The Cabinet in the Executive branch serves as a principal advisory body to the head of government, typically the president or prime minister. This group consists of the leaders of key government departments and agencies, such as the Secretary of State, Secretary of Defense, and the Attorney General. These cabinet members play a crucial role in policy formulation, implementation, and national governance. In the United States, the Cabinet includes entities like the Department of Treasury, Department of Homeland Security, and the Environmental Protection Agency. Each cabinet secretary oversees their respective department's operations and advises the president on issues under their jurisdiction. The cabinet's collective expertise strengthens decision-making in addressing complex governmental challenges and executing executive policies effectively.
Table of Comparison
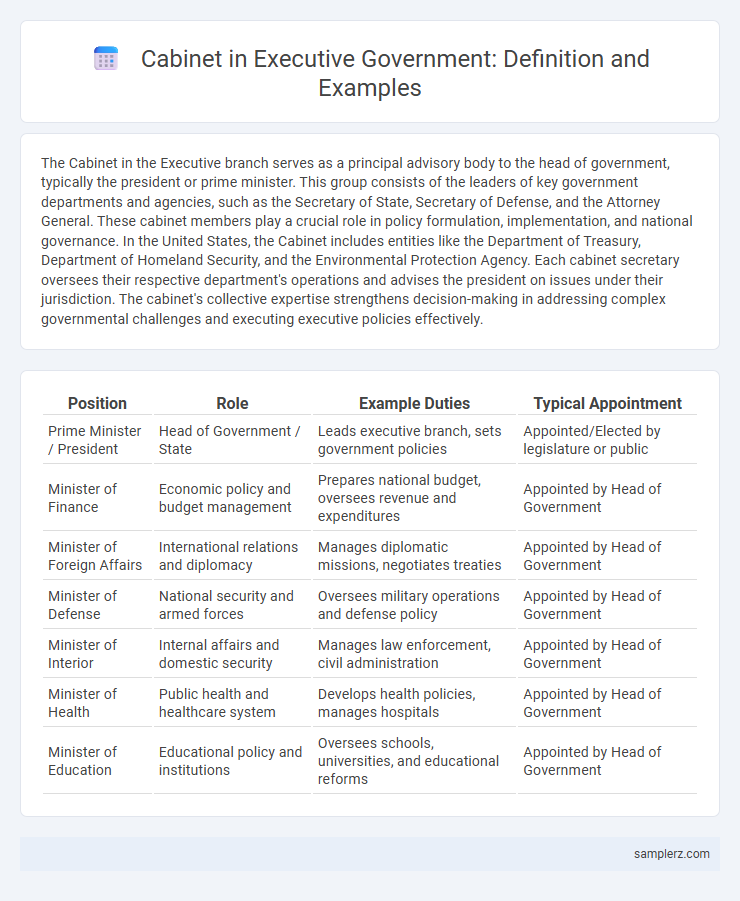
| Position | Role | Example Duties | Typical Appointment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prime Minister / President | Head of Government / State | Leads executive branch, sets government policies | Appointed/Elected by legislature or public |
| Minister of Finance | Economic policy and budget management | Prepares national budget, oversees revenue and expenditures | Appointed by Head of Government |
| Minister of Foreign Affairs | International relations and diplomacy | Manages diplomatic missions, negotiates treaties | Appointed by Head of Government |
| Minister of Defense | National security and armed forces | Oversees military operations and defense policy | Appointed by Head of Government |
| Minister of Interior | Internal affairs and domestic security | Manages law enforcement, civil administration | Appointed by Head of Government |
| Minister of Health | Public health and healthcare system | Develops health policies, manages hospitals | Appointed by Head of Government |
| Minister of Education | Educational policy and institutions | Oversees schools, universities, and educational reforms | Appointed by Head of Government |
Definition and Role of the Executive Cabinet
The Executive Cabinet is a group of senior government officials, typically appointed by the head of state or government, who lead key departments and advise on policy decisions. This body coordinates the implementation of government policies and ensures that different ministries work together efficiently to achieve national objectives. Acting as both advisors and administrators, cabinet members play a critical role in shaping legislative agendas and managing public resources.
