Prorogation is the formal ending of a parliamentary session by the government, effectively pausing all legislative activities until the next session begins. For instance, in the United Kingdom, the Prime Minister can advise the monarch to prorogue Parliament, which temporarily suspends all debates, bills, and committee meetings. This action typically clears the legislative agenda, allowing the government to set new priorities for the upcoming session. In Canada, prorogation also serves as a tool for the executive branch to reset the parliamentary calendar, influencing the legislative process and political dynamics. The government requests the Governor General to prorogue Parliament, halting all ongoing discussions and returning all unfinished bills to their initial stages when Parliament reconvenes. This practice impacts the balance of power between the legislative and executive branches by controlling parliamentary activity and timing.
Table of Comparison
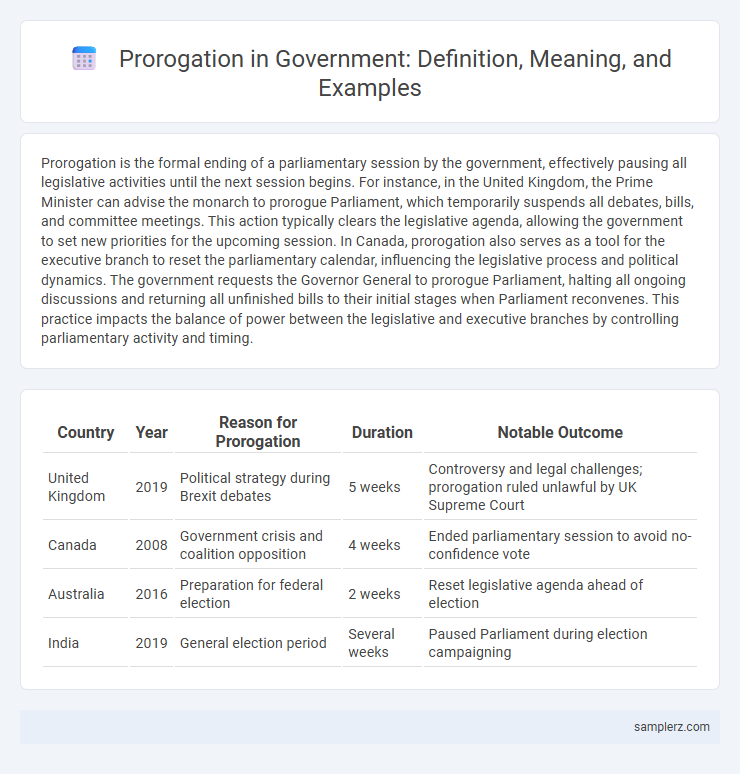
| Country | Year | Reason for Prorogation | Duration | Notable Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | 2019 | Political strategy during Brexit debates | 5 weeks | Controversy and legal challenges; prorogation ruled unlawful by UK Supreme Court |
| Canada | 2008 | Government crisis and coalition opposition | 4 weeks | Ended parliamentary session to avoid no-confidence vote |
| Australia | 2016 | Preparation for federal election | 2 weeks | Reset legislative agenda ahead of election |
| India | 2019 | General election period | Several weeks | Paused Parliament during election campaigning |
Understanding Prorogation: Definition and Importance
Prorogation refers to the formal ending of a parliamentary session by the head of state, typically on the advice of the prime minister, suspending all parliamentary business until the next session begins. This constitutional mechanism plays a critical role in allowing governments to reset their legislative agenda, prepare new policies, and manage parliamentary operations without dissolving the legislature. Understanding prorogation is essential for grasping how executive power interacts with parliamentary democracy and impacts the timing and content of legislative activity.
Historical Overview of Prorogation in Parliamentary Systems
Prorogation historically serves as a formal mechanism to end a parliamentary session without dissolving the legislature, exemplified by the British Parliament's use since the 16th century. In the UK, prorogation allows the Crown, on the advice of the Prime Minister, to suspend Parliament for a period before a new session begins, often marked by the Queen's Speech outlining the government's agenda. This practice has influenced numerous Commonwealth countries, embedding prorogation as a tool for managing legislative timelines and political strategy within parliamentary systems.
