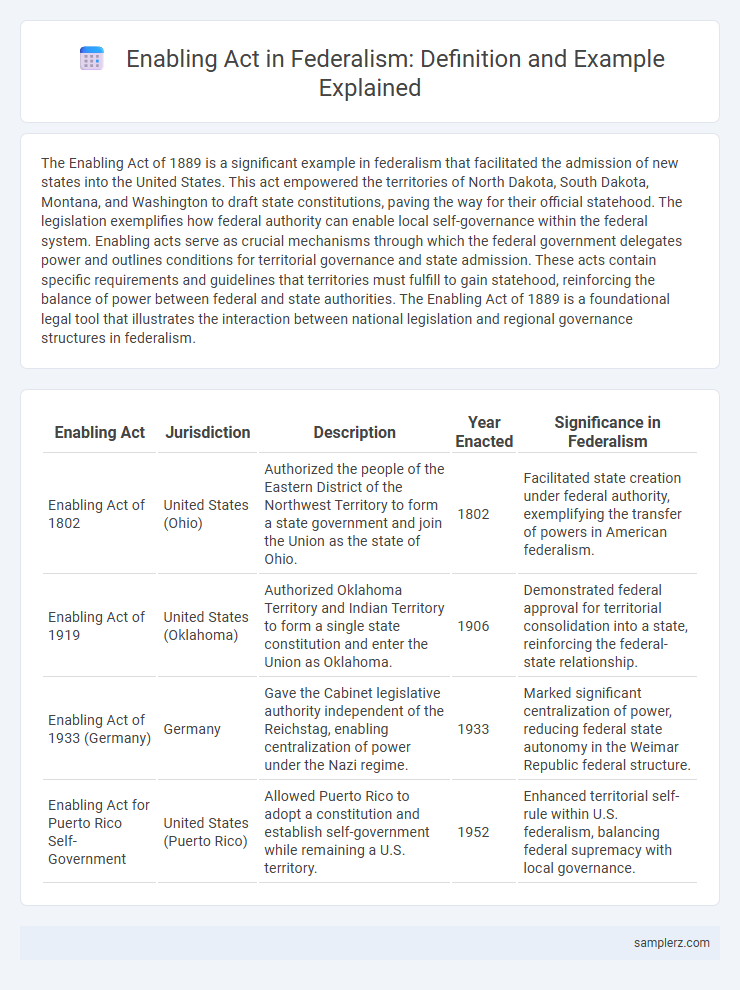
The Enabling Act of 1889 is a significant example in federalism that facilitated the admission of new states into the United States. This act empowered the territories of North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington to draft state constitutions, paving the way for their official statehood. The legislation exemplifies how federal authority can enable local self-governance within the federal system. Enabling acts serve as crucial mechanisms through which the federal government delegates power and outlines conditions for territorial governance and state admission. These acts contain specific requirements and guidelines that territories must fulfill to gain statehood, reinforcing the balance of power between federal and state authorities. The Enabling Act of 1889 is a foundational legal tool that illustrates the interaction between national legislation and regional governance structures in federalism.
Table of Comparison
| Enabling Act | Jurisdiction | Description | Year Enacted | Significance in Federalism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enabling Act of 1802 | United States (Ohio) | Authorized the people of the Eastern District of the Northwest Territory to form a state government and join the Union as the state of Ohio. | 1802 | Facilitated state creation under federal authority, exemplifying the transfer of powers in American federalism. |
| Enabling Act of 1919 | United States (Oklahoma) | Authorized Oklahoma Territory and Indian Territory to form a single state constitution and enter the Union as Oklahoma. | 1906 | Demonstrated federal approval for territorial consolidation into a state, reinforcing the federal-state relationship. |
| Enabling Act of 1933 (Germany) | Germany | Gave the Cabinet legislative authority independent of the Reichstag, enabling centralization of power under the Nazi regime. | 1933 | Marked significant centralization of power, reducing federal state autonomy in the Weimar Republic federal structure. |
| Enabling Act for Puerto Rico Self-Government | United States (Puerto Rico) | Allowed Puerto Rico to adopt a constitution and establish self-government while remaining a U.S. territory. | 1952 | Enhanced territorial self-rule within U.S. federalism, balancing federal supremacy with local governance. |
Introduction to Enabling Acts in Federalism
Enabling acts serve as legislative tools that grant authority to territorial governments or colonies to draft constitutions and establish formal governance structures within the federal system. These acts outline the specific powers and limitations of the regional entity, ensuring alignment with federal laws and constitutional principles. The process designated by enabling acts is crucial for the orderly expansion of state governments and the integration of new states into the federal union.
