An example of an ombudsman in government bureaucracy is the United States Office of the Ombudsman, which addresses complaints related to federal agency practices. This entity ensures transparency and accountability by investigating grievances brought forward by citizens and employees. It serves as an independent office, providing recommendations to improve administrative processes and resolve conflicts. Another notable ombudsman is the European Ombudsman, responsible for examining complaints about maladministration in the institutions and bodies of the European Union. The office collects and analyzes data on bureaucratic inefficiencies and misconduct to promote good governance practices. Its role is crucial in enhancing public trust by offering an impartial platform for addressing government-related issues.
Table of Comparison
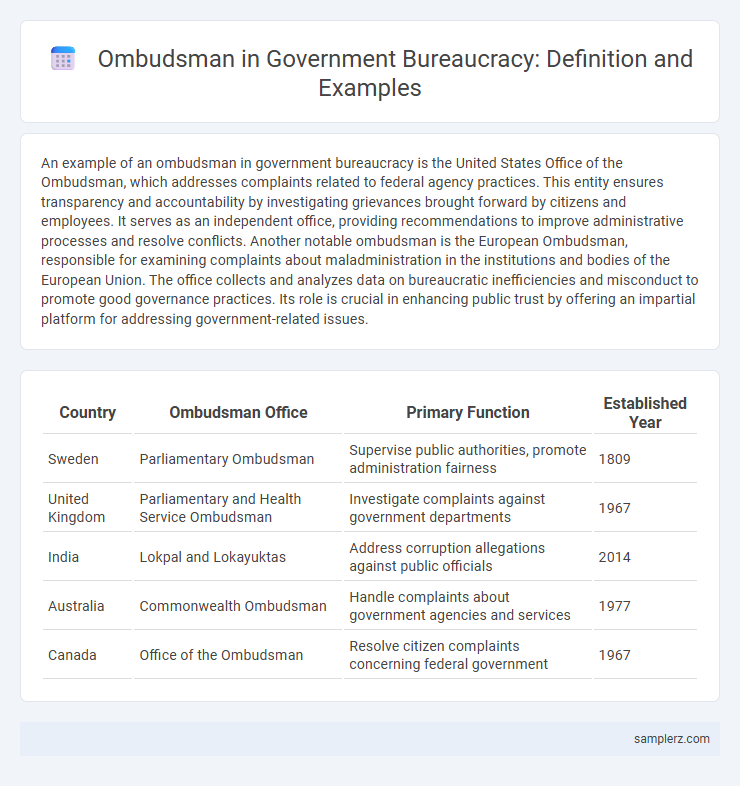
| Country | Ombudsman Office | Primary Function | Established Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sweden | Parliamentary Ombudsman | Supervise public authorities, promote administration fairness | 1809 |
| United Kingdom | Parliamentary and Health Service Ombudsman | Investigate complaints against government departments | 1967 |
| India | Lokpal and Lokayuktas | Address corruption allegations against public officials | 2014 |
| Australia | Commonwealth Ombudsman | Handle complaints about government agencies and services | 1977 |
| Canada | Office of the Ombudsman | Resolve citizen complaints concerning federal government | 1967 |
Introduction to Ombudsman in Government Bureaucracy
The ombudsman plays a critical role in government bureaucracy by investigating complaints of maladministration and ensuring accountability within public institutions. Established as an independent authority, the ombudsman addresses grievances from citizens concerning unfair treatment, bureaucratic delays, and corruption in government agencies. This mechanism promotes transparency and enhances public trust by holding officials responsible and recommending corrective actions.
Key Functions of an Ombudsman within Bureaucratic Systems
An ombudsman within bureaucratic systems primarily addresses citizen complaints by ensuring government accountability and transparency in administrative actions. They investigate maladministration, abuse of power, and procedural failures, providing recommendations for corrective measures without direct enforcement authority. Their role fosters trust between the public and governmental institutions by promoting fair treatment and adherence to established rules and regulations.
Notable National Ombudsman Institutions Worldwide
Notable national ombudsman institutions include the Swedish Parliamentary Ombudsman, established in 1809 as the world's first, which oversees public administration to ensure legal compliance and protect citizens' rights. The Australian Commonwealth Ombudsman provides independent investigation of federal government agencies, enhancing transparency and accountability in bureaucracy. India's Lokpal, instituted in 2014, serves as an anti-corruption ombudsman addressing grievances against public officials and promoting integrity within governmental processes.
Examples of Public Sector Ombudsman Roles
Public sector ombudsmen serve as independent watchdogs addressing complaints against government agencies, ensuring transparency and accountability in bureaucratic processes. Notable examples include the United Kingdom's Parliamentary and Health Service Ombudsman, which investigates disputes related to public administration and health services, and Australia's Commonwealth Ombudsman, overseeing complaints about federal government departments and agencies. These offices enhance public trust by providing accessible channels for redress and promoting fair treatment within the public sector.
Ombudsman Impact on Administrative Transparency
The Ombudsman plays a critical role in enhancing administrative transparency by investigating complaints against government agencies and promoting accountability. Through independent oversight, Ombudsmen facilitate public access to information and ensure compliance with legal standards, reducing corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies. This impact strengthens citizens' trust in government institutions and supports democratic governance.
Case Study: Parliamentary Ombudsman in the UK
The Parliamentary Ombudsman in the UK resolves complaints about maladministration in government departments and public organizations, ensuring accountability in the bureaucracy. Established in 1967, it investigates issues such as delays, unfair treatment, and errors in public services, promoting transparency and fairness. Its recommendations, though not legally binding, carry significant moral authority and often lead to systemic improvements in government operations.
Ombudsman in Local Government Departments
The Ombudsman in local government departments serves as an independent authority to investigate complaints against bureaucratic inefficiencies and maladministration, ensuring transparency and accountability. By addressing grievances related to public service delivery, the Ombudsman enhances trust between citizens and local authorities. This role is vital for upholding ethical standards and improving the responsiveness of municipal institutions.
Effectiveness of Ombudsman in Reducing Bureaucratic Corruption
The Ombudsman institution has proven effective in reducing bureaucratic corruption by providing independent oversight and facilitating transparent complaint mechanisms against public officials. Empirical data from countries like the Philippines and Sweden show significant declines in corruption cases and increased public trust following the establishment of empowered Ombudsman offices. These agencies enhance accountability by investigating misconduct, recommending corrective actions, and promoting ethical governance within government bureaucracy.
Comparison of Ombudsman Models in Different Countries
The Swedish Parliamentary Ombudsman model emphasizes independent oversight with direct reporting to the legislature, ensuring accountability within bureaucratic agencies. In contrast, the Indian Lokpal system combines ombudsman functions with anti-corruption enforcement, targeting both maladministration and corruption. The UK's Parliamentary Ombudsman serves as a specialized complaint mechanism, focusing primarily on administrative fairness without prosecutorial powers.
Future Trends for Ombudsman in Government Bureaucracies
Future trends for ombudsman offices in government bureaucracies include increased integration of artificial intelligence to streamline case management and enhance data analysis, improving responsiveness and transparency. Expanding the role of ombudsmen to address digital rights and cybersecurity issues reflects the growing complexity of governmental interactions. Emphasizing proactive conflict resolution and citizen engagement through online platforms is set to redefine accountability in public administration.
example of ombudsman in bureaucracy Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com