An amicus curiae, or "friend of the court," is a person or organization that is not a party to a legal case but offers information, expertise, or insight relevant to the issues before the court. In government-related cases, amicus curiae briefs are often submitted by advocacy groups, public interest organizations, or government agencies to influence judicial decisions. These briefs provide data, legal arguments, or policy perspectives to assist judges in understanding the broader implications of their rulings. A notable example of an amicus curiae brief in a government context is when the U.S. Department of Justice filed a brief in support of same-sex marriage during the Obergefell v. Hodges case. The DOJ's submission highlighted legal precedents and constitutional arguments to aid the Supreme Court's analysis. This intervention exemplifies how government entities can act as friends of the court to shape important legal outcomes.
Table of Comparison
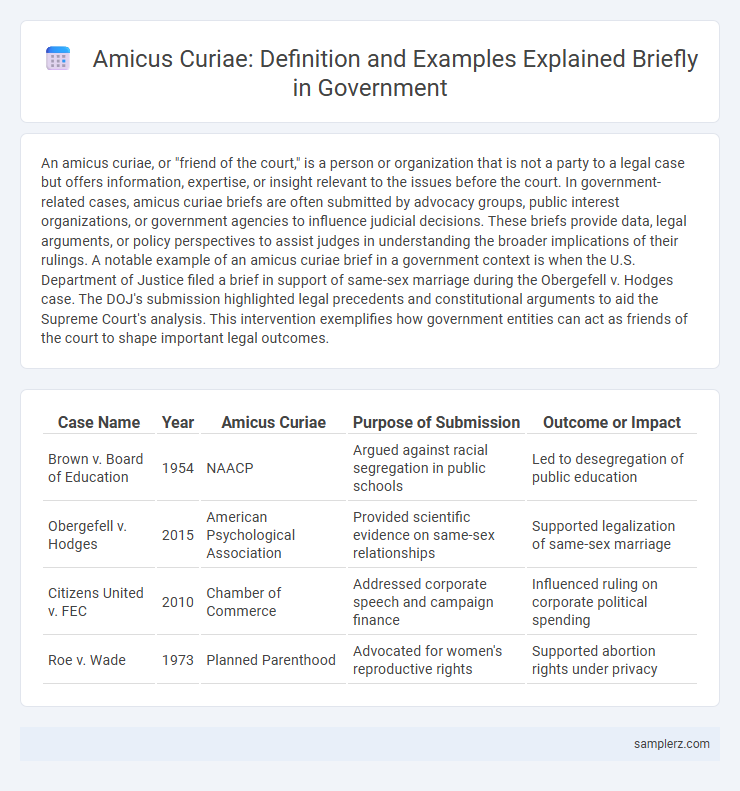
| Case Name | Year | Amicus Curiae | Purpose of Submission | Outcome or Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown v. Board of Education | 1954 | NAACP | Argued against racial segregation in public schools | Led to desegregation of public education |
| Obergefell v. Hodges | 2015 | American Psychological Association | Provided scientific evidence on same-sex relationships | Supported legalization of same-sex marriage |
| Citizens United v. FEC | 2010 | Chamber of Commerce | Addressed corporate speech and campaign finance | Influenced ruling on corporate political spending |
| Roe v. Wade | 1973 | Planned Parenthood | Advocated for women's reproductive rights | Supported abortion rights under privacy |
Understanding the Role of Amicus Curiae in Government Cases
Amicus curiae, or "friend of the court," plays a crucial role in government cases by providing expert knowledge or additional perspectives that may influence judicial decisions. In landmark cases like Brown v. Board of Education, amicus briefs from civil rights organizations helped highlight societal impacts beyond the immediate parties. Their submissions assist courts in understanding broader public interests and complex policy implications within government litigation.
Historical Origins of Amicus Curiae in Judicial Proceedings
Amicus curiae, meaning "friend of the court," originated in English common law during the 18th century as a mechanism for individuals or organizations not party to a case to offer expertise or insight to assist judicial decision-making. Historically, these submissions provided courts with perspectives that might influence the outcome in complex cases without the litigants' biases. This practice evolved to enhance the court's understanding of broader social, legal, or public interests beyond the immediate parties involved.
