Logrolling in the legislature refers to the practice where lawmakers exchange support for each other's proposed bills or amendments to secure mutual benefits. For example, a senator from an agricultural state might agree to vote for a transportation funding bill sponsored by a colleague from an industrial state if that colleague supports agricultural subsidies. This strategic collaboration enables legislators to advance their priorities by building alliances and leveraging reciprocal commitments. Legislative logrolling often influences budget allocations and policy outcomes by promoting coalition-building among diverse interest groups. Data from congressional voting records show that logrolling can increase the passage rate of complex bills requiring broad support across party lines or regions. The phenomenon underscores the bargaining dimension of legislative processes, where vote trading shapes the content and success of legislation.
Table of Comparison
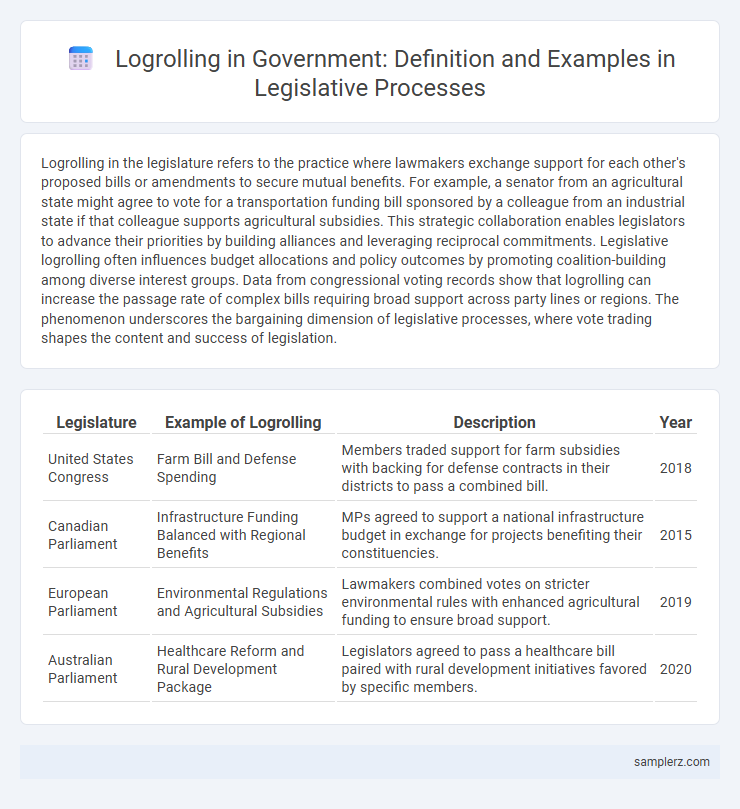
| Legislature | Example of Logrolling | Description | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States Congress | Farm Bill and Defense Spending | Members traded support for farm subsidies with backing for defense contracts in their districts to pass a combined bill. | 2018 |
| Canadian Parliament | Infrastructure Funding Balanced with Regional Benefits | MPs agreed to support a national infrastructure budget in exchange for projects benefiting their constituencies. | 2015 |
| European Parliament | Environmental Regulations and Agricultural Subsidies | Lawmakers combined votes on stricter environmental rules with enhanced agricultural funding to ensure broad support. | 2019 |
| Australian Parliament | Healthcare Reform and Rural Development Package | Legislators agreed to pass a healthcare bill paired with rural development initiatives favored by specific members. | 2020 |
Understanding Logrolling in Legislative Processes
Logrolling in legislative processes involves legislators exchanging support for each other's bills to secure mutual benefits and pass more legislation efficiently. This strategic collaboration often arises when lawmakers trade votes on unrelated policy issues, thereby enhancing the chances of approval for proposals with localized or specialized interests. Understanding logrolling reveals its role in coalition-building and navigating complex legislative negotiations within government institutions.
Historical Background of Logrolling in Government
Logrolling in government traces back to early legislative practices where lawmakers exchanged support for each other's bills to secure mutual benefits, notably during the 19th century in the U.S. Congress. This practice became prominent as representatives from different regions traded votes on infrastructure projects and tariffs to promote local interests. Historical records show that logrolling facilitated the passage of major legislation by forming coalitions based on reciprocal agreements rather than ideological alignment.
Key Characteristics of Legislative Logrolls
Legislative logrolls involve mutual agreements among lawmakers to support each other's proposals, maximizing the passage of multiple bills through vote trading. Key characteristics include reciprocal voting, issue linkage across different policy areas, and the strategic bundling of projects to secure coalition building. This practice enables legislators to achieve policy goals that might be unattainable individually by leveraging collective negotiation power.
Classic Examples of Logrolling in Congress
Classic examples of logrolling in Congress include the 1965 Voting Rights Act, which secured bipartisan support by trading votes between southern legislators and civil rights advocates. Another prominent instance occurred during the passage of the 1986 Tax Reform Act, where lawmakers exchanged support to eliminate specific tax loopholes in return for other fiscal benefits. These deals exemplify strategic vote trading essential to legislative success in the U.S. government.
Logrolling and the Passage of Major Bills
Logrolling in legislatures involves legislators exchanging support for each other's bills to secure majority votes, enabling the passage of major legislation. This strategic trading allows controversial or costly policies to pass by bundling them with popular measures, ensuring mutual benefits for involved lawmakers. Examples include comprehensive budget bills where representatives agree to fund district-specific projects in return for backing broader government initiatives.
Modern Instances of Logrolling in State Legislatures
Modern instances of logrolling in state legislatures frequently involve the exchange of support among lawmakers to pass budget allocations favoring their districts, such as infrastructure projects or educational funding. For example, representatives from rural and urban areas often trade votes to ensure mutual backing for road improvements and public transit initiatives, balancing constituent needs. This strategic vote trading accelerates legislative approval but raises concerns about prioritizing local interests over statewide policy coherence.
Case Study: Logrolling in Budget Appropriations
Logrolling in budget appropriations occurs when legislators exchange support for each other's funding projects to secure passage of a comprehensive budget. A notable case study is the U.S. Congress's 2018 budget deal, where members traded votes to fund infrastructure and defense programs, ensuring mutual benefits. This strategic vote trading enables legislators to advance pet projects while maintaining coalition stability.
Controversies Surrounding Logrolling Practices
Logrolling in legislatures often sparks controversies due to the perceived corruption and ethical concerns it raises, as lawmakers trade votes to pass bills that might not individually merit approval. Critics argue that this practice can undermine transparent policymaking and result in pork-barrel spending, where legislators prioritize local projects over national interest. High-profile cases have highlighted how logrolling can distort budget allocations, leading to inefficiencies and public distrust in government institutions.
Impact of Logrolling on Policy Outcomes
Logrolling in legislatures often leads to the passage of policies that might not succeed independently by encouraging vote trading among lawmakers. This practice can result in the creation of comprehensive bills that bundle diverse interests, increasing the likelihood of legislative approval. The impact on policy outcomes includes the potential for enhanced bipartisan cooperation but also risks producing inefficient or pork-barrel projects that cater to narrow interests rather than public welfare.
Reform Efforts and Alternatives to Legislative Logrolling
Legislative logrolling often emerges in reform efforts as lawmakers trade votes to pass complex bills, exemplified by infrastructure packages where unrelated projects receive funding through reciprocal agreements. Alternatives to traditional logrolling include increasing transparency with public disclosures of vote trading and adopting committee-based deliberations to reduce backroom bargaining. Reform proposals emphasize stricter lobbying regulations and promoting policy-focused negotiations to limit reliance on vote trading in legislative processes.
example of logroll in Legislature Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com