In the United States Senate, the President pro tempore is a constitutionally recognized officer who presides over the Senate in the absence of the Vice President. This position is traditionally held by the longest-serving member of the majority party, reflecting seniority rather than political power. The President pro tempore plays a crucial role in maintaining order and overseeing legislative procedures. One notable example of a President pro tempore was Senator Strom Thurmond, who served in this capacity during the 1980s and early 1990s. Thurmond's tenure exemplified the importance of experience and continuity in Senate leadership. The role includes signing legislation, administering oaths, and representing the Senate in ceremonial functions, highlighting its significance in government operations.
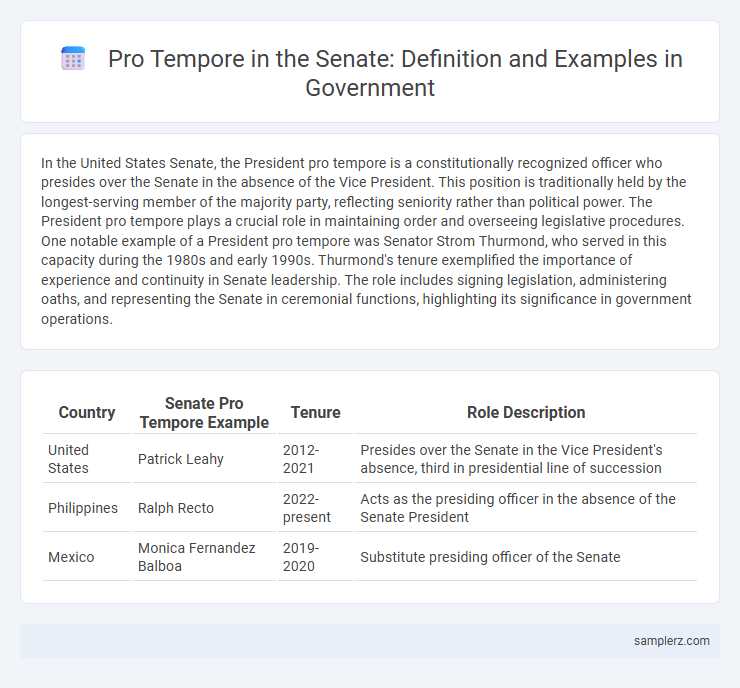
Table of Comparison
| Country | Senate Pro Tempore Example | Tenure | Role Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Patrick Leahy | 2012-2021 | Presides over the Senate in the Vice President's absence, third in presidential line of succession |
| Philippines | Ralph Recto | 2022-present | Acts as the presiding officer in the absence of the Senate President |
| Mexico | Monica Fernandez Balboa | 2019-2020 | Substitute presiding officer of the Senate |
Understanding the Role of Pro Tempore in the Senate
The President pro tempore of the Senate is a constitutionally recognized officer who presides over Senate sessions in the absence of the Vice President. Typically, this role is held by the longest-serving member of the majority party, reflecting seniority and experience. The position carries significant responsibilities, including overseeing legislative proceedings and maintaining order, making it crucial for Senate operations and continuity.
Historical Background of Senate Pro Tempore
The position of President pro tempore in the Senate dates back to the early sessions of the United States Senate in 1789, established to preside over the chamber in the absence of the Vice President. Historically, this role has been held by senior members of the majority party, reflecting experience and continuity in legislative leadership. Notable figures such as William R. King and Robert C. Byrd have exemplified the evolution and significance of the pro tempore office in Senate governance.
Functions and Duties of Senate Pro Tempore
The Senate Pro Tempore primarily presides over Senate sessions in the absence of the Vice President, ensuring the maintenance of order and adherence to procedural rules. This role includes signing legislation, issuing warrants, and overseeing Senate administration to facilitate legislative continuity. As third in the presidential line of succession, the Pro Tempore also plays a crucial role in maintaining governmental stability during leadership transitions.
Process of Selecting a Senate Pro Tempore
The process of selecting a Senate Pro Tempore typically involves the majority party nominating a senior member based on tenure and experience, followed by a formal vote in the Senate. This position is traditionally granted to the longest-serving senator of the majority party, reflecting institutional respect and continuity. The Senate Pro Tempore presides over Senate sessions in the absence of the Vice President, making the selection process crucial for legislative leadership and order.
Notable Examples of Senate Pro Tempore in History
Senate Pro Tempore positions have been held by influential figures such as Strom Thurmond, who served the longest term from 1995 to 2001, demonstrating significant seniority and leadership in the U.S. Senate. Another notable example is Robert Byrd, who was Senate Pro Tempore multiple times and holds the record for longest-serving senator, known for his deep knowledge of Senate procedures. Daniel Inouye also served as Pro Tempore, exemplifying bipartisan respect and commitment to public service during his tenure.
Pro Tempore vs. Senate Majority Leader: Key Differences
The President Pro Tempore of the Senate typically presides over the chamber in the absence of the Vice President and is traditionally the most senior member of the majority party, whereas the Senate Majority Leader holds significant power in setting the legislative agenda and managing party strategy. Unlike the Pro Tempore, whose role is largely ceremonial, the Majority Leader actively negotiates with committee chairs and the minority party to advance bills and priorities. The distinction between these positions reflects the balance between formal authority and practical influence within Senate operations.
Case Study: Longest-Serving Senate Pro Tempore
Senator Strom Thurmond holds the record as the longest-serving President pro tempore of the United States Senate, serving from 1981 to 1987 and again from 1995 to 2001. His tenure exemplifies the significant role of the pro tempore in presiding over Senate sessions during the Vice President's absence and maintaining legislative order. Thurmond's extended service highlights the position's importance in Senate tradition and seniority-based leadership.
Constitutional Basis for Senate Pro Tempore
The position of Senate President Pro Tempore is constitutionally established under Article I, Section 3 of the U.S. Constitution, which mandates this officer to preside over the Senate in the absence of the Vice President. Traditionally, the Senate Pro Tempore is the longest-serving member of the majority party, reflecting seniority and experience. This constitutional basis ensures continuity and order in Senate proceedings when the Vice President is unavailable.
Succession and the Importance of Pro Tempore in Government
The President pro tempore of the Senate serves as the second-highest-ranking official, stepping in to preside over Senate sessions when the Vice President is absent, ensuring legislative continuity. In the presidential line of succession, the pro tempore holds a crucial position, following the Vice President and Speaker of the House, safeguarding executive authority during emergencies. This role maintains stability within the government by providing an experienced, senior senator who can assume responsibilities swiftly, reinforcing the balance of power and legislative function.
Impact of Pro Tempore Leadership on Senate Proceedings
The Senate President Pro Tempore plays a crucial role in maintaining order and guiding legislative debates when the Vice President is absent, ensuring continuity and efficiency in Senate proceedings. Their leadership influences committee assignments, legislative priorities, and procedural rulings, which directly affect the pace and outcome of policy development. Historical examples, such as Senator Patrick Leahy's tenure as Pro Tempore, demonstrate how experienced leadership can enhance bipartisan cooperation and uphold institutional traditions.
example of pro tempore in senate Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com