Notable Amicus Curiae Brief Examples in Supreme Court Decisions
The Supreme Court has frequently relied on notable amicus curiae briefs to provide expert insights and broader societal perspectives in landmark cases like Brown v. Board of Education, where civil rights organizations highlighted the impact of segregation on public education. In Obergefell v. Hodges, numerous amici curiae including legal scholars and advocacy groups submitted briefs emphasizing constitutional principles of equality and human dignity underlying marriage rights. These briefs serve as critical tools for the Court, enhancing judicial understanding beyond the immediate parties involved in complex constitutional matters.
Government Agencies as Amicus Curiae: Key Examples
Government agencies often participate as amicus curiae to provide expert perspectives in significant legal cases, such as the Department of Justice submitting briefs in landmark civil rights litigation. The Environmental Protection Agency frequently acts as amicus to clarify regulatory intent in cases involving environmental law and public health standards. These interventions by governmental bodies help courts understand policy implications and technical details beyond the parties' arguments, shaping critical judicial decisions.
Impactful Amicus Curiae Briefs: Landmark Case Studies
In the landmark case of Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the NAACP's amicus curiae brief played a pivotal role by presenting extensive social science evidence demonstrating the detrimental effects of segregation on African American children, which significantly influenced the Supreme Court's decision to declare school segregation unconstitutional. Another impactful example is the 2015 Obergefell v. Hodges case, where over 80 amicus briefs from advocacy groups, civil rights organizations, and businesses highlighted the widespread support for marriage equality, shaping the Court's ruling that legalized same-sex marriage nationwide. These cases exemplify how strategic amicus curiae briefs can provide critical expertise and persuasive evidence that shape landmark government and judicial decisions.
The Process for Submitting Amicus Curiae Briefs
Amicus curiae briefs can be submitted by non-parties seeking to provide expert insights or legal arguments in government-related cases. The process typically involves obtaining permission from the court, either through a motion or by the court's invitation, and complying with specific formatting and filing requirements. Timely submission aligned with the court's schedule ensures that the amicus brief is considered during the judicial review of government policies or regulations.
NGOs and Civil Society as Amici Curiae in Government Litigation
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and civil society groups frequently serve as amici curiae in government litigation to provide expert insights and represent public interests. These amici curiae offer specialized knowledge on human rights, environmental policy, and social justice that can influence judicial decisions in cases involving government actions. Their participation enhances transparency and accountability by ensuring diverse perspectives are considered in complex legal disputes.
Influence of Amicus Curiae on Policy and Legislation
Amicus curiae briefs have significantly influenced government policy and legislation by providing courts with expert perspectives that extend beyond the immediate interests of the parties involved. These briefs often shape judicial interpretations that inform legislative reforms, such as in landmark cases involving civil rights or environmental regulation. Through strategic presentations, amicus curiae effectively guide policy makers by highlighting broader social, economic, and constitutional implications.
Criticisms and Challenges of Amicus Curiae Participation
Amicus curiae briefs often face criticism for potentially biasing judicial decisions due to the influence of well-funded interest groups, which may overshadow less-resourced parties. Challenges include questions about the relevance and impartiality of the information submitted, with courts sometimes struggling to manage the volume and quality of these briefs. Such participation can complicate case proceedings by introducing external policy arguments that diverge from the core legal issues under review.
Future Trends in Amicus Curiae Involvement in Government Cases
Future trends in amicus curiae involvement in government cases indicate increasing participation by advocacy groups and academic institutions, providing expert opinions on complex regulatory and constitutional issues. Enhanced digital platforms facilitate wider dissemination of amicus briefs, promoting transparency and public engagement in government litigation. The growing reliance on data-driven analysis and interdisciplinary perspectives is shaping informed judicial decision-making in evolving policy areas.
example of amicus curiae in brief Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com