Deviance in social contexts refers to behaviors or actions that violate established norms and expectations within a community or society. One common example is vandalism, where individuals deliberately damage or destroy public or private property, challenging legal rules and social standards. This act not only disrupts communal harmony but also signals underlying social issues such as disenfranchisement or rebellion against authority. Another instance involves public intoxication, which contradicts accepted conduct in many cultures and legal systems. People engaging in excessive drinking in public spaces often face social stigma and legal penalties due to potential harm and disorderly behavior. Such deviant acts highlight the tension between individual freedom and societal regulation, showcasing how norms serve to maintain social order and protect community welfare.
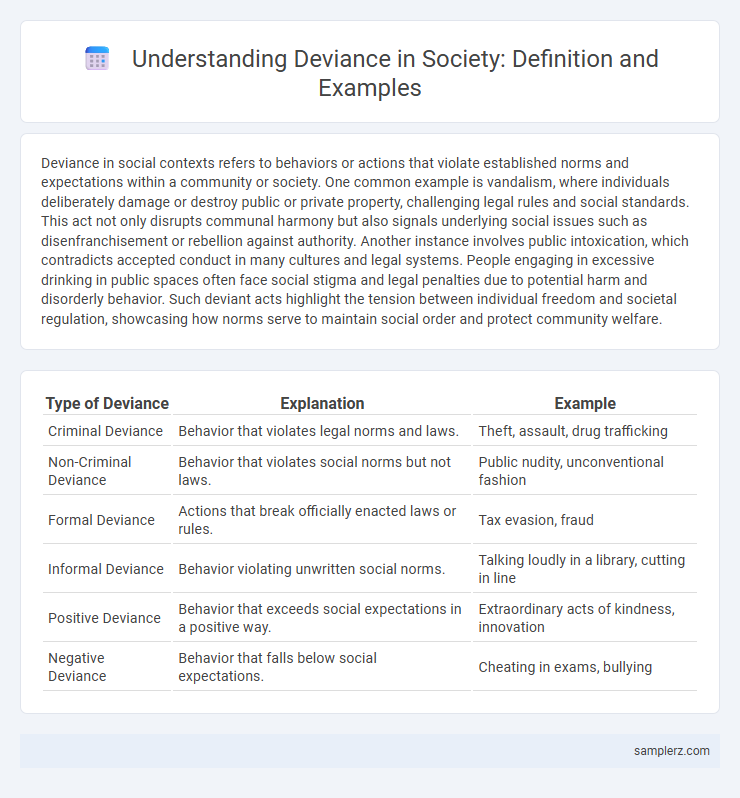
Table of Comparison
| Type of Deviance | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Criminal Deviance | Behavior that violates legal norms and laws. | Theft, assault, drug trafficking |
| Non-Criminal Deviance | Behavior that violates social norms but not laws. | Public nudity, unconventional fashion |
| Formal Deviance | Actions that break officially enacted laws or rules. | Tax evasion, fraud |
| Informal Deviance | Behavior violating unwritten social norms. | Talking loudly in a library, cutting in line |
| Positive Deviance | Behavior that exceeds social expectations in a positive way. | Extraordinary acts of kindness, innovation |
| Negative Deviance | Behavior that falls below social expectations. | Cheating in exams, bullying |
Breaking Social Norms: Everyday Deviant Acts
Breaking social norms through everyday deviant acts, such as jaywalking, dressing unconventionally, or speaking loudly in quiet settings, disrupts societal expectations and challenges collective behavior standards. These minor infractions reveal the fluid boundaries of social order and illustrate how individuals negotiate conformity and individuality. Understanding such deviance provides insight into societal control mechanisms and cultural tolerance levels.
Public Displays of Unconventional Behavior
Public displays of unconventional behavior, such as streaking at major sporting events or flash mobs disrupting public spaces, exemplify deviance by breaking social norms in highly visible ways. These acts challenge societal expectations of appropriate conduct, generating mixed reactions ranging from amusement to outrage. Sociologists study these behaviors to understand how norms are enforced and how social boundaries are negotiated.
Dress Code Violations in Society
Dress code violations in society often symbolize resistance to established social norms, reflecting deeper cultural or generational divides. Individuals who challenge conventional attire standards can face social sanctions such as exclusion or stigmatization, highlighting the role of clothing in maintaining social order. These violations reveal how dress codes function as mechanisms of social control, reinforcing group identity and conformity.
Acts of Civil Disobedience
Acts of civil disobedience represent a form of deviance in social contexts where individuals deliberately violate laws or regulations to protest perceived injustices. Famous examples include the 1963 March on Washington led by Martin Luther King Jr., which challenged racial segregation, and Mahatma Gandhi's Salt March in 1930 opposing British colonial rule in India. These acts emphasize moral resistance and aim to provoke social change through nonviolent means.
Nonconformity in Educational Settings
Nonconformity in educational settings often manifests as students challenging established norms, such as questioning authority or rejecting standardized curricula. This type of deviance can lead to innovative thinking but may also result in disciplinary actions or social exclusion. Research shows that nonconformist behavior in schools is linked to both individual creativity and systemic resistance to change.
Digital Deviance: Online Social Norm Breakers
Digital deviance manifests through behaviors such as cyberbullying, spreading misinformation, and hacking online platforms, which violate established digital norms and ethical standards. These actions disrupt social cohesion and trust within virtual communities, challenging traditional definitions of deviant conduct. Understanding online social norm breakers requires examining the impact of anonymity, technological affordances, and the rapid evolution of digital environments on deviant behaviors.
Substance Use and Social Reactions
Substance use often represents a form of social deviance, as it violates established norms and legal standards within a community. Social reactions to substance use vary widely, ranging from stigmatization and exclusion to support and rehabilitation efforts, reflecting cultural attitudes and policies. These responses influence both individual behavior and broader social dynamics, shaping patterns of acceptance or condemnation.
Social Deviance in Group Dynamics
Social deviance in group dynamics often manifests through behaviors that violate established norms, such as peer pressure leading to rule-breaking or exclusion of non-conforming members. Examples include group conformity to risky behaviors, like substance abuse, or collective resistance to authority that disrupts social order. These deviant acts reveal the powerful influence of group norms on individuals' actions within social contexts.
Deviant Acts in the Workplace
Deviant acts in the workplace include behaviors such as theft, sabotage, bullying, and chronic absenteeism, which disrupt organizational productivity and morale. These actions violate formal policies and informal norms, leading to decreased trust and increased turnover rates among employees. Addressing workplace deviance requires comprehensive strategies like employee training, clear communication of expectations, and robust disciplinary measures to maintain a healthy work environment.
Challenging Gender Role Expectations
Challenging gender role expectations often manifests through behaviors that defy traditional norms, such as men pursuing careers in nursing or women engaging in competitive sports historically dominated by men. These acts of deviance highlight the fluidity of gender identity and roles, encouraging society to reconsider rigid stereotypes. The rise of non-binary and transgender visibility further disrupts conventional gender frameworks, fostering inclusivity and diverse expressions of self.
example of deviance in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com