Habeas corpus is a fundamental legal principle that protects individual freedom by ensuring that a person cannot be detained without just cause. In judiciary proceedings, habeas corpus allows a detainee to challenge the legality of their imprisonment before a court. This writ compels the government to present the detained individual in court and justify their detention with valid evidence or legal grounds. An example of habeas corpus in the judiciary is when a prisoner files a petition claiming unlawful imprisonment. The court then reviews the case, examines the detention order, and determines whether the person's rights have been violated. If the detention is found to be unlawful, the court orders the immediate release of the detainee, reinforcing the protection of civil liberties within the government framework.
Table of Comparison
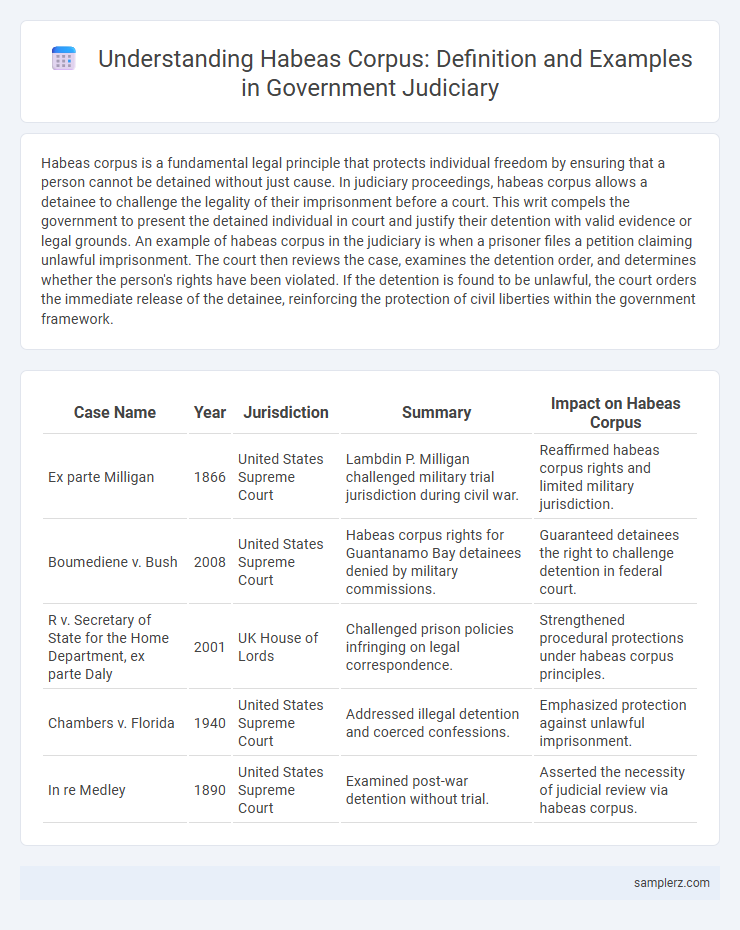
| Case Name | Year | Jurisdiction | Summary | Impact on Habeas Corpus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ex parte Milligan | 1866 | United States Supreme Court | Lambdin P. Milligan challenged military trial jurisdiction during civil war. | Reaffirmed habeas corpus rights and limited military jurisdiction. |
| Boumediene v. Bush | 2008 | United States Supreme Court | Habeas corpus rights for Guantanamo Bay detainees denied by military commissions. | Guaranteed detainees the right to challenge detention in federal court. |
| R v. Secretary of State for the Home Department, ex parte Daly | 2001 | UK House of Lords | Challenged prison policies infringing on legal correspondence. | Strengthened procedural protections under habeas corpus principles. |
| Chambers v. Florida | 1940 | United States Supreme Court | Addressed illegal detention and coerced confessions. | Emphasized protection against unlawful imprisonment. |
| In re Medley | 1890 | United States Supreme Court | Examined post-war detention without trial. | Asserted the necessity of judicial review via habeas corpus. |
Historical Overview of Habeas Corpus in the Judiciary
Habeas corpus, a fundamental legal principle, originated in English common law during the 12th century under King Henry II, serving as a safeguard against unlawful detention. The landmark case of *Ex parte Bollman* (1807) in the United States Supreme Court affirmed its critical role in protecting individual liberty by requiring courts to examine the legality of a detainee's imprisonment. Historically, habeas corpus has evolved into a pivotal judicial tool ensuring governmental accountability and the protection of constitutional rights against arbitrary state action.
