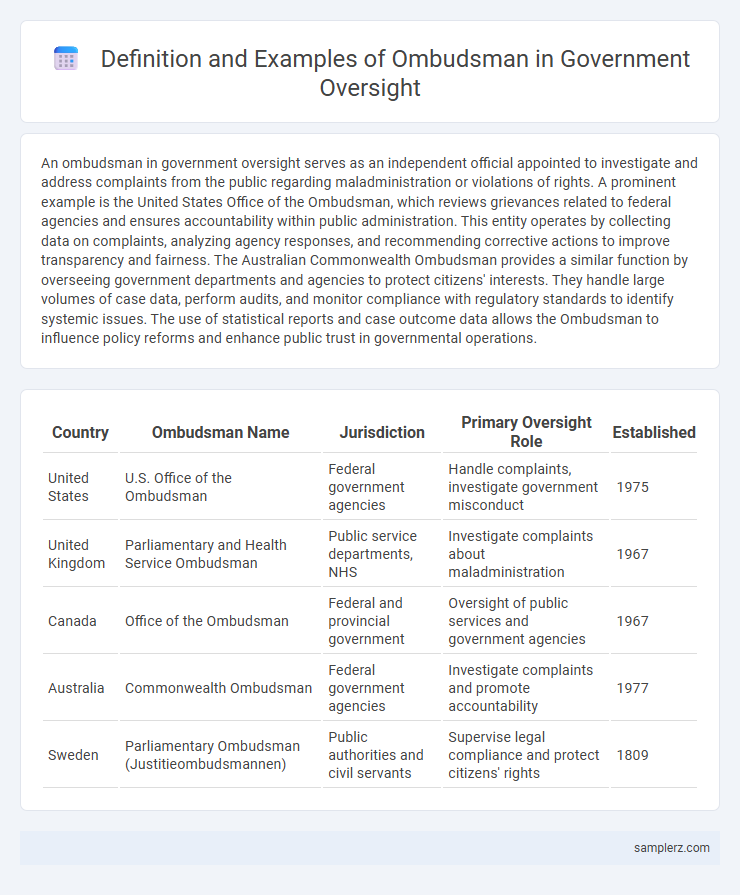
An ombudsman in government oversight serves as an independent official appointed to investigate and address complaints from the public regarding maladministration or violations of rights. A prominent example is the United States Office of the Ombudsman, which reviews grievances related to federal agencies and ensures accountability within public administration. This entity operates by collecting data on complaints, analyzing agency responses, and recommending corrective actions to improve transparency and fairness. The Australian Commonwealth Ombudsman provides a similar function by overseeing government departments and agencies to protect citizens' interests. They handle large volumes of case data, perform audits, and monitor compliance with regulatory standards to identify systemic issues. The use of statistical reports and case outcome data allows the Ombudsman to influence policy reforms and enhance public trust in governmental operations.
Table of Comparison
| Country | Ombudsman Name | Jurisdiction | Primary Oversight Role | Established |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | U.S. Office of the Ombudsman | Federal government agencies | Handle complaints, investigate government misconduct | 1975 |
| United Kingdom | Parliamentary and Health Service Ombudsman | Public service departments, NHS | Investigate complaints about maladministration | 1967 |
| Canada | Office of the Ombudsman | Federal and provincial government | Oversight of public services and government agencies | 1967 |
| Australia | Commonwealth Ombudsman | Federal government agencies | Investigate complaints and promote accountability | 1977 |
| Sweden | Parliamentary Ombudsman (Justitieombudsmannen) | Public authorities and civil servants | Supervise legal compliance and protect citizens' rights | 1809 |
Defining the Role of the Ombudsman in Government Oversight
The Ombudsman in government oversight acts as an independent authority tasked with investigating complaints against public institutions, ensuring transparency and accountability within governmental operations. This role involves scrutinizing administrative actions and recommending corrective measures to address maladministration or injustice, thereby strengthening public trust. Established by statutes or constitutional provisions, the Ombudsman operates without political influence, serving as a crucial watchdog that upholds citizens' rights and promotes ethical governance.
