A sunset provision in government legislation refers to a clause that sets an expiration date for the law unless further legislative action is taken to extend it. One notable example is the USA PATRIOT Act, which initially included sunset provisions for several of its surveillance and security measures. These provisions required Congress to review and reauthorize the act periodically, allowing lawmakers to evaluate its effectiveness and impact on civil liberties. Sunset provisions help ensure government accountability by preventing permanent laws without reassessment. The Affordable Care Act also contained sunset clauses for certain funding programs, prompting regular assessment of their performance. This legislative tool balances the need for timely government action with systematic oversight and policy reevaluation.
Table of Comparison
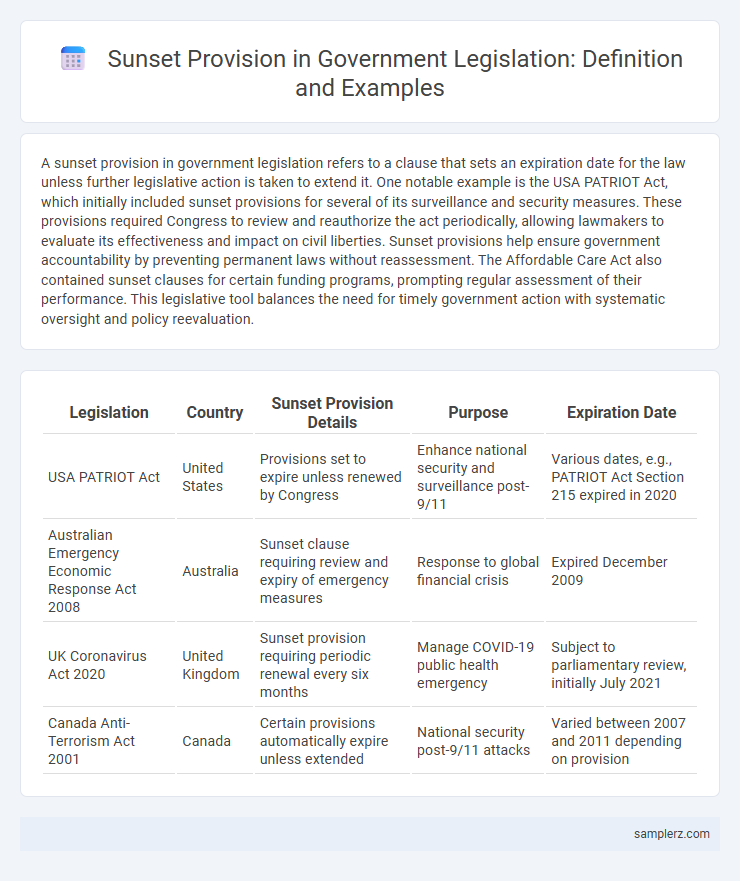
| Legislation | Country | Sunset Provision Details | Purpose | Expiration Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USA PATRIOT Act | United States | Provisions set to expire unless renewed by Congress | Enhance national security and surveillance post-9/11 | Various dates, e.g., PATRIOT Act Section 215 expired in 2020 |
| Australian Emergency Economic Response Act 2008 | Australia | Sunset clause requiring review and expiry of emergency measures | Response to global financial crisis | Expired December 2009 |
| UK Coronavirus Act 2020 | United Kingdom | Sunset provision requiring periodic renewal every six months | Manage COVID-19 public health emergency | Subject to parliamentary review, initially July 2021 |
| Canada Anti-Terrorism Act 2001 | Canada | Certain provisions automatically expire unless extended | National security post-9/11 attacks | Varied between 2007 and 2011 depending on provision |
Understanding Sunset Provisions in Government Legislation
Sunset provisions in government legislation are clauses that set an expiration date for laws unless further legislative action is taken to extend them, ensuring laws remain relevant and effective over time. A notable example is the USA PATRIOT Act, which included sunset clauses for certain surveillance authorities to balance national security with civil liberties. These provisions compel periodic review, fostering accountability and adaptation within legislative frameworks.
