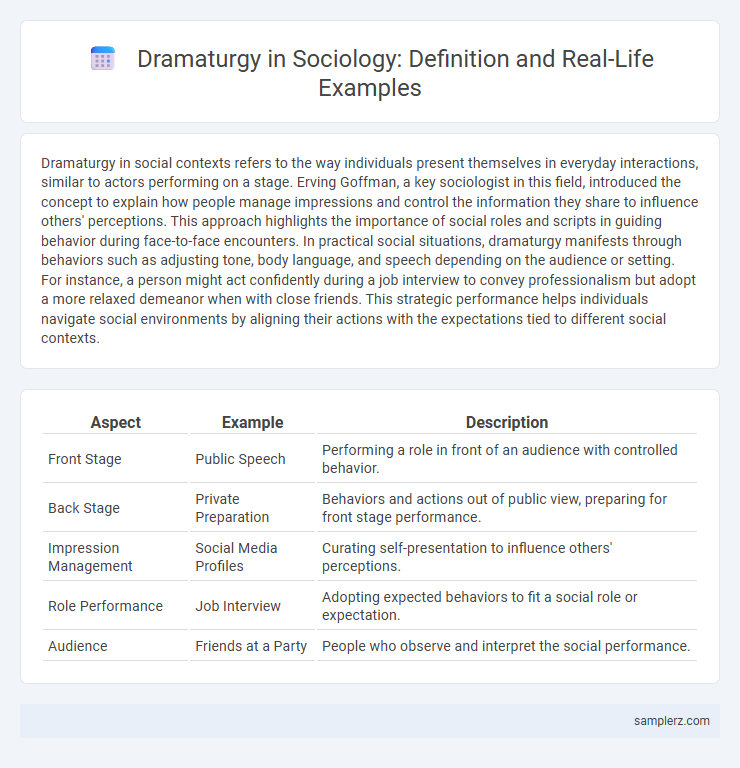
Dramaturgy in social contexts refers to the way individuals present themselves in everyday interactions, similar to actors performing on a stage. Erving Goffman, a key sociologist in this field, introduced the concept to explain how people manage impressions and control the information they share to influence others' perceptions. This approach highlights the importance of social roles and scripts in guiding behavior during face-to-face encounters. In practical social situations, dramaturgy manifests through behaviors such as adjusting tone, body language, and speech depending on the audience or setting. For instance, a person might act confidently during a job interview to convey professionalism but adopt a more relaxed demeanor when with close friends. This strategic performance helps individuals navigate social environments by aligning their actions with the expectations tied to different social contexts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Front Stage | Public Speech | Performing a role in front of an audience with controlled behavior. |
| Back Stage | Private Preparation | Behaviors and actions out of public view, preparing for front stage performance. |
| Impression Management | Social Media Profiles | Curating self-presentation to influence others' perceptions. |
| Role Performance | Job Interview | Adopting expected behaviors to fit a social role or expectation. |
| Audience | Friends at a Party | People who observe and interpret the social performance. |
Everyday Interactions: Dramaturgy in Public Spaces
Everyday interactions in public spaces exemplify dramaturgy by showcasing how individuals perform social roles based on context and audience. People adjust their behavior, appearance, and speech to manage impressions during routine encounters at parks, cafes, or public transit. This dynamic performance highlights the fluid negotiation of identity through frontstage and backstage behavior in social environments.
Social Roles: Performing Identity in Daily Life
Dramaturgy in social contexts illustrates how individuals perform social roles to negotiate identity, similar to actors on a stage adapting their behavior based on audience expectations. Erving Goffman's theory highlights impression management, where people consciously or unconsciously tailor their actions, language, and appearance to fit societal norms and situational demands. This dynamic performance reinforces social cohesion and allows individuals to navigate complex social interactions effectively.
The “Front Stage” and “Back Stage” of Online Profiles
Online profiles exemplify dramaturgy by showcasing a carefully curated "Front Stage" where users present idealized versions of themselves through selective photos, posts, and interactions. Behind the scenes, the "Back Stage" involves private settings or unshared content revealing more authentic, unfiltered behaviors and emotions. This dichotomy reflects Erving Goffman's theory, emphasizing impression management in digital social environments.
Dramaturgy in Workplace Behavior
Dramaturgy in workplace behavior illustrates how employees perform roles and manage impressions to navigate organizational social dynamics effectively. Goffman's concept emphasizes the front stage, where individuals present polished professional personas, and the back stage, where authentic behaviors emerge away from managerial scrutiny. Understanding these role performances enhances team collaboration and leadership strategies within corporate environments.
Managing Impressions During Social Gatherings
Managing impressions during social gatherings involves carefully controlling verbal and nonverbal cues to influence how others perceive an individual's identity and social status. Dramaturgy, as introduced by Erving Goffman, highlights the use of "front stage" behaviors where people perform roles to present an idealized version of themselves. Techniques such as adjusting tone of voice, selecting appropriate attire, and strategically sharing information help maintain favorable impressions and navigate social interactions effectively.
Family Dynamics: Acting Differently at Home
Family dynamics often resemble dramaturgy, where individuals adopt distinct roles and behaviors in the home setting compared to public spaces. Parents might perform authoritative roles while children alternate between compliant and rebellious personas, creating a complex social script. This theatrical interaction shapes communication patterns and emotional bonds, influencing overall family cohesion and conflict resolution.
Peer Groups: Shaping Behavior for Acceptance
Peer groups play a crucial role in dramaturgy by influencing individuals to adopt specific behaviors and social roles that align with group expectations, fostering a sense of acceptance and belonging. Through constant social interaction and feedback, members negotiate their identities and perform roles that reflect the group's norms and values. This dynamic process exemplifies how social acceptance is constructed and maintained via dramaturgical strategies within peer groups.
Social Media Stories: Curating the Perfect Performance
Social media stories exemplify dramaturgy by crafting a narrative arc that engages audiences through carefully timed posts and authentic emotional expressions. Platforms like Instagram and Snapchat enable users to curate moments that build suspense, reveal conflict, and deliver resolution within a limited timeframe. This performative storytelling shapes social identity and fosters community interaction by blending real-life events with strategic self-presentation.
Navigating First Impressions Through Dramaturgy
Navigating first impressions through dramaturgy involves consciously managing the social performance individuals present in initial encounters. This concept, rooted in Erving Goffman's theory, highlights how people use front-stage behavior to shape others' perceptions and establish desired social identities. Effective dramaturgy in social interactions enables smoother relationship building by strategically controlling expressions, body language, and context cues.
Cultural Norms and the Scripts We Follow
Dramaturgy in social contexts often illustrates how individuals perform roles based on cultural norms and socially constructed scripts, such as greeting rituals and conversational etiquette that vary across societies. These scripts guide behavior by establishing expectations for appropriate conduct in different social settings, like formal ceremonies or casual interactions. Understanding dramaturgy reveals how people manage impressions and navigate social roles to maintain cohesion and order within their cultural frameworks.
example of dramaturgy in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com