Cloture in parliament is a procedure used to end a debate and bring a matter to an immediate vote. This mechanism is often employed to overcome filibusters or extended discussions that delay legislative decisions. The United States Senate is well-known for using cloture, requiring three-fifths of the senators (usually 60 out of 100) to vote in favor to cut off debate. The use of cloture ensures efficient legislative processes and prevents minority groups from indefinitely stalling bills. In the UK House of Commons, cloture is referred to as "closure," where a simple majority vote can end debate on a particular motion. These procedural tools are critical in maintaining the balance between thorough discussion and timely decision-making within parliamentary systems.
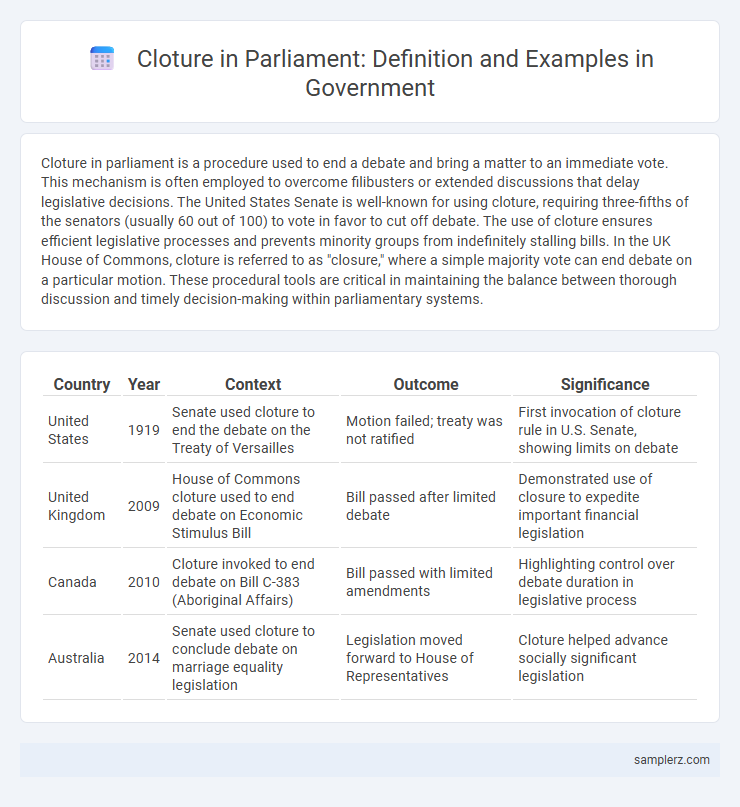
Table of Comparison
| Country | Year | Context | Outcome | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 1919 | Senate used cloture to end the debate on the Treaty of Versailles | Motion failed; treaty was not ratified | First invocation of cloture rule in U.S. Senate, showing limits on debate |
| United Kingdom | 2009 | House of Commons cloture used to end debate on Economic Stimulus Bill | Bill passed after limited debate | Demonstrated use of closure to expedite important financial legislation |
| Canada | 2010 | Cloture invoked to end debate on Bill C-383 (Aboriginal Affairs) | Bill passed with limited amendments | Highlighting control over debate duration in legislative process |
| Australia | 2014 | Senate used cloture to conclude debate on marriage equality legislation | Legislation moved forward to House of Representatives | Cloture helped advance socially significant legislation |
Understanding Cloture Procedures in Parliamentary Systems
Cloture procedures in parliamentary systems serve as critical mechanisms to end prolonged debates and prevent filibusters, ensuring legislative efficiency. For instance, the United States Senate requires a three-fifths majority, or 60 out of 100 senators, to invoke cloture and proceed to a vote. This tool balances minority rights with the need to expedite decision-making in government.
Historical Milestones: First Use of Cloture in Parliament
The first use of cloture in the United States Senate occurred in 1917 during a debate over arming merchant ships in World War I, effectively ending a filibuster that blocked legislation. This historic milestone marked a significant shift in parliamentary procedure, allowing the majority to limit debate and expedite legislative action. The cloture rule has since become a crucial tool for managing extended debates and preventing filibusters in modern democratic governments.