Historical Evolution of Ombudsman Institutions
The ombudsman institution originated in Sweden in 1809 as a mechanism for citizens to address grievances against public authorities, setting a precedent for governmental oversight worldwide. Over time, this concept expanded globally, with variations tailored to different legal systems, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and citizens' rights in public administration. Modern ombudsman offices operate as independent entities, providing checks on government actions and reinforcing the rule of law through impartial investigation and resolution of complaints.
Types of Governmental Oversight Performed by Ombudsmen
Ombudsmen perform various types of governmental oversight, including administrative, legislative, and judicial oversight. Administrative oversight involves investigating complaints from the public about government agencies' adherence to laws and regulations. Legislative oversight requires monitoring and evaluating government programs to ensure accountability and transparency, while judicial oversight protects individual rights by addressing grievances related to unfair treatment or procedural errors in public administration.
Case Study: National Ombudsman Impact on Public Administration
The National Ombudsman has significantly enhanced public administration by addressing citizen complaints and ensuring governmental transparency. In one notable case, the Ombudsman intervened to rectify bureaucratic delays in social welfare benefits, leading to improved process efficiency and greater accountability within local agencies. This oversight role demonstrates how the National Ombudsman contributes to upholding citizen rights and fostering trust in government institutions.
Ombudsman Interventions in Human Rights Issues
The Ombudsman plays a crucial role in government oversight by investigating complaints related to human rights violations and ensuring accountability within public institutions. Notable interventions include addressing cases of unlawful detention, discrimination, and abuse of power, thereby strengthening the protection of individual rights. These actions enhance transparency and promote the enforcement of national and international human rights standards.
Ombudsman Contributions to Anti-Corruption Efforts
The Ombudsman plays a critical role in anti-corruption efforts by independently investigating complaints against public officials and government agencies, ensuring accountability and transparency. Key contributions include reducing instances of bribery, abuse of power, and maladministration through systematic oversight and public reporting. By promoting ethical governance, the Ombudsman strengthens public trust and supports the enforcement of anti-corruption laws.
Mechanisms for Citizen Complaints and Redress
Ombudsman offices serve as independent oversight bodies that provide accessible mechanisms for citizen complaints and redress, ensuring government accountability. These institutions investigate maladministration, address violations of rights, and facilitate conflict resolution between citizens and public agencies. By offering impartial reviews and recommendations, ombudsman services strengthen trust in public administration and promote transparent governance.
International Examples of Effective Ombudsman Offices
The Office of the Parliamentary Ombudsman in Sweden serves as a leading example of effective government oversight by independently investigating complaints against public authorities and ensuring administrative accountability. New Zealand's Ombudsman plays a crucial role in promoting transparency by providing an accessible mechanism for citizens to challenge decisions of public agencies and uphold human rights. Similarly, the Commonwealth Ombudsman in Australia offers comprehensive oversight by addressing public grievances, enhancing administrative fairness, and supporting anti-corruption measures across federal government departments.
Challenges Faced by Ombudsman in Oversight Functions
Ombudsmen in government oversight face challenges such as limited access to classified information, which hampers thorough investigations into public sector misconduct. Budget constraints and insufficient staffing reduce their ability to respond promptly to complaints and conduct comprehensive audits. Political interference and lack of enforcement power also undermine the effectiveness of ombudsman offices in holding public officials accountable.
Future Trends in Ombudsman-Led Government Accountability
Emerging trends in ombudsman-led government accountability highlight increased integration of digital technologies such as AI and blockchain to enhance transparency and expedite complaint resolution processes. Ombudsman offices are expanding their roles toward proactive oversight by employing data analytics to detect systemic issues before they escalate. Future developments also emphasize greater collaboration between ombudsman institutions and citizen engagement platforms to strengthen participatory governance and trust in public administration.
example of ombudsman in oversight Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com