A blue slip is a Senate tradition used during federal judicial nominations to allow home-state senators to express their approval or disapproval of a nominee. When the President submits a judicial nominee for Senate confirmation, the Senate Judiciary Committee sends a blue-colored form, the blue slip, to the senators from the nominee's home state. The return or non-return of the blue slip can significantly influence the Committee's decision to hold confirmation hearings for the nominee. This process involves the identification of senators as key entities responsible for gatekeeping in the confirmation. Data on blue slip returns is often analyzed to understand partisan dynamics and judicial appointment trends. The blue slip mechanism embodies the balance of power and regional representation in federal judicial confirmations within the U.S. government.
Table of Comparison
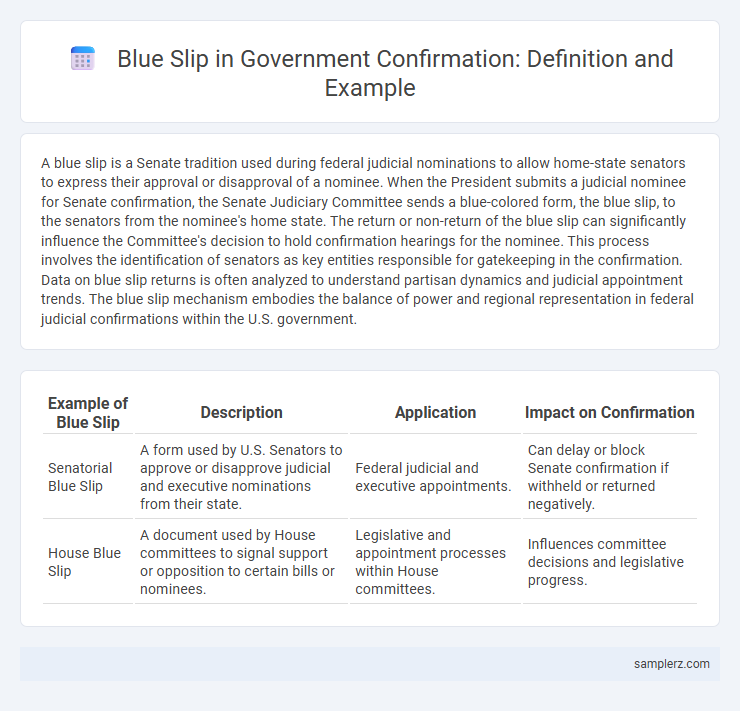
| Example of Blue Slip | Description | Application | Impact on Confirmation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Senatorial Blue Slip | A form used by U.S. Senators to approve or disapprove judicial and executive nominations from their state. | Federal judicial and executive appointments. | Can delay or block Senate confirmation if withheld or returned negatively. |
| House Blue Slip | A document used by House committees to signal support or opposition to certain bills or nominees. | Legislative and appointment processes within House committees. | Influences committee decisions and legislative progress. |
Understanding the Blue Slip Process in Government Confirmations
The blue slip process serves as a key procedural tool in U.S. Senate confirmations, allowing home-state senators to express approval or disapproval of judicial nominees. This mechanism influences the timeline and outcome of confirmations by granting senators substantial input on appointments within their jurisdiction. Understanding the nuances of blue slip returns, refusals, and waivers is essential for navigating the complex dynamics of government confirmations and maintaining senatorial courtesy.
Historical Overview of Blue Slip Practices
The blue slip process originated in the early 20th century as a Senate tradition allowing home-state senators to approve or block judicial nominees. Historically, the practice served as a key senatorial courtesy ensuring nominees received bipartisan support before confirmation hearings. Over time, variations in blue slip enforcement have reflected shifting political dynamics within the Senate Judiciary Committee.
Key Cases: Notable Blue Slip Examples in Senate Confirmations
Key cases of blue slip use in Senate confirmations include the 2017 dispute over Jeff Sessions' attorney general nomination, where Republican senators withheld blue slips to signal opposition. Another notable example occurred during Merrick Garland's Supreme Court nomination in 2016, when Senate Republicans blocked the process without returning blue slips. These instances illustrate how blue slip traditions influence the judicial confirmation process by allowing home-state senators to exert significant control.
The Role of the Blue Slip in Judicial Appointments
The blue slip serves as a Senate tradition allowing home-state senators to express approval or objections to judicial nominees, significantly influencing confirmation outcomes. This practice grants individual senators substantial leverage in the vetting process, often halting or advancing judicial appointments based on their feedback. The blue slip system underscores the balance of powers and local senatorial input in federal judicial confirmations.
How Blue Slip Affects Presidential Nominations
The Blue Slip process allows home-state senators to approve or block presidential judicial nominations by returning or withholding a blue slip form, significantly influencing the Senate Judiciary Committee's decision to hold confirmation hearings. This tradition empowers senators to exercise senatorial courtesy, often enabling them to delay or derail nominations without a formal vote. Consequently, the use or refusal of blue slips shapes the composition and pace of judicial appointments during a president's term.
Political Implications of Withholding Blue Slips
Withholding blue slips in the Senate confirmation process can halt the appointment of federal judges, significantly impacting the judiciary's composition and altering the balance of ideological power. This tactic empowers senators to influence presidential nominations, often leading to political standoffs and delays that affect the efficiency of the judicial system. Consequently, the strategic use of blue slips can serve as a critical leverage point in partisan battles over federal judiciary control.
Blue Slip Controversies: High-Profile Incidents
The Blue Slip controversy has repeatedly surfaced during Senate confirmations, notably in the 2017 blockade of judicial nominees under Senator Chuck Grassley's tenure. This tradition allows home-state senators to approve or reject federal judicial appointments, often leading to stalled confirmations and political standoffs. High-profile incidents like the rejection of D.C. Circuit nominee Caitlin Halligan exemplify how Blue Slips can be wielded as potent tools of senatorial influence.
Comparative Analysis: Blue Slip Usage Across Administrations
Blue slip usage has varied significantly across presidential administrations, with some prioritizing senatorial input as a critical factor in judicial confirmations, while others have adopted a more flexible approach, reducing the blue slip's veto power. For instance, the Obama administration maintained stringent adherence to blue slip objections, effectively allowing single senators to block nominees, whereas the Trump administration limited this power, enabling confirmations to proceed despite missing or negative blue slips. This comparative analysis reveals how the political context and leadership priorities influence procedural norms in the Senate's role in judicial appointments.
Senate Rules and Changes to the Blue Slip Tradition
The blue slip process is a Senate tradition allowing home-state senators to approve or block judicial nominees by returning or withholding a blue slip form. Senate Rules have evolved, with recent changes empowering Judiciary Committee chairs to proceed on nominations despite negative or unreturned blue slips, particularly for circuit court appointments. This shift reflects a balance between senatorial courtesy and efficient judicial confirmations.
The Future of the Blue Slip in Government Confirmations
The future of the blue slip in government confirmations remains uncertain as evolving Senate practices challenge its traditional role in judicial nominations. While historically granting home-state senators significant influence over nominees, recent shifts have seen varying degrees of enforcement, reflecting broader political strategies. This ongoing change signals potential redefinition of senatorial courtesy and imbalance in the confirmation process.
example of blue slip in confirmation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com