Historical Overview of Sunset Clauses in Lawmaking
Sunset provisions have been integral to legislative processes since the early 20th century, with one of the earliest notable examples being the Volstead Act of 1919, which included a built-in expiration date for Prohibition enforcement. In the 1970s, the rise of regulatory reform in the United States further institutionalized sunset clauses, notably through the Congressional Budget and Impoundment Control Act of 1974, which mandated periodic review of federal programs. These historical implementations highlight the strategic use of sunset clauses to ensure timely legislative reassessment and prevent indefinite continuation of laws.
Key Examples of Sunset Provisions in National Legislation
The USA PATRIOT Act, initially enacted after September 11, 2001, included sunset provisions that required periodic renewal by Congress to ensure oversight of surveillance powers. Australia's Telecommunications (Interception and Access) Amendment Act 2015 incorporated sunset clauses for data retention requirements, mandating regular review and potential expiration. Canada's Anti-Terrorism Act contained sunset provisions to assess the law's impact on civil liberties, promoting balance between security measures and individual rights.
Sunset Clauses in Taxation and Fiscal Policies
Sunset clauses in taxation and fiscal policies are implemented to ensure temporary tax provisions or spending measures automatically expire after a set period unless renewed by the legislature. For example, the U.S. Internal Revenue Code often includes sunset provisions for tax credits and deductions, such as the Research & Experimentation Tax Credit, which requires periodic reauthorization to remain effective. These clauses promote fiscal responsibility by limiting long-term commitments and encouraging legislative review of tax incentives and budgetary programs.
Temporary Emergency Powers and Sunset Provisions
Temporary Emergency Powers, often granted to governments during crises, are commonly subject to sunset provisions to ensure they do not extend beyond the immediate need. For example, the USA PATRIOT Act included sunset clauses for sections related to surveillance powers, requiring periodic congressional review and renewal to maintain checks on governmental authority. These sunset provisions help balance rapid response capabilities with protections against potential abuse of emergency powers.
Case Study: The Patriot Act Sunset Clauses
The Patriot Act included sunset provisions that required certain key sections to expire after a set period unless Congress renewed them, ensuring periodic legislative review. Notably, provisions related to surveillance and roving wiretaps were initially set to sunset after four years, prompting debates on balancing national security and civil liberties. These sunset clauses functioned as accountability mechanisms, compelling lawmakers to evaluate the ongoing necessity and impact of the legislation.
Environmental Regulations and Sunset Provision Examples
Environmental regulations often incorporate sunset provisions to ensure periodic review and adaptation to evolving scientific data and policy goals. For instance, the Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990 include sunset clauses for certain emission standards, mandating reevaluation after specified periods to determine their continued efficacy. These provisions help balance environmental protection objectives with economic considerations by allowing sunset review and potential modification or expiration of regulations.
Sunset Provisions in Healthcare Legislation
Sunset provisions in healthcare legislation often mandate that specific programs or regulatory requirements automatically expire after a set period unless reauthorized by the legislature. For example, the Affordable Care Act includes sunset clauses for certain taxes and fees raised to fund healthcare exchanges. These sunset provisions encourage periodic review and adjustment of healthcare policies to ensure continued relevance and fiscal responsibility.
Impact of Sunset Clauses on Legislative Effectiveness
Sunset clauses, such as those in the USA PATRIOT Act, ensure periodic review and reevaluation of legislative provisions, preventing outdated or ineffective laws from remaining in force indefinitely. This mechanism enhances legislative effectiveness by promoting accountability, encouraging timely amendments, and adapting policies to current societal needs. Empirical studies indicate governments with sunset provisions experience increased legislative responsiveness and improved policy outcomes.
Lessons Learned from Notable Sunset Provisions in Government
The USA PATRIOT Act included notable sunset provisions that required periodic congressional review, highlighting the importance of balancing national security with civil liberties. The sunset clause in the UK's Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act (RIPA) demonstrated the necessity of sunset provisions in ensuring that surveillance laws adapt to evolving technological landscapes. Lessons learned emphasize that well-designed sunset provisions promote accountability, foster legislative updates, and prevent outdated or overreaching laws from persisting indefinitely.
example of sunset provision in legislation Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com