A filibuster in government legislation occurs when a senator extends debate to delay or block a vote on a bill. This tactic allows minority parties to influence legislative decisions by prolonging discussion, often through lengthy speeches or procedural motions. The U.S. Senate filibuster is a prominent example, where unlimited debate can only be ended by a cloture vote requiring a supermajority of 60 senators. The most famous filibuster in U.S. history involved Senator Strom Thurmond's 24-hour speech in 1957 opposing the Civil Rights Act. More recently, filibusters have played a critical role in contentious legislation, such as immigration reform and health care bills. Data shows that filibusters have increased significantly since the 1970s, reflecting the growing polarization and strategic use of Senate rules.
Table of Comparison
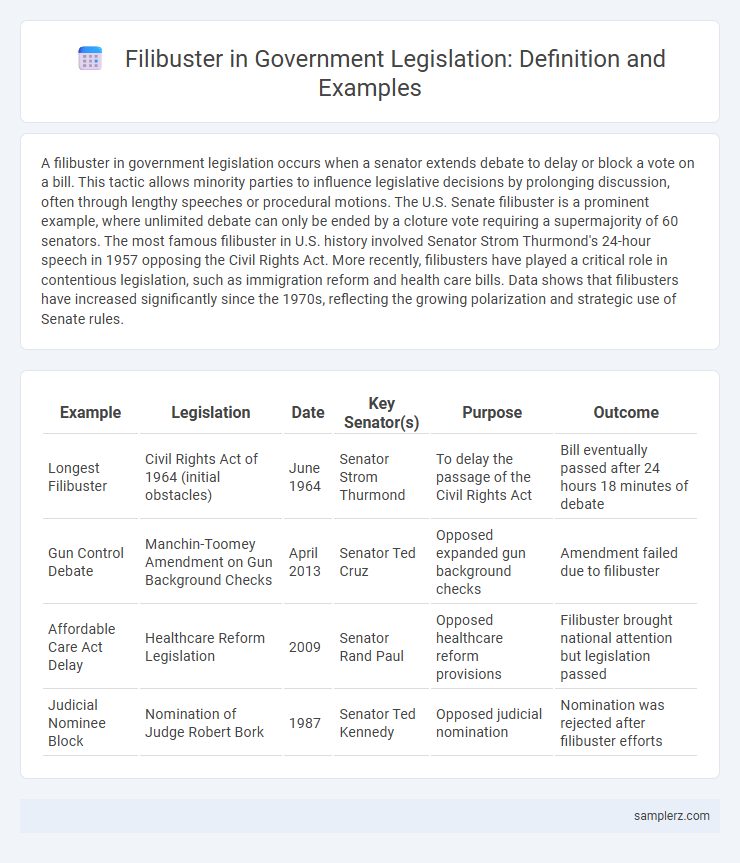
| Example | Legislation | Date | Key Senator(s) | Purpose | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longest Filibuster | Civil Rights Act of 1964 (initial obstacles) | June 1964 | Senator Strom Thurmond | To delay the passage of the Civil Rights Act | Bill eventually passed after 24 hours 18 minutes of debate |
| Gun Control Debate | Manchin-Toomey Amendment on Gun Background Checks | April 2013 | Senator Ted Cruz | Opposed expanded gun background checks | Amendment failed due to filibuster |
| Affordable Care Act Delay | Healthcare Reform Legislation | 2009 | Senator Rand Paul | Opposed healthcare reform provisions | Filibuster brought national attention but legislation passed |
| Judicial Nominee Block | Nomination of Judge Robert Bork | 1987 | Senator Ted Kennedy | Opposed judicial nomination | Nomination was rejected after filibuster efforts |
Notable Filibuster Incidents in Legislative History
Senator Strom Thurmond's 1957 filibuster against the Civil Rights Act lasted 24 hours and 18 minutes, marking one of the longest individual speeches in U.S. Senate history. Another notable filibuster was led by Senator Huey Long in 1935, who spoke for over 15 hours to block the nomination of a federal official. These incidents showcase the filibuster's strategic use to delay or prevent legislative action in American government.