Historical Overview of Enabling Acts
Enabling Acts in federalism historically facilitated the transition of territories into statehood by granting authority to draft state constitutions and establish governance frameworks. The Enabling Act of 1802, which allowed the Ohio Territory to form a state constitution, set a precedent for subsequent territorial admissions. These Acts function as crucial legislative tools that balance federal oversight with regional autonomy, underpinning the development of the United States' federal system.
Key Features of Enabling Acts
Enabling Acts in federalism grant specific legislative powers to lower levels of government, allowing states or provinces to self-govern within the framework of the federal constitution. Key features include delegation of authority, legal empowerment for constitutional or statutory changes, and clear limits to maintain federal oversight. These acts facilitate decentralization while preserving national unity by balancing autonomy and control.
The Role of Enabling Acts in State Formation
Enabling Acts play a crucial role in state formation by granting territories the legal authority to draft constitutions and establish state governments within a federal system. These acts, such as the Enabling Act of 1889 for North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington, facilitate the transition from federal territory to statehood by providing a clear framework for political organization and self-governance. They ensure compliance with federal requirements, enabling new states to integrate seamlessly into the union while maintaining adherence to constitutional principles.
Classic Example: The United States Enabling Act of 1802
The United States Enabling Act of 1802 is a classic example of an enabling act in federalism, authorizing the territory of Ohio to form a state constitution and government within the federal framework. This act established a constitutional process for transitioning from territorial status to statehood, exemplifying how federal authority can empower local governance. The Enabling Act of 1802 set a precedent for integrating new states into the Union while maintaining federal oversight.
Enabling Acts and Constitutional Development
Enabling Acts play a crucial role in federalism by granting territories the authority to draft state constitutions as a step toward statehood, exemplified by the Enabling Act of 1889 which facilitated the admission of North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington into the United States. These legislative measures serve as foundational instruments for constitutional development, outlining specific guidelines and conditions that shape the governance framework of emerging states. The use of Enabling Acts ensures a structured transition from federal oversight to autonomous state government, reinforcing the balance of power inherent in federal systems.
Comparative Analysis: Enabling Acts in Federal Systems Globally
Enabling acts in federal systems empower subnational governments by granting them legislative authority while maintaining constitutional balance between central and regional powers. For instance, the United States' Enabling Act of 1889 facilitated the admission of North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington as states, demonstrating how enabling acts support territorial integration within federal frameworks. Similarly, Germany's Basic Law allows Lander to exercise significant legislative competencies through enabling provisions, highlighting diverse approaches to decentralization in global federal systems.
Legal Implications of Enabling Acts in Federalism
Enabling acts in federalism grant specific legislative authority to local governments, allowing them to enact laws tailored to regional needs while remaining within constitutional boundaries. These acts carry significant legal implications by delineating the scope and limits of local self-governance and maintaining the balance of power between federal and state governments. Judicial review often arises to interpret these acts, ensuring they do not infringe on federal supremacy or violate constitutional provisions.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding Enabling Acts
Enabling acts in federalism, such as the Federal Enabling Act of 1889 that admitted North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington into the Union, often face challenges including debates over states' rights and the federal government's scope of authority. Controversies arise when enabling acts impose federal conditions that some states perceive as infringements on their autonomy, leading to legal disputes and political tensions. The ambiguity in interpreting enabling acts sometimes results in prolonged conflicts over resource control, jurisdiction, and the balance of power between state and federal governments.
Contemporary Examples of Enabling Acts in Modern Federal States
Contemporary examples of enabling acts in modern federal states include Germany's Basic Law provisions that empower the federal government to intervene in state affairs during emergencies, ensuring national cohesion. In India, the President's rule under Article 356 allows the central government to take control of a state government if it fails to function according to constitutional norms. Canada's Constitution Act of 1982 enables federal authority to enact laws on matters of national importance while respecting provincial powers, exemplifying cooperative federalism.
example of enabling act in federalism Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com