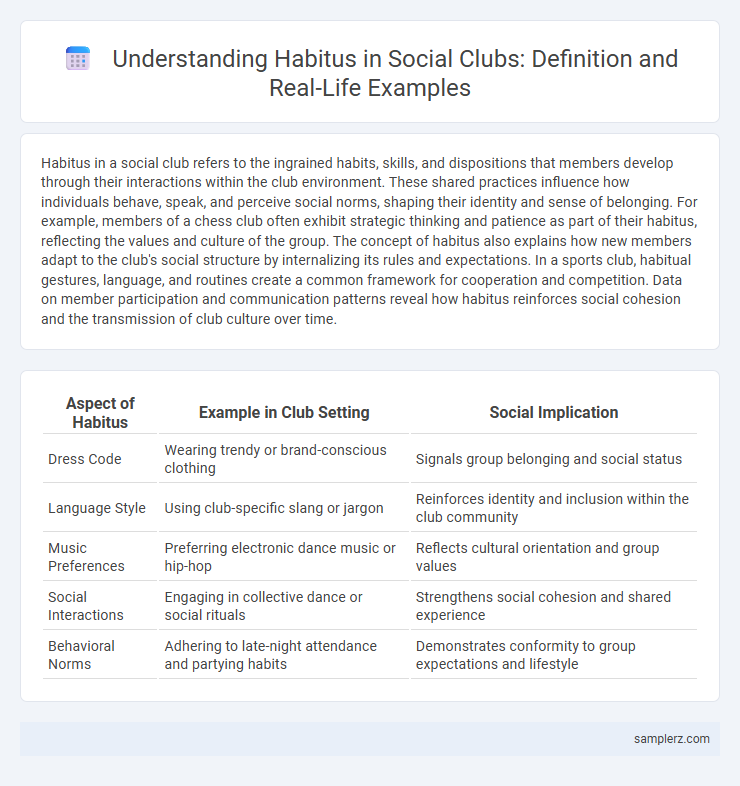
| Aspect of Habitus | Example in Club Setting | Social Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Dress Code | Wearing trendy or brand-conscious clothing | Signals group belonging and social status |
| Language Style | Using club-specific slang or jargon | Reinforces identity and inclusion within the club community |
| Music Preferences | Preferring electronic dance music or hip-hop | Reflects cultural orientation and group values |
| Social Interactions | Engaging in collective dance or social rituals | Strengthens social cohesion and shared experience |
| Behavioral Norms | Adhering to late-night attendance and partying habits | Demonstrates conformity to group expectations and lifestyle |
The Role of Habitus in Shaping Club Culture
Habitus shapes club culture by influencing members' behaviors, tastes, and interactions based on shared social backgrounds and experiences. In clubs, habits, language styles, and unwritten norms reflect collective values, reinforcing social cohesion and group identity. This embodied disposition guides how members navigate social hierarchies and participate in club rituals.
Dress Codes: Physical Habitus Manifestations in Clubs
Physical habitus in clubs is often expressed through strict dress codes that reflect social status and group identity, such as upscale venues requiring tailored suits and designer dresses to signify exclusivity and sophistication. Clubgoers internalize these norms, embodying the aesthetic preferences and cultural capital associated with the club's social hierarchy. The enforcement of such dress codes serves as a mechanism for distinguishing insiders from outsiders, reinforcing social boundaries within the nightlife scene.
Social Interactions: Habitus and Club Networking
Club networking illustrates habitus through ingrained social behaviors and shared cultural codes guiding member interactions. These practices, shaped by past experiences and social positions, influence how individuals communicate, build relationships, and access resources within the club environment. The habitual participation in club events fosters a collective identity that reinforces social capital and networking opportunities.
Music Preferences and Habitus Expression
Music preferences in a club often reflect the habitus of its patrons, shaping social identity through genre choices like techno or hip-hop. These preferences serve as expressions of cultural capital, signaling group membership and lifestyle patterns within the club setting. The selective engagement with specific musical styles reinforces social boundaries and shared values among attendees.
Drinking Rituals: Club Habitus in Action
In club settings, drinking rituals exemplify the habitus by shaping social interactions through shared practices and symbols, such as specific drink choices, timing, and toasting behaviors. These rituals reinforce group identity and social hierarchies, with members often learning and performing the expected conduct to gain acceptance. Observing how individuals follow unspoken rules around alcohol consumption reveals the embodied cultural norms that define the club's social environment.
Dance Styles: Bodily Habitus within Clubs
Bodily habitus in clubs is exemplified through dance styles like hip-hop, salsa, and techno, where embodied movement reflects social identities and cultural capital. These dance forms encode symbols of status, gender roles, and group belonging, shaping individuals' physical expression according to club subcultures. The habitual postures, gestures, and rhythms performed reveal internalized social norms and contribute to the distinctive atmosphere of the club environment.
Club Etiquette: Unwritten Rules as Habitus
Club etiquette functions as a key example of habitus, where unwritten rules like dressing appropriately, waiting your turn at the bar, and respecting personal space shape member behavior. These social norms become deeply ingrained, guiding interactions without explicit instruction and reinforcing group identity. Understanding this habitus helps explain how individuals navigate and maintain order within club environments.
Gatekeeping: Habitus in Club Entry Practices
Gatekeeping in club entry practices exemplifies habitus by reflecting how social norms and embodied dispositions influence who gains access to exclusive spaces. Bouncers and regular members often assess potential entrants based on appearance, behavior, and social cues aligned with the club's cultural capital, reinforcing class distinctions and group identity. This selective inclusion perpetuates power structures, maintaining the club's social hierarchy through subtle, ingrained habits.
VIP Sections: Social Stratification and Habitus
In club settings, VIP sections embody Bourdieu's concept of habitus by reflecting ingrained social distinctions and elite cultural capital. The exclusive access, personalized service, and spatial separation reinforce social stratification, signaling status and tastes among patrons. Regular attendees internalize and reproduce these social hierarchies through behavior, dress codes, and interaction patterns within these privileged zones.
Clique Formation: Group Dynamics and Habitus in Clubs
Clique formation within clubs exemplifies how habitus shapes social interactions, as members unconsciously adopt shared behaviors, language, and values that reinforce group identity. The club's specific cultural practices and norms influence individual dispositions, creating a cohesive social environment where inclusion depends on alignment with established group dynamics. These ingrained social structures perpetuate exclusivity and affect how members navigate power relations and social capital within the club.
example of habitus in club Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com