In kinship terminology, an agnat is an individual related through male lineage or patrilineal descent. For example, a man's paternal uncle, who shares a common male ancestor, is considered his agnat. This relationship emphasizes the importance of the male bloodline in the structure of family ties. A classic example of an agnatic bond occurs in traditional societies where inheritance and family name pass through the male line. Brothers and their sons form an agnatic kin group, maintaining continuity of property and social status. Data from anthropological studies highlight agnation as a key factor in clan organization and social hierarchy.
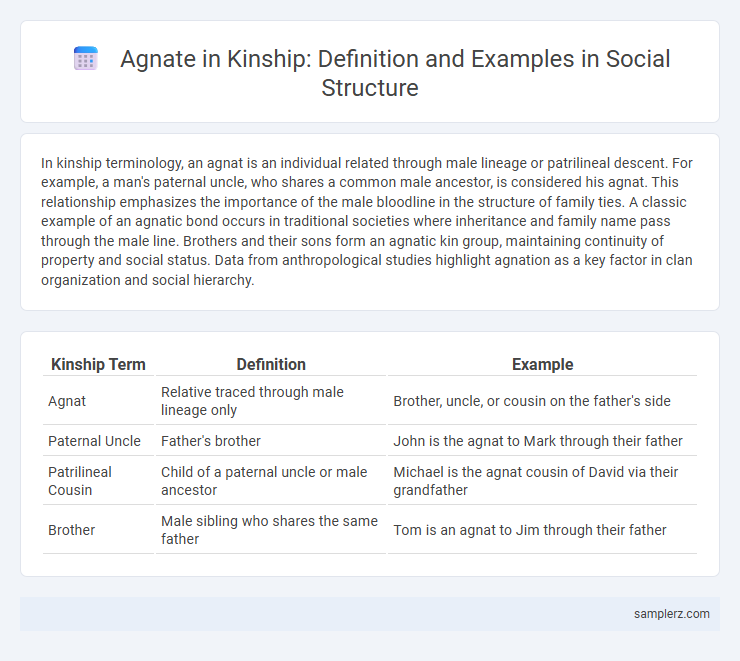
Table of Comparison
| Kinship Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Agnat | Relative traced through male lineage only | Brother, uncle, or cousin on the father's side |
| Paternal Uncle | Father's brother | John is the agnat to Mark through their father |
| Patrilineal Cousin | Child of a paternal uncle or male ancestor | Michael is the agnat cousin of David via their grandfather |
| Brother | Male sibling who shares the same father | Tom is an agnat to Jim through their father |
Understanding Agnatic Kinship: A Social Perspective
Agnatic kinship refers to relationships traced through the male lineage, emphasizing paternal connections such as father, son, and male ancestors. This form of kinship plays a crucial role in many societies for inheritance, social status, and familial responsibilities. Understanding agnatic ties reveals how male-descended lineages influence social organization and identity in diverse cultural contexts.
Core Examples of Agnat Relations in Traditional Societies
Agnat relations in traditional societies typically emphasize paternal lineage, where individuals trace descent exclusively through the male line. Core examples include the father-son relationship, brotherhood among males sharing the same paternal grandfather, and patrilineal clans that control inheritance and social status. These agnatic bonds reinforce social cohesion and inheritance rights within patriarchal kinship systems.
Agnat in Modern Family Structures
Agnatic kinship in modern family structures typically emphasizes lineage traced through male ancestors, reflecting patrilineal descent common in many cultures. This system governs inheritance, family name transmission, and social responsibilities, often influencing familial roles and power dynamics. Contemporary societies increasingly challenge strict agnatic traditions, blending both paternal and maternal affiliations within evolving family frameworks.
The Role of Agnatic Kin in Inheritance and Succession
Agnatic kin refers to relatives traced exclusively through the male lineage, playing a crucial role in inheritance and succession in many traditional societies. Property, titles, and family leadership often pass through agnatic lines to ensure continuity of the paternal heritage and maintain family authority. This patrilineal system reinforces social structure by prioritizing male descendants and their rights within kinship networks.
Agnatic Lineage: Influence on Social Organization
Agnatic lineage, tracing descent exclusively through the male line, profoundly shapes social organization by determining inheritance, residence, and authority patterns. In many patrilineal societies, such as among the Nuer of South Sudan, agnatic kinship establishes clan membership and political alliances, reinforcing male roles in governance and resource control. This male-centered descent system reinforces social cohesion and hierarchical structures through clearly defined obligations and privileges linked to agnatic ties.
Cultural Variations of Agnatic Kinship Systems
Agnatic kinship systems emphasize lineage traced through the male line, commonly found in patrilineal societies such as the Maasai of East Africa, where inheritance and social status pass from father to son. In contrast, the Nuer people of Sudan practice a form of agnatic kinship where clan identity hinges on male ancestry, shaping marriage alliances and political power structures. These cultural variations highlight how agnatic systems adapt to socio-political environments, influencing property rights, leadership roles, and group cohesion within different ethnic groups.
Agnatic Networks and Social Support Mechanisms
Agnatic networks, rooted in patrilineal kinship systems, facilitate social support by ensuring resource distribution and mutual aid among male relatives. These networks strengthen social cohesion through shared ancestry, reinforcing obligations related to inheritance, lineage continuity, and collective defense. Such support mechanisms prove crucial in times of economic hardship or social conflict, enabling members to rely on kin for labor, protection, and emotional assistance.
Agnatic Kinship in Community Decision-Making
Agnatic kinship, traced through the male lineage, plays a pivotal role in community decision-making by establishing authority and responsibility among male relatives. In many traditional societies, elders from the agnatic line hold decision-making power, which ensures the preservation of family honor and property within the paternal clan. This system reinforces social cohesion by aligning community leadership with agnatic descent, promoting stability and continuity in collective governance.
Challenges Facing Agnatic Kinship in Contemporary Society
Agnatic kinship, emphasizing lineage through male ancestors, faces significant challenges in contemporary society due to evolving gender roles and increasing recognition of maternal and bilateral descent. Legal frameworks and social norms increasingly support matrilineal and egalitarian kinship structures, undermining the traditional agnatic emphasis on paternal inheritance and authority. These shifts complicate inheritance rights, family identity, and social obligations tied exclusively to male lineage, demanding adaptive kinship practices in modern social contexts.
The Future of Agnat Relations in Changing Social Landscapes
Agnat relations, defined by patrilineal descent, play a crucial role in maintaining social cohesion and inheritance patterns within traditional communities. As modernization and globalization reshape family dynamics, the future of agnat bonds depends on their ability to adapt to evolving social norms and legal frameworks. Emerging trends indicate a subtle shift toward more inclusive kinship models, blending agnatic ties with bilateral recognition to balance heritage preservation and contemporary social integration.
example of agnat in kinship Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com