Pharmacoepidemiology plays a critical role in medication safety by analyzing data on drug use and adverse effects in large populations. For example, researchers use pharmacoepidemiologic methods to identify rare side effects of newly approved medications through post-marketing surveillance. This data-driven approach helps regulatory agencies update safety guidelines and issue warnings to minimize patient risks. One notable example involves the detection of cardiovascular risks associated with certain nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Pharmacoepidemiologic studies across diverse populations collected data on hospitalization rates and cardiovascular events, linking specific NSAIDs to increased heart attack risk. These findings influenced clinical prescribing practices and led to label changes that enhance patient safety worldwide.
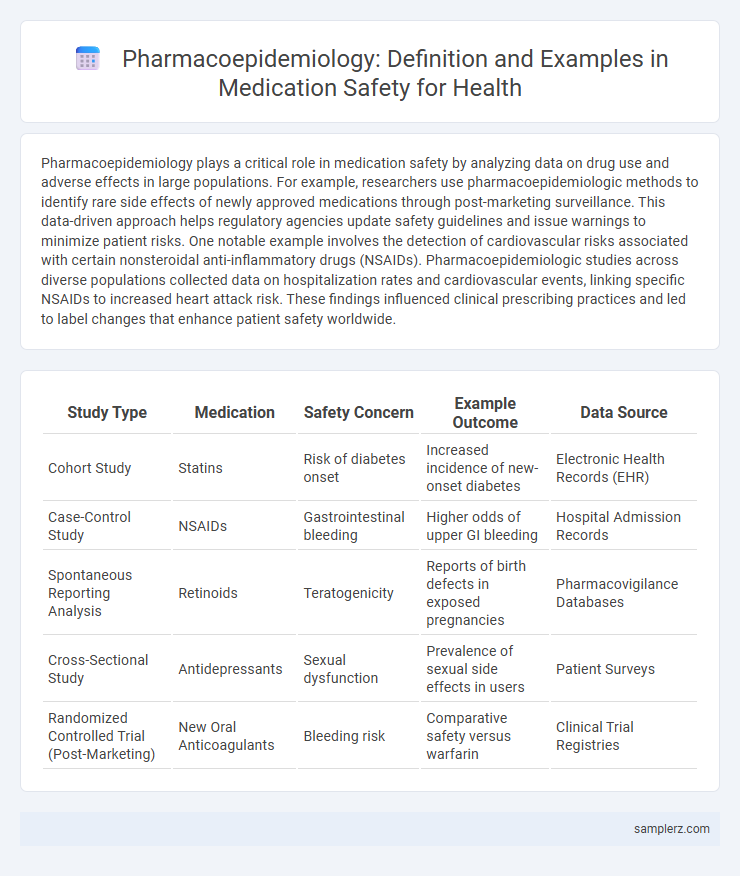
Table of Comparison
| Study Type | Medication | Safety Concern | Example Outcome | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cohort Study | Statins | Risk of diabetes onset | Increased incidence of new-onset diabetes | Electronic Health Records (EHR) |
| Case-Control Study | NSAIDs | Gastrointestinal bleeding | Higher odds of upper GI bleeding | Hospital Admission Records |
| Spontaneous Reporting Analysis | Retinoids | Teratogenicity | Reports of birth defects in exposed pregnancies | Pharmacovigilance Databases |
| Cross-Sectional Study | Antidepressants | Sexual dysfunction | Prevalence of sexual side effects in users | Patient Surveys |
| Randomized Controlled Trial (Post-Marketing) | New Oral Anticoagulants | Bleeding risk | Comparative safety versus warfarin | Clinical Trial Registries |
Introduction to Pharmacoepidemiology in Medication Safety
Pharmacoepidemiology plays a crucial role in medication safety by studying the effects and patterns of drug use in large populations to identify adverse drug reactions and prevent medication errors. It utilizes real-world data from electronic health records, prescription databases, and spontaneous reporting systems to monitor drug safety post-marketing. This field integrates clinical pharmacology and epidemiology principles to enhance risk assessment and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
The Role of Pharmacoepidemiology in Adverse Drug Reaction Surveillance
Pharmacoepidemiology plays a critical role in adverse drug reaction (ADR) surveillance by systematically analyzing large populations to detect, assess, and prevent medication-related risks. Utilizing real-world data from electronic health records, spontaneous reporting systems, and patient registries enhances the identification of rare and serious ADRs, thereby improving drug safety profiles. This approach supports regulatory decisions and informs clinical guidelines by providing robust evidence on the frequency and severity of ADRs across diverse patient groups.
