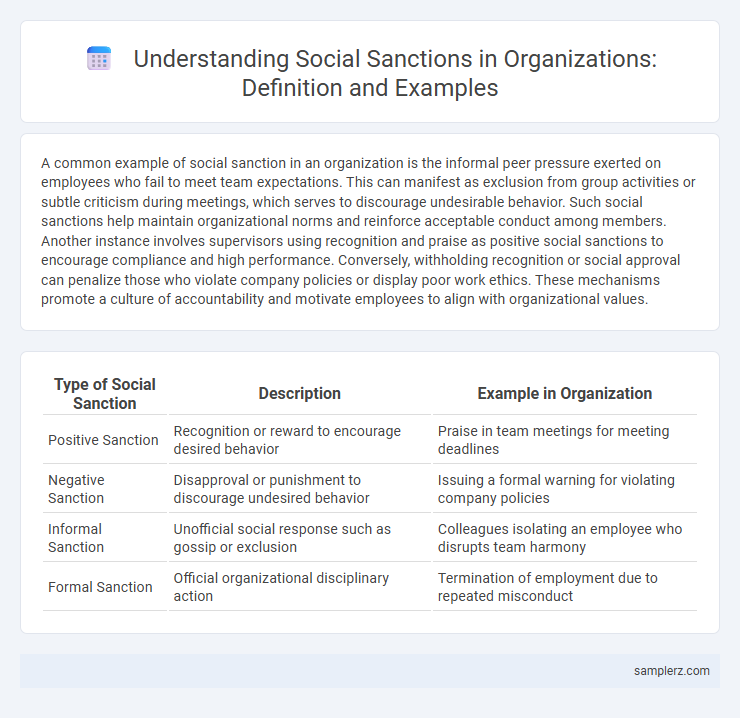
A common example of social sanction in an organization is the informal peer pressure exerted on employees who fail to meet team expectations. This can manifest as exclusion from group activities or subtle criticism during meetings, which serves to discourage undesirable behavior. Such social sanctions help maintain organizational norms and reinforce acceptable conduct among members. Another instance involves supervisors using recognition and praise as positive social sanctions to encourage compliance and high performance. Conversely, withholding recognition or social approval can penalize those who violate company policies or display poor work ethics. These mechanisms promote a culture of accountability and motivate employees to align with organizational values.
Table of Comparison
| Type of Social Sanction | Description | Example in Organization |
|---|---|---|
| Positive Sanction | Recognition or reward to encourage desired behavior | Praise in team meetings for meeting deadlines |
| Negative Sanction | Disapproval or punishment to discourage undesired behavior | Issuing a formal warning for violating company policies |
| Informal Sanction | Unofficial social response such as gossip or exclusion | Colleagues isolating an employee who disrupts team harmony |
| Formal Sanction | Official organizational disciplinary action | Termination of employment due to repeated misconduct |
Understanding Social Sanctions in the Workplace
Social sanctions in the workplace include informal reprimands such as exclusion from team activities or subtle negative feedback from colleagues, which enforce organizational norms and expectations. Employees who repeatedly violate workplace policies may face formal sanctions like written warnings or suspension, reflecting the organization's commitment to maintaining discipline and productivity. Understanding these mechanisms helps foster a culture of accountability and reinforces positive behavior within corporate environments.
Common Forms of Social Sanction in Organizations
Common forms of social sanction in organizations include informal reprimands, social exclusion, and reduced collaboration opportunities, which enforce adherence to workplace norms. Employees who violate organizational values may face gossip, negative feedback, or loss of trust from peers and supervisors. These social sanctions help maintain organizational culture and encourage compliance without formal disciplinary measures.
Peer Pressure as a Social Sanction Tool
Peer pressure acts as a powerful social sanction tool within organizations by influencing employee behavior through group norms and expectations. When team members observe peers adhering to policies or ethical standards, non-compliance often leads to subtle social exclusion or criticism, effectively motivating conformity. This informal sanction reinforces organizational culture and drives collective accountability without formal disciplinary actions.
The Role of Gossip and Rumors in Social Discipline
Gossip and rumors serve as informal social sanctions within organizations by enforcing norms and discouraging deviant behavior. They function as a mechanism for maintaining social discipline, where negative information spread about individuals who violate group expectations often leads to reputational damage and corrective actions. This informal regulation helps sustain organizational cohesion and accountability without formal intervention.
Exclusion and Ostracism in Office Culture
Exclusion and ostracism in office culture serve as powerful social sanctions that reinforce organizational norms by isolating employees who deviate from expected behaviors. This social exclusion can lead to decreased job satisfaction, lower productivity, and increased turnover rates, ultimately impacting overall team dynamics and company performance. Organizations that recognize and address these sanctions promote a more inclusive environment, fostering collaboration and employee well-being.
Impact of Social Sanctions on Team Dynamics
Social sanctions in organizations, such as peer feedback, exclusion from group activities, or public recognition, significantly influence team dynamics by reinforcing acceptable behavior and discouraging rule-breaking. These sanctions promote accountability, enhance cooperation, and align individual actions with organizational goals, resulting in improved team cohesion and productivity. Conversely, overly harsh or inconsistent sanctions can lead to decreased morale, increased conflict, and reduced trust among team members.
Social Reprimands: Public Criticism in Meetings
Public criticism in meetings serves as a powerful social sanction within organizations, reinforcing behavioral norms by openly addressing misconduct or underperformance. This form of social reprimand not only deters undesirable actions but also promotes accountability and transparency among team members. The collective visibility of such feedback encourages employees to align with organizational expectations and maintain professional standards.
Informal Rewards and Punishments Among Colleagues
Informal rewards in organizations often include verbal praise, peer recognition, or increased social inclusion, which enhance motivation and reinforce positive behaviors without formal procedures. Conversely, informal punishments such as social exclusion, gossip, or subtle disapproval serve to discourage undesirable actions and maintain group norms. These social sanctions play a crucial role in shaping workplace culture by leveraging colleagues' influence to regulate behavior effectively.
Social Sanctions and Organizational Norm Enforcement
Social sanctions in organizations include informal reprimands, exclusion from team activities, and negative performance evaluations, which enforce adherence to organizational norms. These sanctions regulate behavior by signaling disapproval when employees violate established rules or cultural expectations. Consistent application of such social sanctions fosters a culture of accountability and reinforces organizational values.
Mitigating Negative Effects of Social Sanctions
Implementing restorative justice practices within organizations mitigates the negative effects of social sanctions by promoting open communication and accountability. Encouraging peer support networks helps individuals cope with social exclusion, fostering reintegration rather than prolonged isolation. Training leadership in empathetic conflict resolution further reduces the adverse impacts of social sanctions on employee morale and productivity.
example of social sanction in organization Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com