Socialization in family is a crucial process where children learn norms, values, and behaviors from their parents and siblings. For instance, a child observing respectful communication during family dinners develops interpersonal skills. These early interactions shape emotional intelligence and social competence, laying a foundation for future relationships. Parents often use discipline and praise as tools to teach appropriate social conduct, reinforcing societal expectations within the family setting. Participating in family traditions and routines helps individuals internalize cultural norms and build a sense of identity. Family socialization influences language development, empathy, and problem-solving abilities, which are essential for navigating broader social environments.
Table of Comparison
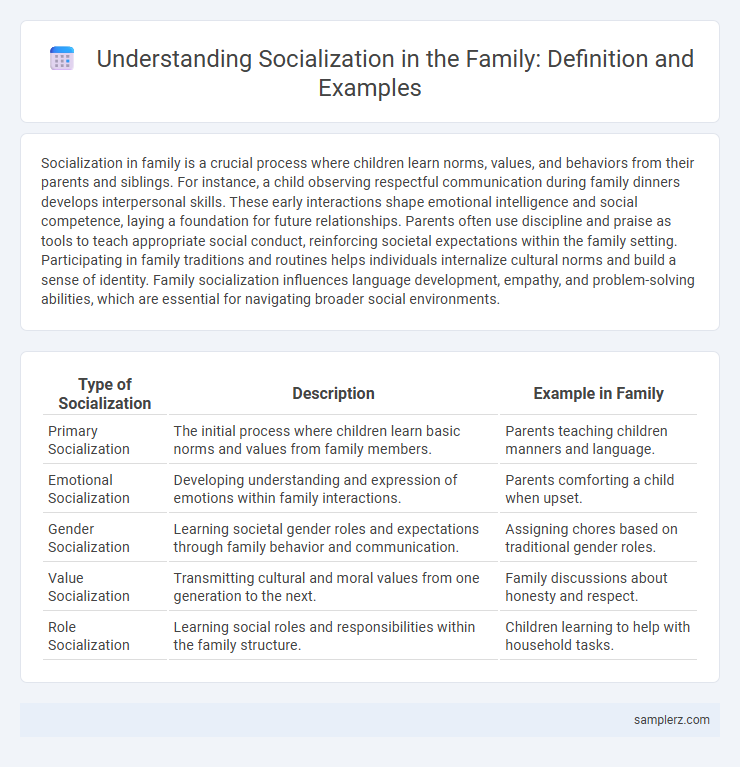
| Type of Socialization | Description | Example in Family |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Socialization | The initial process where children learn basic norms and values from family members. | Parents teaching children manners and language. |
| Emotional Socialization | Developing understanding and expression of emotions within family interactions. | Parents comforting a child when upset. |
| Gender Socialization | Learning societal gender roles and expectations through family behavior and communication. | Assigning chores based on traditional gender roles. |
| Value Socialization | Transmitting cultural and moral values from one generation to the next. | Family discussions about honesty and respect. |
| Role Socialization | Learning social roles and responsibilities within the family structure. | Children learning to help with household tasks. |
Importance of Family in Early Socialization
Family plays a crucial role in early socialization by providing the first environment where children learn communication skills, cultural norms, and emotional regulation. Through daily interactions with parents and siblings, children develop foundational behaviors such as empathy, cooperation, and conflict resolution. These early family experiences shape social competence and influence lifelong relationships and social integration.
Parental Roles in Teaching Social Norms
Parental roles in teaching social norms are crucial in early childhood development, as parents model behavior and set expectations for respect, communication, and cooperation. Through daily interactions and guidance, parents instill values such as empathy, responsibility, and social etiquette that form the foundation for interpersonal relationships. Consistent reinforcement of these norms within the family unit enhances children's social competence and adaptability in broader social environments.
Sibling Interactions and Social Skills Development
Sibling interactions play a crucial role in socialization within the family by fostering communication, conflict resolution, and empathy skills. Through cooperative play and shared responsibilities, siblings develop essential social competencies such as negotiation, cooperation, and emotional regulation. These interactions contribute significantly to children's ability to navigate complex social environments outside the family unit.
Family Traditions as Tools for Socialization
Family traditions serve as vital tools for socialization by fostering shared values and cultural identity among members. Rituals such as holiday celebrations and weekly family meals create consistent opportunities for communication and role modeling. These practices promote emotional bonding and teach social norms, helping children develop a sense of belonging and interpersonal skills.
Socialization Through Family Communication
Family communication serves as a primary channel for socialization, where children learn language, social norms, and cultural values through daily interactions with parents and siblings. Conversations during meals, storytelling, and shared activities foster emotional bonds and teach important social skills like empathy and cooperation. This communication shapes identity formation and prepares individuals for broader social participation.
Learning Values and Ethics Within the Family
Family serves as the primary environment where children absorb core values and ethical principles through daily interactions and modeled behaviors. Parents and siblings reinforce lessons in honesty, respect, and responsibility by setting consistent examples and providing guidance during conflicts or decision-making moments. This foundational socialization shapes individuals' moral frameworks and influences their behavior in broader societal contexts.
Influence of Extended Family on Social Behavior
Extended family members play a crucial role in shaping social behavior by providing diverse perspectives, cultural values, and emotional support that influence individual attitudes and interactions. Intergenerational interactions within extended families foster social skills such as communication, empathy, and cooperation, which are essential for community engagement. Studies indicate that children exposed to extended family environments tend to develop stronger social networks and enhanced conflict resolution abilities.
Gender Role Socialization in the Home
Gender role socialization in the home shapes children's understanding of societal expectations through parental behaviors, household chores, and communication patterns. Boys may be encouraged to exhibit traits like assertiveness and independence, while girls often receive reinforcement for nurturing and cooperation. These early interactions significantly influence individual identity formation and perpetuate cultural norms about masculinity and femininity.
Emotional Support and Social Competence in Families
Emotional support in families fosters secure attachments and resilience by providing children with a safe environment to express feelings and develop empathy. Parents model social competence through consistent communication, conflict resolution, and collaborative problem-solving, which enhances children's interpersonal skills. These interactions shape effective social behaviors essential for positive relationships outside the family unit.
Impact of Family Structure on Socialization Patterns
Family structure significantly shapes socialization patterns by influencing the emotional support and communication styles children experience. Nuclear families often promote independence and peer integration, while extended families provide a broader social network fostering intergenerational learning. Single-parent households may face challenges in time and resource allocation, impacting social skill development and behavioral outcomes.
example of socialization in family Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com