Case Study: Reducing Medication Errors Using Pharmacoepidemiological Methods
Pharmacoepidemiological methods identified patterns of adverse drug reactions and high-risk medication errors in hospital settings, enabling targeted interventions to improve patient safety. By analyzing large-scale electronic health records and prescription data, researchers pinpointed specific drug combinations and administration errors contributing to preventable harm. This case study demonstrated that systematic pharmacoepidemiological surveillance significantly reduces medication errors and enhances clinical decision-making processes.
Pharmacoepidemiological Approaches to Monitoring Vaccine Safety
Pharmacoepidemiological approaches to monitoring vaccine safety involve analyzing large-scale population data to identify and assess adverse events following immunization. Active surveillance systems like the Vaccine Safety Datalink utilize electronic health records to detect rare but serious vaccine-related side effects in real time. These methods enable timely risk-benefit evaluations, ensuring optimal vaccine safety profiles in public health programs.
Real-World Evidence: Drug Safety Signal Detection
Pharmacoepidemiology leverages real-world evidence from electronic health records and post-marketing surveillance databases to identify drug safety signals, enabling early detection of adverse drug reactions that clinical trials may overlook. Advanced data mining techniques and disproportionality analyses are applied to spontaneous reporting systems like the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) to systematically monitor medication safety. This approach enhances pharmacovigilance by providing actionable insights into drug safety profiles across diverse patient populations in real-world clinical settings.
Pharmacoepidemiology and Post-Marketing Drug Surveillance
Pharmacoepidemiology plays a crucial role in medication safety by analyzing real-world drug usage and monitoring adverse effects after market approval. Post-marketing drug surveillance systems, such as the FDA's MedWatch program, collect and evaluate data on drug-related side effects to identify risks not detected in clinical trials. This ongoing surveillance helps healthcare professionals update prescribing guidelines and improves patient safety by minimizing medication-related harm.
Evaluating Risk Factors for Medication-Related Harm
Pharmacoepidemiology plays a critical role in evaluating risk factors for medication-related harm by analyzing large-scale patient data to identify associations between drug use and adverse events. Studies often focus on populations such as the elderly or those with comorbidities, using electronic health records and prescription databases to detect high-risk medications and dosage patterns. The field informs clinical guidelines and regulatory decisions by quantifying risks linked to polypharmacy, drug interactions, and patient-specific factors, ultimately enhancing medication safety.
Impact of Pharmacoepidemiology on Regulatory Decision-Making
Pharmacoepidemiology plays a crucial role in medication safety by analyzing real-world drug usage and adverse event data, which informs regulatory agencies like the FDA in evaluating drug risk-benefit profiles. Post-marketing surveillance studies conducted through pharmacoepidemiologic methods enable early detection of safety signals that influence regulatory decisions on drug labeling, restrictions, or withdrawals. This empirical evidence supports evidence-based policy making, ensuring safer medication usage and improved public health outcomes.
Cross-National Pharmacoepidemiology Studies in Medication Safety
Cross-national pharmacoepidemiology studies in medication safety analyze drug utilization and adverse drug reactions across different countries to identify patterns and risks. These studies leverage large-scale healthcare databases and electronic medical records to compare safety profiles and optimize pharmacovigilance strategies globally. By examining diverse populations, they provide critical evidence for regulatory agencies to improve medication guidelines and reduce preventable drug-related harm.
Future Directions for Pharmacoepidemiology in Enhancing Drug Safety
Emerging trends in pharmacoepidemiology emphasize the integration of big data analytics and real-world evidence to improve medication safety surveillance. Advanced machine learning algorithms are increasingly deployed to detect rare adverse drug reactions more efficiently across diverse populations. Future directions prioritize personalized medicine approaches and pharmacogenomics to tailor drug therapies, minimizing safety risks and optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
example of pharmacoepidemiology in medication safety Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com