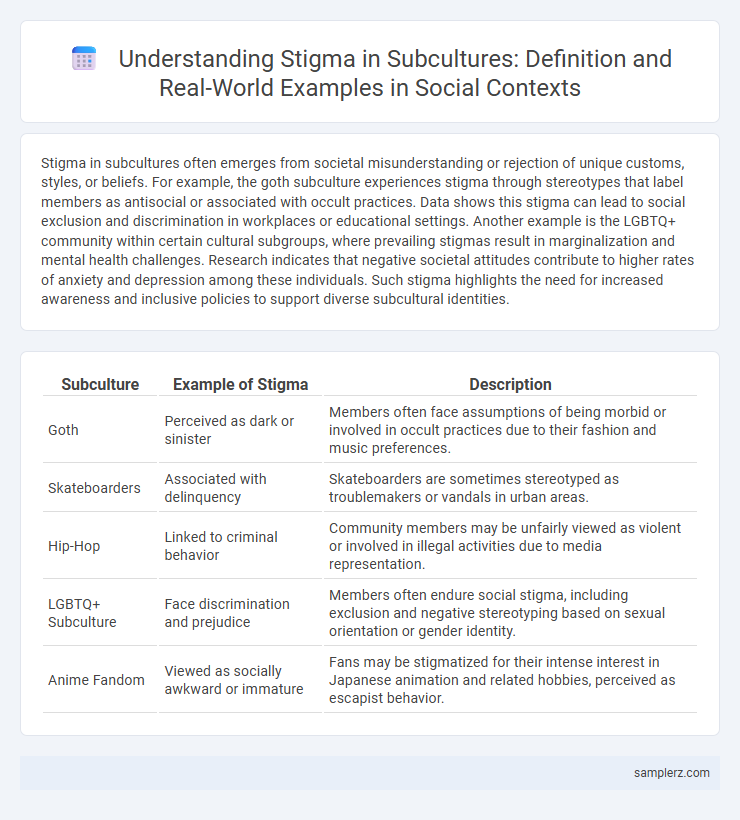
Stigma in subcultures often emerges from societal misunderstanding or rejection of unique customs, styles, or beliefs. For example, the goth subculture experiences stigma through stereotypes that label members as antisocial or associated with occult practices. Data shows this stigma can lead to social exclusion and discrimination in workplaces or educational settings. Another example is the LGBTQ+ community within certain cultural subgroups, where prevailing stigmas result in marginalization and mental health challenges. Research indicates that negative societal attitudes contribute to higher rates of anxiety and depression among these individuals. Such stigma highlights the need for increased awareness and inclusive policies to support diverse subcultural identities.
Table of Comparison
| Subculture | Example of Stigma | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Goth | Perceived as dark or sinister | Members often face assumptions of being morbid or involved in occult practices due to their fashion and music preferences. |
| Skateboarders | Associated with delinquency | Skateboarders are sometimes stereotyped as troublemakers or vandals in urban areas. |
| Hip-Hop | Linked to criminal behavior | Community members may be unfairly viewed as violent or involved in illegal activities due to media representation. |
| LGBTQ+ Subculture | Face discrimination and prejudice | Members often endure social stigma, including exclusion and negative stereotyping based on sexual orientation or gender identity. |
| Anime Fandom | Viewed as socially awkward or immature | Fans may be stigmatized for their intense interest in Japanese animation and related hobbies, perceived as escapist behavior. |
Understanding Stigma Within Subcultures
Stigma within subcultures often arises from societal misconceptions and internal group norms that label certain behaviors or identities as deviant, such as the stigmatization of mental health issues among biker communities. This internalized stigma can lead to isolation and hinder access to support networks crucial for well-being. Exploring these dynamics reveals how subcultural values shape the experience and management of stigma.
Common Forms of Stigma in Subcultural Groups
Common forms of stigma in subcultural groups include negative stereotyping, social exclusion, and discrimination based on alternative lifestyles or beliefs. Members of subcultures such as goths, punks, and gamers often face prejudices that label them as deviant, dangerous, or socially awkward. These stigmas impact their social interactions, access to opportunities, and overall mental health within broader society.
How Stereotypes Fuel Subcultural Stigma
Stereotypes such as assuming all goths are antisocial or all gamers are lazy perpetuate subcultural stigma by reducing complex identities to simplistic labels. These distorted generalizations lead to social exclusion and discrimination within mainstream society. Understanding how stereotypes fuel stigma is crucial for fostering acceptance of diverse subcultures.
Case Study: Stigmatization in the Goth Community
The Goth community often faces stigmatization due to stereotypes linking their dark fashion and music preferences with delinquency or morbidity. Studies reveal that mainstream society frequently misinterprets Goth culture as inherently rebellious or threatening, leading to social exclusion and discrimination. This case exemplifies how subcultural identity can be marginalized through imposed negative labels and misunderstanding.
Peer Rejection in Fandom Subcultures
Peer rejection in fandom subcultures often manifests through exclusion based on differing levels of knowledge or devotion, such as dismissing newcomers as "fake fans." This stigma reinforces insider-outsider dynamics, where members police authenticity by questioning others' engagement with the fandom's content, rituals, or language. Such social policing can lead to alienation and discourage diversity within the fandom community.
Stigma Faced by LGBTQ+ Subcultures
LGBTQ+ subcultures often face stigma manifested through social exclusion, discrimination, and negative stereotypes that affect mental health and community acceptance. These stigmas include misconceptions about sexuality and gender identity, leading to systemic barriers in employment, healthcare, and legal rights. Persistent societal bias perpetuates internalized stigma, influencing the well-being and visibility of LGBTQ+ individuals within broader social contexts.
Mental Health Stigma in Gaming Communities
Mental health stigma in gaming communities often manifests through stereotypes that label players with mental health issues as weak or unstable, which discourages open discussions about psychological well-being. Studies reveal that gamers facing anxiety or depression may experience isolation and judgment, reducing their willingness to seek support. Online platforms increasingly promote awareness campaigns to challenge these stigmas and foster inclusive environments that prioritize mental health care.
Dress Codes and Visible Markers of Subcultural Stigma
Dress codes within subcultures often serve as visible markers that trigger stigma, such as the negative stereotypes directed at goths wearing dark clothing and heavy makeup. These outward symbols can lead to social exclusion or discrimination in mainstream settings, reinforcing boundaries between subcultural members and the dominant culture. The stigma attached to subcultural dress highlights the power of appearance in expressing identity while simultaneously shaping social perceptions and interactions.
The Role of Media in Amplifying Subcultural Stigma
Media often amplifies subcultural stigma by selectively portraying group behaviors or appearances as deviant or threatening, reinforcing negative stereotypes. Sensationalized reporting and biased representation contribute to public misunderstanding, fostering discrimination against subcultures such as goths, punks, or gamers. Social media algorithms further intensify stigma by promoting polarizing content that highlights conflict rather than nuanced cultural expressions.
Overcoming Stigma: Strategies for Empowering Subcultures
Stigma in subcultures often manifests through stereotypes that marginalize group identities, such as the assumption that punk subculture is inherently rebellious or criminal. Empowering subcultures involves creating inclusive platforms that celebrate unique cultural expressions and promote positive visibility, reinforcing self-identity and group cohesion. Community-led initiatives, education campaigns, and allyship are effective strategies to dismantle stigma and foster acceptance within broader society.
example of stigma in subculture Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com