Redistricting is the process of redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes, ensuring equal representation. An example of redistricting in government elections occurred following the 2020 United States Census. States like Texas and Florida adjusted their congressional districts to accommodate population growth and shifts. In addition to population growth, redistricting can influence political power by altering district lines. The state of Arizona implemented new congressional maps in 2022, following independent commission guidelines designed to reduce gerrymandering. This redistricting affected the balance of seats in the U.S. House of Representatives for the upcoming election cycle.
Table of Comparison
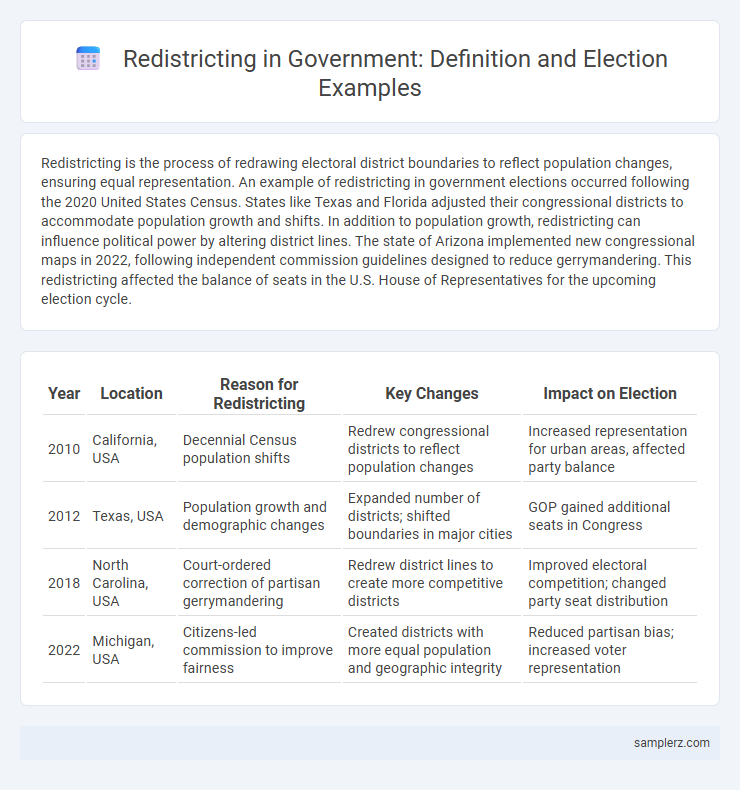
| Year | Location | Reason for Redistricting | Key Changes | Impact on Election |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | California, USA | Decennial Census population shifts | Redrew congressional districts to reflect population changes | Increased representation for urban areas, affected party balance |
| 2012 | Texas, USA | Population growth and demographic changes | Expanded number of districts; shifted boundaries in major cities | GOP gained additional seats in Congress |
| 2018 | North Carolina, USA | Court-ordered correction of partisan gerrymandering | Redrew district lines to create more competitive districts | Improved electoral competition; changed party seat distribution |
| 2022 | Michigan, USA | Citizens-led commission to improve fairness | Created districts with more equal population and geographic integrity | Reduced partisan bias; increased voter representation |
Understanding Redistricting in Elections
Redistricting in elections involves redrawing electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes captured in the decennial census, significantly impacting political representation and voter distribution. States like North Carolina have experienced contentious redistricting processes, where changes in district maps have led to legal challenges over gerrymandering and voter disenfranchisement. Understanding the criteria and methods of redistricting, such as equal population mandates and compliance with the Voting Rights Act, is essential to ensuring fair and competitive elections.
Historical Examples of Redistricting
Historical examples of redistricting include the landmark 1960s case of Baker v. Carr, which established the principle of "one person, one vote" and led to widespread reapportionment across U.S. states. The 1990s saw significant redistricting following the 1990 Census, with shifts in district boundaries affecting partisan balances and minority representation. Another notable example is the 2010 redistricting cycle, marked by aggressive gerrymandering strategies in states like North Carolina and Pennsylvania, influencing electoral outcomes for over a decade.
Redistricting and Its Impact on Representation
Redistricting, the process of redrawing electoral district boundaries, significantly influences political representation by shaping voter demographics within each district. For instance, the 2010 U.S. congressional redistricting led to shifts in party dominance in several states, affecting the balance of power in the House of Representatives. Gerrymandering during redistricting can dilute minority voting strength, undermining fair representation and altering election outcomes.
Case Study: Gerrymandering in the United States
Gerrymandering in the United States exemplifies strategic redistricting where electoral district boundaries are manipulated to favor a specific political party, often undermining democratic representation. Notable cases include the 2010 redistricting cycle post-census, where states like North Carolina and Maryland saw districts redrawn to consolidate partisan power, prompting multiple legal challenges. This manipulation impacts electoral competitiveness and voter influence, spurring ongoing debates over redistricting reform and the use of independent commissions.
Notable International Redistricting Examples
Japan's 2017 electoral redistricting reduced disparities by merging rural districts to balance urban vote weight, addressing malapportionment concerns. India's 2008 delimitation redefined parliamentary constituencies based on 2001 census data, impacting political representation significantly. South Africa's post-apartheid 1994 redistricting established new electoral boundaries promoting equitable representation across diverse regions.
Legal Challenges to Redistricting Plans
Legal challenges to redistricting plans often arise from allegations of partisan gerrymandering and violations of the Voting Rights Act, as seen in the 2018 North Carolina congressional map case where courts ruled the plan unconstitutional for diluting minority voting power. In 2019, the U.S. Supreme Court acknowledged these challenges but declined to rule on partisan gerrymandering claims, leaving lower courts to address the complex issues of fair district boundaries. These legal disputes emphasize the ongoing tension between state legislatures' authority to redraw maps and federal protections designed to ensure equitable representation.
Redistricting and Voter Demographics
Redistricting significantly influences voter demographics by reshaping electoral district boundaries to reflect population changes recorded in the decennial census. This process can alter the political landscape by concentrating or dispersing specific communities, affecting party representation and voter influence. Strategic redistricting often targets demographic shifts to create electoral advantages, impacting policymaking and resource allocation.
Technology’s Role in Modern Redistricting
Geographic Information System (GIS) technology plays a crucial role in modern redistricting by enabling precise mapping and demographic analysis, ensuring more accurate and representative electoral boundaries. Advanced data analytics and machine learning algorithms assist in identifying population shifts and voting patterns to create fairer districts. Automated redistricting tools reduce human bias, increase transparency, and facilitate compliance with legal requirements such as the Voting Rights Act.
Public Participation in the Redistricting Process
Public participation in the redistricting process is integral to ensuring fair electoral boundaries and preventing gerrymandering. States like California have implemented independent commissions that hold public hearings, allowing citizens to submit maps and provide feedback, enhancing transparency and accountability. These efforts empower voters to influence district boundaries, promoting equitable representation in legislative bodies.
Future Trends and Reforms in Redistricting
Future trends in redistricting include the increased use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to create more balanced and competitive electoral districts, reducing gerrymandering. State legislatures and independent commissions are adopting data-driven approaches with greater transparency to enhance voter representation and equity. Legal reforms are also underway to strengthen criteria for district boundaries, emphasizing community integrity and proportional representation in upcoming election cycles.
example of redistricting in election Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com