Logrolling in government committees occurs when members exchange support for each other's proposals to ensure mutual legislative success. For instance, a committee member representing agriculture might agree to back a colleague's transportation funding bill in return for support on a farm subsidy measure. This practice enhances coalition-building by allowing diverse interests to align and push multiple legislative priorities forward. Committees serve as critical loci for logrolling because members have focused agendas and detailed knowledge of specific policy areas. Data shows that logrolling can increase the number of bills passed by creating voting blocs that combine resources and influence. Entities such as congressional committees, state legislative panels, and municipal councils regularly witness this strategic vote trading during budget approvals and policy amendments.
Table of Comparison
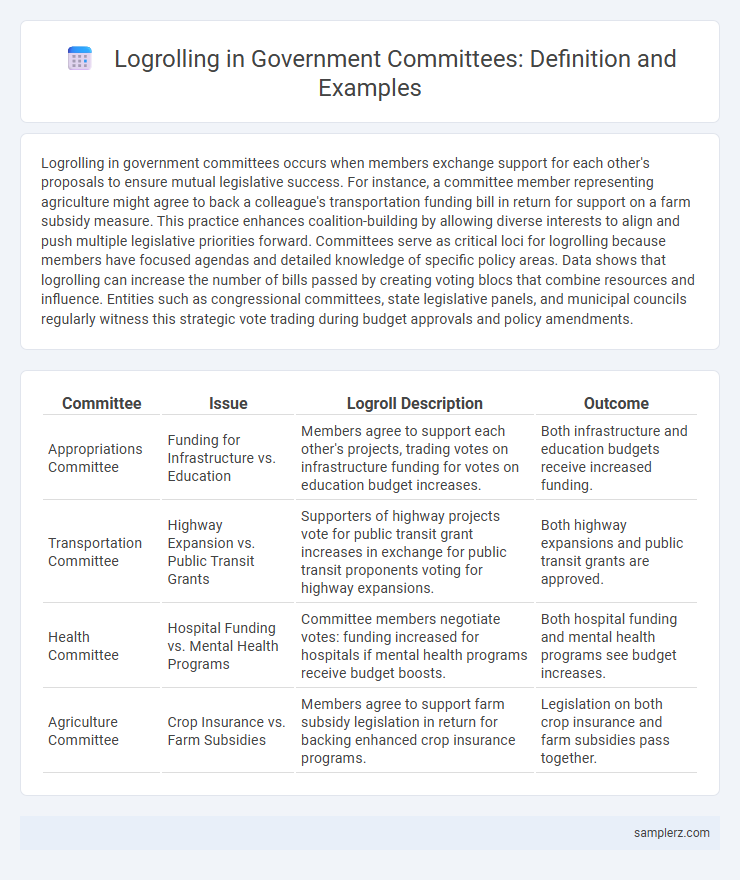
| Committee | Issue | Logroll Description | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appropriations Committee | Funding for Infrastructure vs. Education | Members agree to support each other's projects, trading votes on infrastructure funding for votes on education budget increases. | Both infrastructure and education budgets receive increased funding. |
| Transportation Committee | Highway Expansion vs. Public Transit Grants | Supporters of highway projects vote for public transit grant increases in exchange for public transit proponents voting for highway expansions. | Both highway expansions and public transit grants are approved. |
| Health Committee | Hospital Funding vs. Mental Health Programs | Committee members negotiate votes: funding increased for hospitals if mental health programs receive budget boosts. | Both hospital funding and mental health programs see budget increases. |
| Agriculture Committee | Crop Insurance vs. Farm Subsidies | Members agree to support farm subsidy legislation in return for backing enhanced crop insurance programs. | Legislation on both crop insurance and farm subsidies pass together. |
Understanding Logrolling in Government Committees
Logrolling in government committees occurs when members exchange support for each other's proposals to secure mutual benefits, often trading votes on different bills. This practice helps pass legislation that may struggle to gain approval independently by building coalitions of interest. Understanding logrolling reveals its impact on policymaking, highlighting how strategic vote trading influences legislative outcomes.