Key Examples of Cloture Motions in Legislative Bodies
Cloture motions serve as a critical mechanism in parliamentary systems to limit debate and overcome filibusters, exemplified by the 1917 U.S. Senate cloture rule which requires a three-fifths majority to end debate. The Canadian Parliament's use of cloture motions to expedite legislative processes, notably during the 2011 budget bill discussions, highlights its strategic role in ensuring timely decision-making. In the UK House of Commons, the guillotine or allocation of time motions functions similarly to cloture, managing debate length on government bills to maintain legislative efficiency.
Notable Cloture Votes in Modern Parliamentary History
The 2013 U.S. Senate vote on the nomination of John Brennan as CIA Director stands out as a notable example of cloture, where Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid invoked cloture to end a filibuster and confirm Brennan with a 63-34 vote. In the UK Parliament, the use of the 1911 Parliament Act to enforce legislative cloture notably limited the House of Lords' power of delay, streamlining the passage of key government bills. Canadian Parliament's 2010 invocation of cloture on a controversial budget bill highlights the mechanism's role in overcoming prolonged debate and ensuring timely budget approval.
Case Study: Cloture in the UK House of Commons
Cloture in the UK House of Commons was notably invoked during the 2005 Brexit-related debates to limit extensive filibustering and expedite the legislative process. The use of cloture helped ensure timely decision-making amid intense parliamentary divisions on the European Union withdrawal. This mechanism exemplifies how procedural tools manage debate duration and maintain legislative efficiency within the British parliamentary system.
Cloture and Filibuster: Comparative Parliamentary Examples
Cloture is a parliamentary procedure used to end filibusters and bring debates to a close, ensuring timely legislative decisions. In the U.S. Senate, invoking cloture requires a three-fifths majority vote, effectively limiting further debate to 30 hours. Comparatively, the French National Assembly employs a motion of closure that can be adopted by a simple majority, highlighting varying thresholds for overcoming filibusters in global legislative bodies.
Impact of Cloture on Parliamentary Debate and Legislation
Cloture is a parliamentary procedure used to end a filibuster and bring debate to a close, significantly impacting legislative efficiency by limiting prolonged discussions. In the U.S. Senate, invoking cloture requires a three-fifths majority, typically 60 out of 100 senators, ensuring that minority parties cannot indefinitely delay legislation. This mechanism accelerates the legislative process, enabling timely voting on bills while balancing thorough debate with the need to prevent legislative gridlock.
Step-by-Step Example of Initiating Cloture in Parliament
Initiating cloture in parliament begins with a member filing a motion to end debate, typically requiring a signature from at least 16 senators in the U.S. Senate. After filing, the motion must be scheduled for a vote two days later, allowing time for limited debate before the final decision. Cloture passes with a three-fifths majority, usually 60 out of 100 senators, effectively curbing filibusters and moving the legislative process forward.
Famous Political Battles Resolved by Cloture Motion
The 1964 Civil Rights Act debate in the U.S. Senate is a famous example where cloture motion ended a 60-day filibuster, allowing the bill to pass. In the UK Parliament, the 1911 Parliament Act was expedited using a procedural equivalent to cloture to overcome House of Lords opposition. The 2013 Immigration Reform Bill saw the U.S. Senate invoke cloture, curbing extensive debate and enabling a decisive vote.
Lessons Learned from Cloture Applications in Parliament
Cloture, a parliamentary procedure used to end debate and expedite decision-making, has demonstrated its effectiveness in managing prolonged legislative discussions and overcoming filibusters. Lessons learned include the importance of clearly defining the thresholds for invoking cloture to balance efficient governance with minority rights. Additionally, repeated cloture applications can impact parliamentary culture, underscoring the need for strategic use to maintain constructive debate and legislative transparency.
example of cloture in parliament Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com