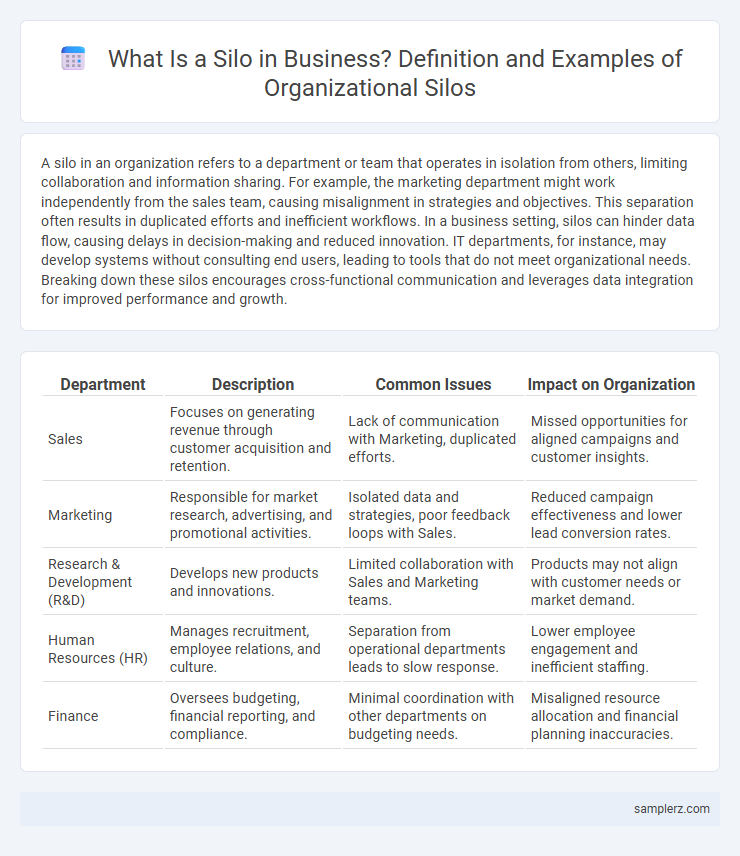
A silo in an organization refers to a department or team that operates in isolation from others, limiting collaboration and information sharing. For example, the marketing department might work independently from the sales team, causing misalignment in strategies and objectives. This separation often results in duplicated efforts and inefficient workflows. In a business setting, silos can hinder data flow, causing delays in decision-making and reduced innovation. IT departments, for instance, may develop systems without consulting end users, leading to tools that do not meet organizational needs. Breaking down these silos encourages cross-functional communication and leverages data integration for improved performance and growth.
Table of Comparison
| Department | Description | Common Issues | Impact on Organization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | Focuses on generating revenue through customer acquisition and retention. | Lack of communication with Marketing, duplicated efforts. | Missed opportunities for aligned campaigns and customer insights. |
| Marketing | Responsible for market research, advertising, and promotional activities. | Isolated data and strategies, poor feedback loops with Sales. | Reduced campaign effectiveness and lower lead conversion rates. |
| Research & Development (R&D) | Develops new products and innovations. | Limited collaboration with Sales and Marketing teams. | Products may not align with customer needs or market demand. |
| Human Resources (HR) | Manages recruitment, employee relations, and culture. | Separation from operational departments leads to slow response. | Lower employee engagement and inefficient staffing. |
| Finance | Oversees budgeting, financial reporting, and compliance. | Minimal coordination with other departments on budgeting needs. | Misaligned resource allocation and financial planning inaccuracies. |
Understanding Organizational Silos: Definition and Impact
Organizational silos are departmental divisions that hinder communication and collaboration, often resulting in inefficiencies and duplicated efforts within business operations. For example, a marketing team working independently from sales can create misaligned strategies and lost revenue opportunities due to poor information flow. Addressing these silos improves cross-functional teamwork, streamlines processes, and enhances overall organizational performance.
Common Causes of Silos in Business Environments
Departments working in isolation, such as marketing and sales refusing to share data, create communication barriers that halt collaboration. Divergent goals and metrics across teams cause misaligned priorities, leading to fragmented efforts and inefficiencies. Leadership failing to promote cross-functional teamwork reinforces these silos, reducing overall organizational agility and innovation.
Communication Breakdown: How Silos Form in Companies
Departments like marketing, sales, and product development often operate in isolation, leading to communication breakdown and inefficiencies in companies. When teams focus solely on their goals without sharing information, silos form and hinder collaborative decision-making. This fragmentation reduces overall agility and innovation by creating barriers across organizational units.
Departmental Isolation: Real-World Examples of Siloed Teams
Sales and marketing teams often operate in isolation, leading to misaligned strategies and lost revenue opportunities. In many organizations, IT and customer service departments function as separate units without shared communication platforms, causing delays in problem resolution and poor customer experiences. Manufacturing and product development divisions frequently work in silos, hindering innovation and slowing time-to-market due to lack of collaborative feedback loops.
Case Study: Sales vs. Marketing Silo Competition
In a case study examining silo competition between sales and marketing teams, misaligned goals and poor communication often hinder overall business performance, leading to missed revenue opportunities. Sales teams may prioritize immediate customer acquisition, while marketing focuses on brand awareness and long-term lead nurturing, creating conflicting strategies. Bridging this divide through integrated CRM systems and regular interdepartmental meetings has proven effective in enhancing collaboration and driving unified growth.
The Effects of Silo Mentality on Company Performance
Silo mentality in organizations often leads to poor communication between departments, resulting in duplicated efforts and wasted resources that severely hinder company performance. Employees working in isolation fail to share vital information, causing delays in decision-making and reducing overall innovation capacity. This fragmented approach decreases operational efficiency and negatively impacts customer satisfaction, ultimately limiting the company's growth potential.
Examples of Siloed Leadership and Decision-Making
Siloed leadership in organizations often appears when departments operate independently, such as sales and marketing teams making separate strategic decisions without collaboration, leading to misaligned goals and inefficiencies. Another example is when the finance department restricts budget approvals without input from project managers, causing delays and internal conflicts. This lack of integrated decision-making hampers overall organizational agility and innovation.
Silo Structures in Global vs. Local Operations
Silo structures in organizations often emerge when global operations prioritize standardized processes, limiting cross-functional collaboration with local teams who adapt practices to regional markets. This separation creates distinct operational silos where global headquarters dictate strategy, while local units focus on execution tailored to local customer preferences and regulations. Effective organizations balance these silos by establishing clear communication channels and integrated performance metrics to bridge global consistency with local agility.
The Role of Technology in Creating Organizational Silos
Technology can unintentionally create organizational silos by enabling departments to operate in isolated digital environments, hindering cross-functional communication. Proprietary software systems, isolated databases, and lack of integrated platforms often result in fragmented information flow, reducing collaboration between teams. Investing in unified communication tools and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems helps break down these barriers by facilitating seamless data sharing across the organization.
Strategies to Break Down Silos: Lessons from Leading Businesses
Leading businesses implement cross-functional teams and transparent communication platforms to dismantle organizational silos. Collaborative goal-setting and integrated technology systems enhance information sharing and align departmental objectives. By fostering a culture of trust and accountability, companies accelerate innovation and improve operational efficiency across divisions.
example of silo in organization Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com