Historical Examples of Committee Logrolling
Committee logrolling has played a pivotal role in legislative history, exemplified by the U.S. Congress in the 19th century, where members exchanged votes to secure funding for local infrastructure projects. One notable case occurred during the 1820s when southern and western legislators traded support for tariffs and internal improvements, advancing regional economic interests. This practice facilitated legislative compromise but also highlighted the strategic negotiation inherent in committee dynamics.
How Logroll Negotiations Shape Legislation
Logroll negotiations in government committees involve lawmakers trading support for each other's proposals to secure mutual benefits, shaping legislation by enabling the inclusion of diverse interests and priorities. This practice increases the likelihood of bill passage by building coalitions that reflect broader policy compromises. Consequently, logrolling transforms legislative outcomes by balancing competing demands and fostering consensus in complex political environments.
Case Study: Logrolling in Congressional Committees
In congressional committees, logrolling occurs when members exchange support for each other's bills to secure mutual legislative benefits, exemplified by the passage of the 1986 Tax Reform Act, where committee members agreed to back each other's provisions to ensure comprehensive tax code revisions. This strategic vote trading facilitates bipartisan cooperation and advances complex legislation by aligning diverse interests within committees. Such negotiated deals demonstrate the practical application of logrolling in shaping policy outcomes through committee consensus.
Notable Logroll Deals in Appropriations Committees
Notable logroll deals in appropriations committees often involve the strategic exchange of support for funding projects that benefit diverse districts, such as trading backing for infrastructure spending in one member's district for education grants in another's. These deals enable legislators to secure federal resources for local priorities while advancing broader budget agreements. Examples include the allocation of funds for highway construction paired with increases in health services appropriations, illustrating how logrolling facilitates consensus and comprehensive budget enactment.
The Role of Logrolling in Policy Compromises
Logrolling in government committees often involves members exchanging support for each other's policy proposals to secure majority approval, exemplified by lawmakers agreeing to back a colleague's infrastructure bill in return for votes on their own education reform initiatives. This strategic vote trading fosters policy compromises that balance diverse interests, enabling the passage of multifaceted legislation that might otherwise face stalemate. Such practices illustrate how logrolling functions as a vital mechanism in legislative negotiation, promoting collaborative governance and policy outcomes.
Logrolling and Partisanship in Committee Dynamics
Logrolling in government committees often involves legislators exchanging support for each other's proposals to advance partisan agendas, enhancing legislative efficiency despite ideological differences. This strategic vote trading reinforces partisanship by encouraging coalitions that align with political party interests rather than individual policy merits. Consequently, committee dynamics are shaped by negotiated compromises that balance partisan goals with the need for consensus building.
Ethics and Transparency in Committee Logrolling
Logrolling in government committees often involves exchanging support for legislation that benefits individual members' interests, posing significant ethical challenges. Transparency measures, such as public disclosure of voting records and committee discussions, help mitigate conflicts of interest and promote accountability. Implementing strict ethical guidelines and monitoring mechanisms ensures committee decisions prioritize public welfare over political bargaining.
Comparisons of Logrolling Practices Across Governments
Logrolling practices vary significantly across governments, with some legislative committees in the United States exchanging support for budget allocations to secure regional projects, while European parliaments often emphasize issue-based bargaining without explicit vote trading. In contrast, many developing countries display more informal logrolling, relying on personal relationships to negotiate committee support for policy priorities. Comparative studies reveal that transparency and institutional rules heavily influence the prevalence and structure of logrolling in different government systems.
The Impact of Logrolling on Legislative Outcomes
Logrolling in government committees often results in the passage of legislation that may not have succeeded independently, as members trade support for each other's proposals to secure mutual benefits. This practice can lead to the approval of policies with bundled interests, sometimes prioritizing political gain over public welfare. The impact of logrolling on legislative outcomes includes increased complexity in lawmaking and potential challenges in accountability and transparency.
example of logroll in committee Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com