Notable Examples of Prorogation in Modern Governments
Notable examples of prorogation in modern governments include the 2019 UK prorogation, where Prime Minister Boris Johnson suspended Parliament for five weeks amid Brexit debates, causing significant political controversy and legal challenges. In Canada, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau prorogued Parliament twice during his tenure, in 2008 and 2010, to manage political crises and delay opposition motions. These cases illustrate how prorogation is used strategically to pause legislative activities and reshape political agendas.
Prorogation in the UK: Key Sessions and Impacts
Prorogation in the UK is a formal mechanism used to end a parliamentary session, with notable examples including the 2019 prorogation by Prime Minister Boris Johnson, which was later ruled unlawful by the Supreme Court. This act temporarily suspends Parliament, preventing debates or legislation from proceeding, thereby impacting the government's legislative agenda and parliamentary scrutiny. The implications of prorogation influence political strategy, affecting key policy decisions and the timing of parliamentary sessions.
Case Study: Canadian Parliament Prorogation Events
The Canadian Parliament experienced notable prorogation events in 2008 and 2009 when Prime Minister Stephen Harper requested to suspend sessions amid political controversies and confidence challenges. These prorogations paused parliamentary proceedings, allowing the government to reset its agenda but sparked debates on executive power and democratic accountability. The 2008 prorogation occurred during a potential vote of no confidence, while the 2009 event paused debates on economic stimulus measures during the global financial crisis.
Legal Implications of Prorogation for Legislatures
Prorogation temporarily suspends a legislative session without dissolving the legislature, effectively halting all parliamentary business and committee work. This suspension can delay the passage of crucial bills, disrupt legislative oversight, and reduce government accountability during the prorogation period. Courts have intervened in cases where prorogation was deemed to undermine constitutional principles, emphasizing its significant legal implications for democratic governance and the balance of powers.
Political Controversies Surrounding Prorogation
The 2019 prorogation of the UK Parliament by Prime Minister Boris Johnson sparked intense political controversy, as critics argued it was an attempt to limit parliamentary scrutiny over Brexit decisions. Legal challenges ensued, culminating in the UK Supreme Court ruling the prorogation unlawful, emphasizing the constitutional limits on executive power. This event highlighted the tensions between executive authority and parliamentary sovereignty in democratic governance.
Effects of Prorogation on Legislative Agendas
Prorogation suspends parliamentary sessions, halting debates and delaying the progress of bills, which can disrupt legislative agendas and affect policy implementation timelines. During prorogation, all pending committee work and parliamentary business are paused, potentially causing a backlog of legislative activities when sessions resume. This interruption allows the government to reset its priorities but may also limit parliamentary scrutiny and reduce transparency in lawmaking processes.
Constitutional Checks and Prorogation Powers
Prorogation powers allow the executive branch to temporarily suspend parliamentary sessions, a constitutional check designed to balance legislative activity and executive functions. In Canada, the 2008 prorogation by Prime Minister Stephen Harper sparked debate over the limits of executive authority in circumventing parliamentary scrutiny. Constitutional frameworks often require that prorogation decisions respect democratic accountability, preventing misuse that could undermine legislative oversight.
Lessons Learned from Notable Prorogation Examples
The 2019 United Kingdom prorogation controversy highlighted the importance of constitutional checks and the role of courts in reviewing executive power, as the Supreme Court ruled the prorogation unlawful, reinforcing limits on governmental authority. Lessons learned emphasize the need for transparency and parliamentary engagement to maintain democratic legitimacy during session suspensions. Governments must balance executive discretion with institutional accountability to avoid political crises and ensure continued public trust.
example of prorogation in session Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com