Logrolling in government refers to the practice where legislators trade votes to secure mutual support for their respective proposals. For example, a senator from an agricultural state may agree to vote for a transportation bill sponsored by a senator from an industrial state in exchange for a vote supporting a farm subsidy program. This exchange ensures both bills receive the necessary votes to pass, despite differing priorities. The entity involved includes legislators who negotiate vote exchanges to advance bills benefiting their constituencies. Data from congressional voting records often reveal patterns of reciprocal support aligning with specific interest groups, such as agriculture or transportation. Logrolling influences legislative outcomes by enabling coalition-building around diverse policy initiatives that may otherwise face opposition.
Table of Comparison
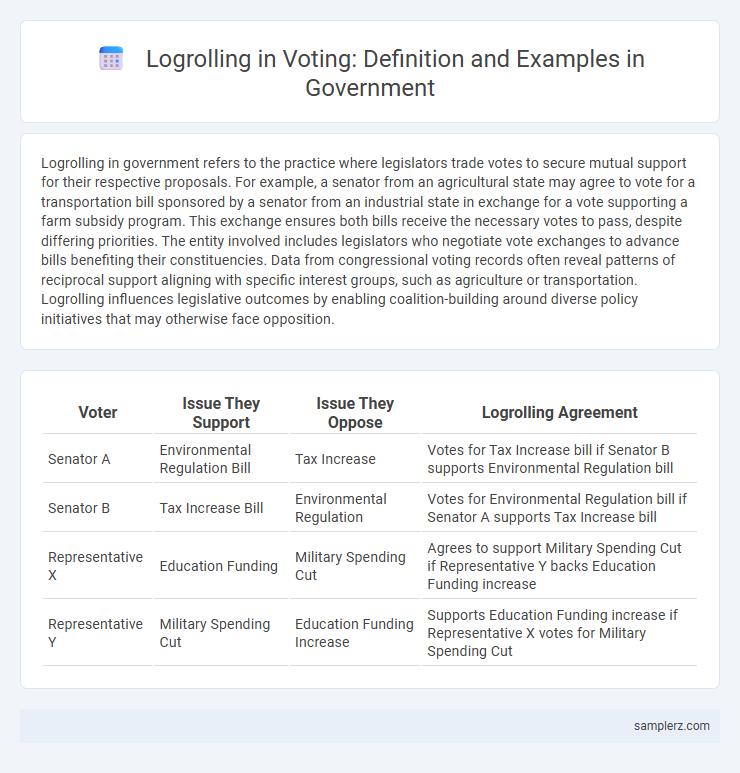
| Voter | Issue They Support | Issue They Oppose | Logrolling Agreement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senator A | Environmental Regulation Bill | Tax Increase | Votes for Tax Increase bill if Senator B supports Environmental Regulation bill |
| Senator B | Tax Increase Bill | Environmental Regulation | Votes for Environmental Regulation bill if Senator A supports Tax Increase bill |
| Representative X | Education Funding | Military Spending Cut | Agrees to support Military Spending Cut if Representative Y backs Education Funding increase |
| Representative Y | Military Spending Cut | Education Funding Increase | Supports Education Funding increase if Representative X votes for Military Spending Cut |
Understanding Logrolling in Government Voting
Logrolling in government voting occurs when legislators exchange support on different bills to secure mutual passage, often prioritizing strategic alliances over individual policy merits. This practice enables lawmakers to advance projects beneficial to their constituencies by trading votes, enhancing legislative efficiency but sometimes compromising transparency. Understanding logrolling reveals the complex negotiation dynamics shaping policy outcomes within congressional decision-making processes.
Historical Examples of Logroll Agreements
Historical examples of logroll agreements include the 1790 Compromise, where Alexander Hamilton secured Southern support for federal assumption of state debts in exchange for locating the U.S. capital in the South. Another notable instance occurred during the New Deal era, when Congress members exchanged votes on relief and infrastructure projects to ensure passage of critical legislation. The practice continues to shape legislative processes by enabling coalitions that advance diverse interests through vote trading.
How Logrolling Shapes Legislative Outcomes
Logrolling in government occurs when legislators exchange support for each other's bills to secure mutual benefits, often resulting in the passage of legislation that might not succeed on its own merits. This practice shapes legislative outcomes by enabling coalitions that merge diverse interests, allowing for the advancement of complex or controversial policies. By promoting strategic vote trading, logrolling influences policy agendas and the allocation of government resources to satisfy various constituencies.
Famous Congressional Logroll Deals
Famous congressional logroll deals include the 1986 Tax Reform Act, where lawmakers exchanged support to secure both tax cuts and corporate loophole closures, balancing diverse interests. Another notable example occurred during the 1965 Voting Rights Act passage, with legislators trading votes to ensure broad civil rights protections. These strategic vote-trading maneuvers highlight how legislative compromises shape pivotal government policies.
Logrolling in U.S. Senate and House Votes
Logrolling in the U.S. Senate and House votes occurs when legislators exchange support for each other's bills to secure mutual passage, often unrelated to their initial priorities. This strategic vote trading facilitates the approval of pork-barrel projects and policy riders that may not pass on their own merits. Such practices underscore the complex negotiation dynamics shaping federal legislation and budget allocations.
Case Study: Logroll in the Agricultural Bill
In the agricultural bill case study, legislators from farming districts exchanged votes to secure subsidies and water rights beneficial to their constituencies, exemplifying logrolling in government. This vote trading enabled the passage of the bill by creating a coalition of lawmakers who prioritized localized agricultural interests. The strategic cooperation highlighted the impact of logrolling on policy outcomes, shaping agricultural subsidies and resource allocations.
The Role of Logrolling in Budget Appropriations
Logrolling plays a crucial role in budget appropriations by enabling legislators to exchange support for specific spending projects, ensuring the passage of comprehensive budget bills. This practice often leads to the inclusion of earmarks or pork-barrel spending that benefits individual districts but may inflate overall government expenditures. By fostering coalition-building among lawmakers, logrolling facilitates consensus in otherwise contentious fiscal negotiations within government institutions.
Logrolling and Bipartisan Compromises
Logrolling in government voting involves legislators exchanging support for each other's bills to secure mutual benefits, often crossing party lines to pass essential legislation. Bipartisan compromises emerge when members from different political parties negotiate terms to achieve policy goals, leveraging logrolling to bridge ideological divides. This strategic collaboration enhances legislative efficiency and facilitates the passage of complex bills in a polarized political environment.
Ethical Implications of Logrolling Practices
Logrolling in government voting often involves legislators exchanging support for each other's bills, raising ethical concerns about the erosion of transparent decision-making and accountability. This practice can prioritize personal or political gains over public interest, leading to policies that may lack thorough scrutiny or fair evaluation. The ethical implications emphasize the need for stricter regulations and oversight to ensure legislative actions reflect genuine constituent needs rather than reciprocal deals.
Modern Instances of Logroll Voting in Politics
Modern instances of logrolling in politics manifest when lawmakers exchange support for each other's bills to secure mutual passage, often seen in budget appropriations and infrastructure projects. For example, members of the U.S. Congress frequently agree to back funding for local district programs in return for votes on broader national legislation, exemplifying strategic vote trading. This practice can influence legislative outcomes by building coalitions that advance diverse policy objectives through negotiated agreements.
example of logroll in voting Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com