Historical Evolution of Executive Cabinets
The historical evolution of executive cabinets traces back to early monarchies where royal advisors formed the basis of modern cabinets, transitioning during the 18th century Enlightenment to more structured bodies of government ministers. In the United Kingdom, the Cabinet emerged as a key executive decision-making body by the 19th century, establishing the model for parliamentary systems worldwide. This evolution reflects the gradual shift from monarchial autocracy to constitutional governance, emphasizing collective responsibility and ministerial accountability.
Key Members of the Executive Cabinet
The Executive Cabinet typically includes key members such as the Prime Minister or President, the Minister of Finance, the Minister of Defense, and the Minister of Foreign Affairs, who play crucial roles in policy-making and governance. These officials oversee major governmental departments, ensuring the implementation of laws and management of public resources. Their collective decisions shape national priorities and international relations.
Structure and Organization of Cabinets Globally
Cabinets in executive branches worldwide typically consist of a group of senior officials or ministers responsible for major government departments, such as finance, defense, and foreign affairs. The structure often includes a prime minister or president as the head, with various ministers overseeing portfolios aligned with national priorities, ensuring coordinated policy implementation. Cabinet size and composition vary by country, reflecting political systems ranging from parliamentary democracies to presidential regimes, with collective decision-making facilitating governance and accountability.
Functions and Responsibilities of Cabinet Ministers
Cabinet ministers are responsible for formulating government policies, overseeing the implementation of laws, and managing their respective departments to ensure efficient public service delivery. They provide expert advice to the head of government, coordinate inter-ministerial activities, and represent the government in parliamentary sessions. Key functions include budget allocation, legislative drafting, and diplomatic engagement to advance national interests.
Examples of Cabinet Structures in Major Governments
The United Kingdom's cabinet, led by the Prime Minister, consists of key ministers heading departments such as the Home Office, Foreign Office, and Treasury, forming a centralized executive decision-making body. In the United States, the cabinet includes heads of 15 executive departments like Defense, State, and Treasury, advising the President on national policy and administration. Germany's Federal Cabinet, chaired by the Chancellor, features ministers responsible for portfolios including Foreign Affairs, Finance, and Interior, reflecting a coalition government structure with collective executive authority.
Selection and Appointment of Cabinet Members
Cabinet members in the Executive branch are typically selected based on their expertise, political alignment, and loyalty to the head of government, such as a president or prime minister. The appointment process often involves vetting by legislative bodies, such as the Senate, to ensure nominees meet qualifications and ethical standards. This rigorous selection and appointment procedure aims to form a cohesive team that can effectively implement government policies and administrative functions.
Cabinet Decision-Making Processes
Cabinet decision-making processes in executive government typically involve collective discussions among key ministers, including the Prime Minister, Finance Minister, and Defense Minister, to ensure coordinated policy development and implementation. These decisions rely on inter-ministerial collaboration, advisory input from senior civil servants, and adherence to established protocols to maintain transparency and accountability. The structured agenda-setting, consensus-building, and formal voting mechanisms help streamline governance and promote unified strategic priorities.
Impact of the Cabinet on Policy Implementation
The Cabinet, composed of key ministers such as the Secretary of State and the Chancellor, plays a pivotal role in shaping and executing government policies by coordinating departmental strategies and resources. Its collective decision-making ensures cohesive policy implementation, directly influencing legislative priorities and public service outcomes. Effective Cabinet collaboration enhances accountability and responsiveness in governance, driving national development goals.
Challenges and Reforms in Modern Executive Cabinets
Modern executive cabinets face challenges such as political polarization, bureaucratic inertia, and the need for transparency and accountability in decision-making processes. Reforms often focus on enhancing inter-ministerial coordination, implementing digital governance tools, and promoting merit-based appointments to strengthen administrative efficiency. These changes aim to increase responsiveness to public demands while maintaining the balance of power within government structures.
example of cabinet in Executive Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com