Landmark Filibusters That Shaped Policy Outcomes
The 1957 filibuster against the Civil Rights Act, led by Senator Strom Thurmond, extended over 24 hours to delay voting on desegregation legislation. The 2013 Senate filibuster reforms, known as the "nuclear option," reduced debate time on certain nominations, shifting legislative procedures and policy outcomes. These landmark filibusters demonstrate the significant role prolonged debate plays in shaping US legislative processes and civil rights advancements.
Famous Filibuster Examples in the U.S. Senate
Senator Strom Thurmond holds the record for the longest filibuster in U.S. Senate history, speaking for 24 hours and 18 minutes in 1957 against the Civil Rights Act. Another notable example is Senator Rand Paul's nearly 13-hour filibuster in 2013 opposing the nomination of John Brennan as CIA Director. These filibusters showcase the strategic use of extended debate to delay or block legislative action in the Senate.
Historical Cases: Filibuster in State Legislatures
The 1917 Texas Senate witnessed a notable filibuster when Senator Jesse H. Jones spoke for over 15 hours to block a bill restricting alcohol sales. In 1972, the Illinois Senate experienced a filibuster aimed at delaying reapportionment legislation, illustrating the tactic's use beyond federal bodies. These historical state-level filibusters demonstrate the strategic use of prolonged debate to influence legislative outcomes.
International Filibuster Examples in Parliamentary Systems
International filibuster examples in parliamentary systems include the use of prolonged speeches and procedural tactics in the Indian Rajya Sabha, where opposition members have delayed bills like the Land Acquisition Act by invoking overnight debates. In Canada's Senate, filibustering has been employed to stall legislation such as the Emergency Debate on National Security measures by extending discussions indefinitely. The United Kingdom's House of Commons occasionally witnesses filibustering during Private Members' Bills, with MPs using lengthy speeches to prevent votes on controversial issues.
Record-Breaking Filibuster Speeches in Congress
Senator Strom Thurmond delivered the longest filibuster in U.S. Senate history, speaking for 24 hours and 18 minutes in 1957 against the Civil Rights Act. More recently, Senator Rand Paul filibustered for nearly 13 hours in 2013, opposing the nomination of John O. Brennan as CIA Director. These record-breaking speeches highlight the strategic use of filibusters to delay or block legislative action in Congress.
Filibuster Tactics Used in Passing or Blocking Legislation
Filibuster tactics in government often involve prolonged speeches or procedural delays used to block or slow down legislation, exemplified by the 2013 U.S. Senate filibuster against gun control reforms where opponents spoke extensively to prevent a vote. Another significant example occurred during the 1964 Civil Rights Act debates, where senators employed extended floor debates to delay passage. These tactics exploit Senate rules requiring a supermajority of 60 votes to invoke cloture and end debate, highlighting strategic obstruction in legislative processes.
Civil Rights Filibusters and Their Impact
Civil rights filibusters, notably during the 1950s and 1960s, obstructed critical legislation aimed at ending racial segregation and protecting voting rights. Senators like Strom Thurmond used extended speeches to delay the Civil Rights Act of 1964, highlighting the filibuster's power to stall transformative social policy. These procedural blockades underscored the tension between legislative strategy and civil rights progress, influencing changes to Senate rules to limit filibuster use in voting rights legislation.
Modern Filibuster Examples in Recent Political Debates
In recent political debates, Senator Ted Cruz's 2013 marathon speech opposing the Affordable Care Act exemplifies a modern filibuster used to delay legislative action. The 2016 Senate filibuster against the confirmation of Merrick Garland to the Supreme Court highlighted a strategic use of the tactic to block judicial appointments. More recently, the debate over voting rights legislation in 2021 saw multiple Democrats threatening filibusters to protect election reforms, emphasizing the filibuster's role in shaping contemporary legislative battles.
Lessons Learned from Filibuster Episodes in Legislation
The 2013 U.S. Senate filibuster on the nomination of Debo Adegbile to the Department of Justice highlighted the legislative gridlock filibusters can create, emphasizing the need for procedural reforms to balance minority rights with legislative efficiency. Analysis of the 2010 Healthcare Reform filibuster revealed that extended debate tactics can mobilize public opinion and delay critical policy implementation despite majority support. These episodes demonstrate the importance of strategic negotiation and the potential impact of filibusters on shaping legislative outcomes and promoting bipartisan dialogue.
example of filibuster in legislation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com