Landmark Habeas Corpus Cases in Government Courts
The landmark habeas corpus case of *Ex parte Milligan* (1866) established that military tribunals cannot try civilians when civil courts are operational, reinforcing the judiciary's role in protecting individual liberty against unlawful detention. In *Boumediene v. Bush* (2008), the Supreme Court affirmed detainees' constitutional right to habeas corpus review, extending judicial oversight to Guantanamo Bay prisoners. These cases collectively underscore the government courts' crucial function in upholding habeas corpus as a fundamental safeguard against executive overreach.
Role of Habeas Corpus in Protecting Civil Liberties
Habeas corpus serves as a fundamental judicial mechanism that protects civil liberties by ensuring individuals are not unlawfully detained without due process. Courts use habeas corpus petitions to review the legality of a person's imprisonment, acting as a crucial check against executive or legislative abuses of power. This legal safeguard upholds the constitutional guarantee of personal freedom and prevents arbitrary detention, reinforcing the rule of law in democratic governance.
Supreme Court Decisions on Habeas Corpus Petitions
The Supreme Court has played a pivotal role in shaping habeas corpus jurisprudence, notably in cases like *Boumediene v. Bush* (2008), which affirmed detainees' rights to challenge unlawful detention. In *Swain v. Pressley* (1964), the Court emphasized procedural fairness in habeas petitions, reinforcing judicial oversight over executive detention. These landmark decisions underscore the judiciary's authority in upholding constitutional protections against arbitrary imprisonment.
Habeas Corpus and Unlawful Detention: Case Studies
Habeas corpus serves as a critical legal instrument to challenge unlawful detention, exemplified by landmark judiciary cases such as Boumediene v. Bush where the U.S. Supreme Court reaffirmed detainees' rights to seek relief from indefinite imprisonment without trial. Another notable case, Ex parte Milligan, demonstrated the judiciary's role in protecting civil liberties by ruling against military tribunals for civilians when civilian courts are operational. These cases highlight habeas corpus as an essential safeguard against arbitrary state power and a foundation of constitutional justice.
Government Responses to Habeas Corpus Applications
Government responses to habeas corpus applications often involve presenting lawful justifications for detention, such as evidence of criminal activity or national security concerns. Courts scrutinize these responses to ensure that individual liberties are protected against unlawful imprisonment under constitutional provisions. Judicial oversight in habeas corpus cases reinforces the balance between state authority and personal freedom within the legal framework.
Habeas Corpus in Times of National Emergency
Habeas corpus serves as a critical legal safeguard during times of national emergency by ensuring individuals are not unlawfully detained without just cause. Courts historically uphold habeas corpus petitions to prevent arbitrary arrests and protect civil liberties, even amidst crises such as martial law or counterterrorism operations. The judiciary maintains the balance between national security and personal freedom by requiring the government to justify detentions promptly and transparently.
Judicial Procedures for Habeas Corpus Review
Judicial procedures for habeas corpus review require courts to promptly examine the legality of a detainee's imprisonment, ensuring compliance with constitutional rights. Judges assess whether the detention violates due process by reviewing trial records, detention orders, and evidence of unlawful restraint. This swift and thorough review safeguards individual liberty by preventing arbitrary or unlawful imprisonment under established legal standards.
Notable Examples of Habeas Corpus in Political Imprisonment
The landmark case of *Boumediene v. Bush* (2008) reinforced the right of Guantanamo Bay detainees to access habeas corpus, challenging indefinite detention without trial. In *Ex parte Milligan* (1866), the Supreme Court ruled that civilians could not be tried by military tribunals when civil courts are operational, emphasizing the judiciary's role in protecting political prisoners' rights. These decisions underscore habeas corpus as a critical judicial tool preventing unlawful political imprisonment and safeguarding civil liberties.
Impact of Habeas Corpus on Government Accountability
Habeas corpus serves as a critical judicial instrument ensuring government accountability by mandating that authorities justify the legality of detentions before a court. This principle prevents unlawful imprisonment and arbitrary state power, reinforcing checks and balances within the legal system. Courts invoking habeas corpus cases uphold individual rights while compelling government transparency and adherence to due process.
example of habeas corpus in judiciary Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com