Folkways are informal norms or everyday customs that guide social behavior within a culture. An example of a folkway in American culture is the practice of shaking hands when greeting someone. This simple gesture signals politeness and respect without involving strict rules or legal consequences. In Japanese culture, bowing serves as a common folkway used to show respect and acknowledgment. The depth and duration of the bow can vary depending on the social context and the relationship between individuals. These customs maintain social harmony and reflect cultural values through unspoken, routine behaviors.
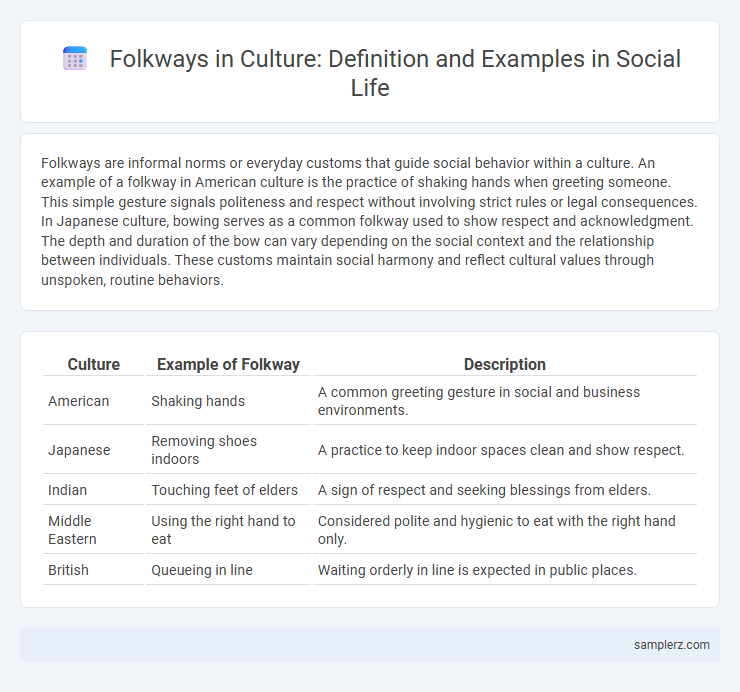
Table of Comparison
| Culture | Example of Folkway | Description |
|---|---|---|
| American | Shaking hands | A common greeting gesture in social and business environments. |
| Japanese | Removing shoes indoors | A practice to keep indoor spaces clean and show respect. |
| Indian | Touching feet of elders | A sign of respect and seeking blessings from elders. |
| Middle Eastern | Using the right hand to eat | Considered polite and hygienic to eat with the right hand only. |
| British | Queueing in line | Waiting orderly in line is expected in public places. |
Introduction to Folkways in Social Culture
Folkways in social culture refer to everyday norms that guide casual interactions, such as greetings, dress codes, and table manners. For example, in many Western cultures, shaking hands upon meeting someone exemplifies a common folkway that promotes politeness and social bonding. These unwritten rules vary across societies but are essential for maintaining social order and cultural identity.
The Role of Folkways in Everyday Life
Folkways guide everyday social interactions such as greeting customs, table manners, and dress codes, reflecting a community's cultural norms. These informal rules shape behavior by promoting social cohesion and predictability within a group. Violations of folkways typically result in mild social sanctions like disapproval or awkwardness rather than harsh penalties.
Greeting Customs: Handshakes, Bows, and Beyond
Greeting customs such as handshakes in Western cultures, bows in Japan, and cheek kisses in Latin America exemplify folkways that shape social interactions and convey respect. These nonverbal gestures serve as essential cultural signals, reflecting societal norms and values in everyday communication. Understanding these varied greeting practices fosters intercultural awareness and smooth social exchanges.
Folkways in Dining Etiquette Around the World
Folkways in dining etiquette vary widely across cultures, reflecting social norms that guide behavior during meals. In Japan, it is customary to avoid sticking chopsticks vertically into rice, as this resembles a funeral ritual and is considered disrespectful. In contrast, in India, eating with the right hand is a deeply ingrained folkway, symbolizing cleanliness and respect, while using the left hand is often frowned upon during meals.
Dress Codes and Modesty Traditions as Folkways
Dress codes and modesty traditions serve as fundamental folkways within various cultures, guiding appropriate attire to reflect respect and social identity. These customs dictate clothing styles, such as the wearing of saris in India or headscarves in Middle Eastern societies, reinforcing cultural values and community cohesion. Violations of these dress norms often lead to social disapproval rather than legal consequences, emphasizing their role in everyday social interactions.
Folkway Examples in Celebration and Festivals
Folkways in celebrations often include traditions like wearing specific costumes during Halloween or exchanging gifts during Christmas, emphasizing community identity and social cohesion. Festivals such as Diwali showcase customs like lighting lamps and sharing sweets, reinforcing cultural values and social norms. These practices, while informal, guide behavior and contribute to the collective cultural experience.
Social Interaction Norms: Politeness and Respect
Folkways in social interaction emphasize politeness and respect, such as greeting others with a handshake or a nod to acknowledge presence. Using appropriate language, like saying "please" and "thank you," reinforces social harmony and mutual respect. These norms facilitate smooth communication and maintain positive relationships within communities.
Gender Roles and Folkway Expectations
Folkways in culture often manifest through gender roles, where societal expectations dictate distinct behaviors and responsibilities for men and women. For example, traditional folkways may assign women the role of caretakers and homemakers, while men are expected to be providers and protectors. These norms guide daily social interactions and reinforce cultural identity by establishing accepted patterns of conduct based on gender.
Greetings and Leave-Taking Rituals
Greetings and leave-taking rituals in culture often include specific gestures such as handshakes, bows, or verbal expressions like "hello" and "goodbye," which function as essential folkways. These social customs vary widely across societies, reflecting values and levels of formality; for instance, bowing in Japan symbolizes respect, while a firm handshake in the United States conveys confidence. Proper observance of these folkways maintains social harmony, signaling politeness and mutual recognition within the cultural context.
Impact of Technology on Modern Folkways
Modern folkways have been significantly transformed by the impact of technology, such as the widespread use of smartphones altering traditional greeting customs by favoring digital communication over face-to-face interactions. Online social norms, like emoji usage and text abbreviations, have become new folkways that shape everyday social behavior across cultures. These shifts reflect how technology reshapes cultural expectations and informal social rules in contemporary society.
example of folkway in culture Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com