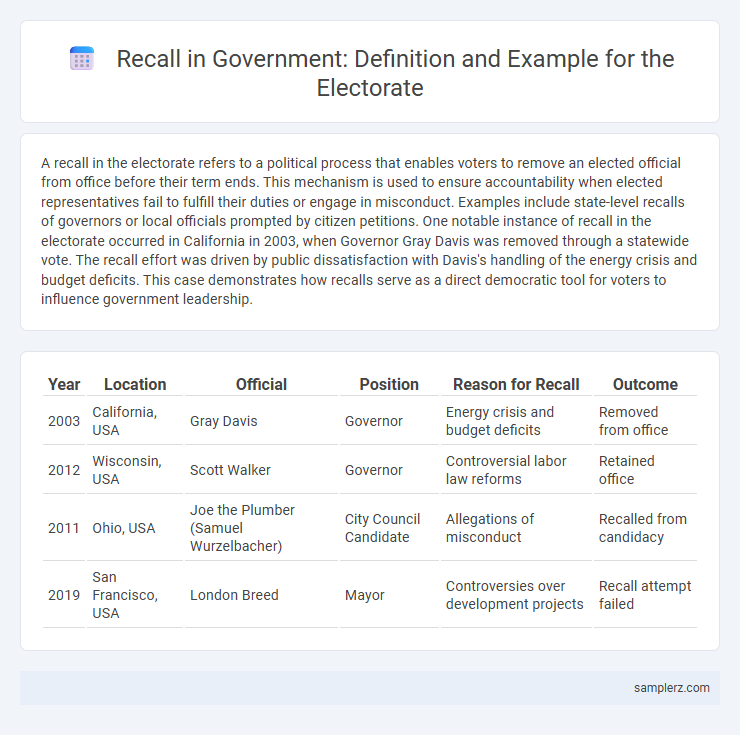
A recall in the electorate refers to a political process that enables voters to remove an elected official from office before their term ends. This mechanism is used to ensure accountability when elected representatives fail to fulfill their duties or engage in misconduct. Examples include state-level recalls of governors or local officials prompted by citizen petitions. One notable instance of recall in the electorate occurred in California in 2003, when Governor Gray Davis was removed through a statewide vote. The recall effort was driven by public dissatisfaction with Davis's handling of the energy crisis and budget deficits. This case demonstrates how recalls serve as a direct democratic tool for voters to influence government leadership.
Table of Comparison
| Year | Location | Official | Position | Reason for Recall | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | California, USA | Gray Davis | Governor | Energy crisis and budget deficits | Removed from office |
| 2012 | Wisconsin, USA | Scott Walker | Governor | Controversial labor law reforms | Retained office |
| 2011 | Ohio, USA | Joe the Plumber (Samuel Wurzelbacher) | City Council Candidate | Allegations of misconduct | Recalled from candidacy |
| 2019 | San Francisco, USA | London Breed | Mayor | Controversies over development projects | Recall attempt failed |
Introduction to Recall in the Electorate
Recall in the electorate is a democratic process allowing voters to remove elected officials from office before their term ends. This mechanism empowers citizens to hold public representatives accountable for misconduct, poor performance, or loss of public trust. States like California and Wisconsin have established legal frameworks for recall elections, ensuring direct voter participation in maintaining government integrity.
Historical Background of Recall Mechanisms
Recall mechanisms in the electorate trace back to ancient Athens, where citizens exercised direct democracy to remove officials. In the United States, the first modern recall law was adopted in Oregon in 1908, aiming to enhance political accountability. These historical instances highlight the evolving democratic practices allowing voters to hold elected officials accountable between elections.
Legal Framework Governing Electoral Recalls
The legal framework governing electoral recalls establishes clear procedures and grounds under which voters can initiate the removal of elected officials before the end of their terms, typically through petitions and subsequent elections. State constitutions and statutes outline specific criteria, such as misconduct or failure to perform duties, that justify recalls, ensuring due process and fair voter participation. This framework balances accountability with stability by setting thresholds for signatures and timelines, thereby protecting the integrity of the electoral system.
Key Examples of Recall Elections Worldwide
Key examples of recall elections worldwide include the 2003 California gubernatorial recall that ousted Governor Gray Davis, and the 2012 recall of Wisconsin State Senator Van Wanggaard, highlighting mechanisms for electorate accountability. In Venezuela, the 2004 recall referendum targeted President Hugo Chavez as a critical exercise in democratic participation. These cases demonstrate how recall elections serve as vital tools for voters to remove elected officials before term completion, reinforcing democratic responsiveness.
Notable Recall Cases in the United States
The 2003 California gubernatorial recall election is one of the most notable recall cases in the United States, resulting in the removal of Governor Gray Davis and the election of Arnold Schwarzenegger. Another significant example is the 2012 recall of Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker, which he survived, highlighting the political polarization in the state. These cases illustrate the use of recall elections as a powerful tool for electorate accountability and direct democracy.
Voter Participation in Recall Processes
Voter participation in recall processes varies significantly across jurisdictions, with turnout rates often influenced by the perceived importance of the issue and the level of campaign mobilization. For example, California's 2003 gubernatorial recall saw a voter turnout of approximately 52%, reflecting moderate engagement in the recall election. Increased voter education and access to voting methods are critical factors that can enhance participation rates in recall elections, ensuring democratic accountability.
Political Impact of Recall Elections
Recall elections significantly influence political accountability by enabling voters to remove elected officials before their terms end, thereby reinforcing democratic control. These elections often shift political power dynamics, prompting incumbents to prioritize constituent satisfaction to avoid potential recall threats. Historical cases, such as California's 2003 gubernatorial recall, demonstrate how recall elections can destabilize established political leadership and alter policy agendas swiftly.
Challenges and Controversies in Recall Procedures
Recall procedures in the electorate often face challenges such as high signature thresholds, which can limit genuine democratic participation and skew political power dynamics. Controversies arise when recall efforts are perceived as tools for political retaliation rather than accountability, undermining public trust in electoral processes. Legal ambiguities and inconsistent enforcement of recall laws further complicate the ability to effectively hold elected officials accountable.
Recall as a Tool for Democratic Accountability
Recall elections empower voters to remove elected officials before the end of their term, serving as a direct mechanism for democratic accountability in government. This process ensures that public representatives remain responsive to constituents, as seen in notable instances like the 2003 California gubernatorial recall election. By providing a constitutional tool to challenge ineffective or corrupt officials, recall elections reinforce transparency and the accountability of elected leaders to the electorate.
Future Trends and Reforms in Recall Elections
Future trends in recall elections indicate increased adoption of digital platforms to streamline petition verification and enhance voter participation. Legislative reforms are trending toward standardized recall procedures to reduce legal ambiguities and ensure fair representation across jurisdictions. Emerging technologies like blockchain are being explored to secure the integrity of recall processes and prevent fraud.
example of recall in electorate Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com