A government committee is a formal group of officials assigned specific tasks related to legislative, administrative, or oversight functions. These committees often consist of members of parliament, government officials, or experts who review policies, scrutinize bills, and oversee government departments. Committees play a vital role in shaping legislation by gathering evidence, conducting hearings, and producing detailed reports. Committees are categorized into standing, select, joint, and special types based on their purpose and duration. Standing committees handle ongoing issues such as finance, health, or defense, while select committees address specific temporary matters. The data produced by these committees, including meeting minutes and report findings, are integral to transparent governance and informed decision-making processes.
Table of Comparison
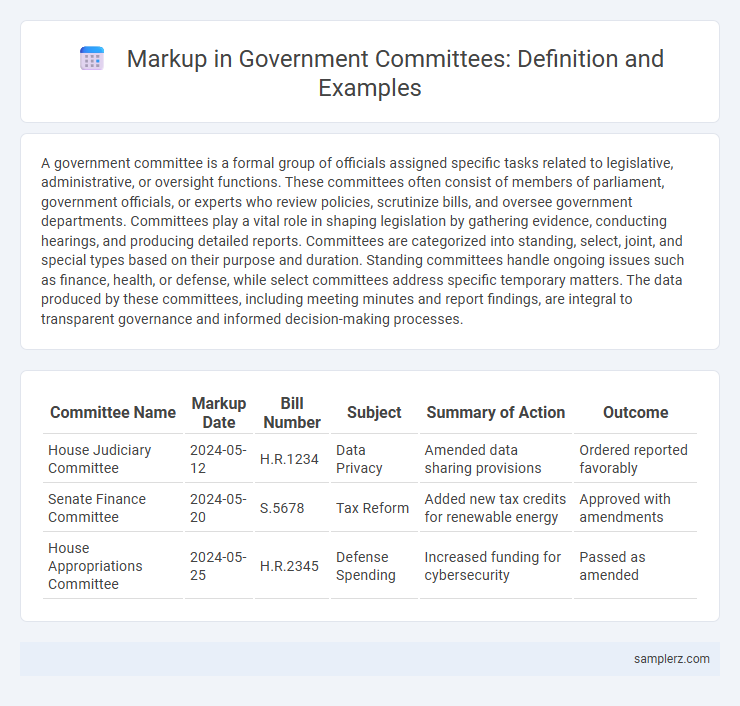
| Committee Name | Markup Date | Bill Number | Subject | Summary of Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| House Judiciary Committee | 2024-05-12 | H.R.1234 | Data Privacy | Amended data sharing provisions | Ordered reported favorably |
| Senate Finance Committee | 2024-05-20 | S.5678 | Tax Reform | Added new tax credits for renewable energy | Approved with amendments |
| House Appropriations Committee | 2024-05-25 | H.R.2345 | Defense Spending | Increased funding for cybersecurity | Passed as amended |
Understanding Markup: Definition and Purpose in Committees
Markup in committees refers to the process where legislators review, amend, and rewrite proposed bills before they proceed to a full legislative vote. This stage allows committee members to debate specific provisions, suggest changes, and clarify legislative intent to improve the bill's effectiveness. Understanding markup is essential for grasping how committees shape policy outcomes and ensure legislation aligns with policy goals.
The Markup Process: Step-by-Step Overview
The markup process in a government committee involves systematically reviewing, amending, and rewriting proposed legislation before it proceeds to the full chamber. Committee members debate the bill's language, propose specific changes, and vote on each amendment to shape the final draft. This step-by-step scrutiny ensures detailed examination and refinement of policy provisions prior to broader legislative consideration.
Key Players Involved During Markup Sessions
Markup sessions in government committees involve key players such as committee chairs, ranking members, and legislative staff who collaboratively review, amend, and refine proposed bills. Congressional members actively propose amendments, debate provisions, and vote on changes to shape the final version of legislation. Expert witnesses and lobbyists may also contribute input, providing testimony and influencing committee decisions during the markup process.
Real-Life Examples of Committee Markup in Congress
Committee markup in Congress involves detailed review and amendment of proposed legislation, exemplified by the House Ways and Means Committee's extensive markup on the tax reform bill in 2017. During this process, committee members debated provisions and offered modifications to optimize tax codes, demonstrating the practical impact of committee markup on final legislative language. These sessions often include expert testimonies, bipartisan negotiations, and documented changes that shape critical government policies before full congressional approval.
How Amendments Are Proposed and Debated in Markup
During markup sessions in government committees, amendments are proposed by members who submit written or oral suggestions to modify the bill's language. Each proposed amendment is debated on the committee floor, allowing members to discuss its merits and implications thoroughly before voting. The markup process ensures transparent consideration and refinement of legislation through structured amendment proposals and member deliberations.
Committee Markup vs. Floor Debate: Key Differences
Committee markup involves detailed line-by-line examination and amendment of a bill by a specialized group of legislators to refine legislative language and policy specifics, often shaping the bill's framework before it reaches the larger legislative body. Floor debate, in contrast, allows all members of the legislative chamber to discuss, amend, and vote on the bill, emphasizing broader political considerations and public accountability. The committee markup process tends to be more technical and focused on policy expertise, whereas floor debate engages wider political perspectives and constituent interests.
Transparency and Public Participation in Markup Proceedings
Markup proceedings in government committees often involve open sessions where proposed legislation is reviewed and amended, ensuring transparency by allowing public access and real-time observation. Committees may publish detailed records and video archives of markup meetings on official websites to enhance accountability. Public participation is further encouraged through online submissions of comments and testimony, fostering civic engagement in legislative development.
Impact of Markup on Final Legislation
Markup sessions in government committees play a crucial role in shaping final legislation by allowing members to debate, amend, and refine bill provisions. These modifications can alter the bill's scope, funding allocations, and regulatory impacts, ultimately determining its effectiveness and public reception. The committee's markup process ensures a thorough review, increases transparency, and can significantly influence the bill's passage through subsequent legislative stages.
Challenges and Controversies During Committee Markup
During committee markup, members often face challenges such as intense partisan disagreements and procedural disputes that delay the legislative process. Controversies frequently arise over specific amendments, with debates centering on the inclusion or exclusion of key provisions impacting policy outcomes. Managing competing interests while maintaining transparency and adherence to parliamentary rules remains a critical hurdle in effectively advancing legislation.
Best Practices for Effective Markup in Government Committees
Effective markup in government committees requires precise amendment tracking and clear differentiation between proposed changes and existing text to ensure transparency and accountability. Utilizing standardized formats such as redlines and strikethroughs enhances collaborative review and facilitates accurate legislative record-keeping. Consistent documentation practices support informed decision-making and streamline the legislative process within government committees.
example of markup in committee Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com