Synergy in business refers to the collaborative interaction between two or more companies or departments that results in a combined effect greater than the sum of their separate effects. A common example is a merger between two firms in complementary industries, such as a software company acquiring a hardware manufacturer. This union creates value by integrating technology development with production capabilities, enhancing product innovation and market reach. Another example of synergy occurs in strategic partnerships where organizations share resources and expertise to achieve common goals. For instance, a marketing agency partnering with a data analytics firm can leverage combined insights to develop more targeted campaigns. This collaboration improves efficiency, reduces costs, and strengthens competitive advantage through shared knowledge and capabilities.
Table of Comparison
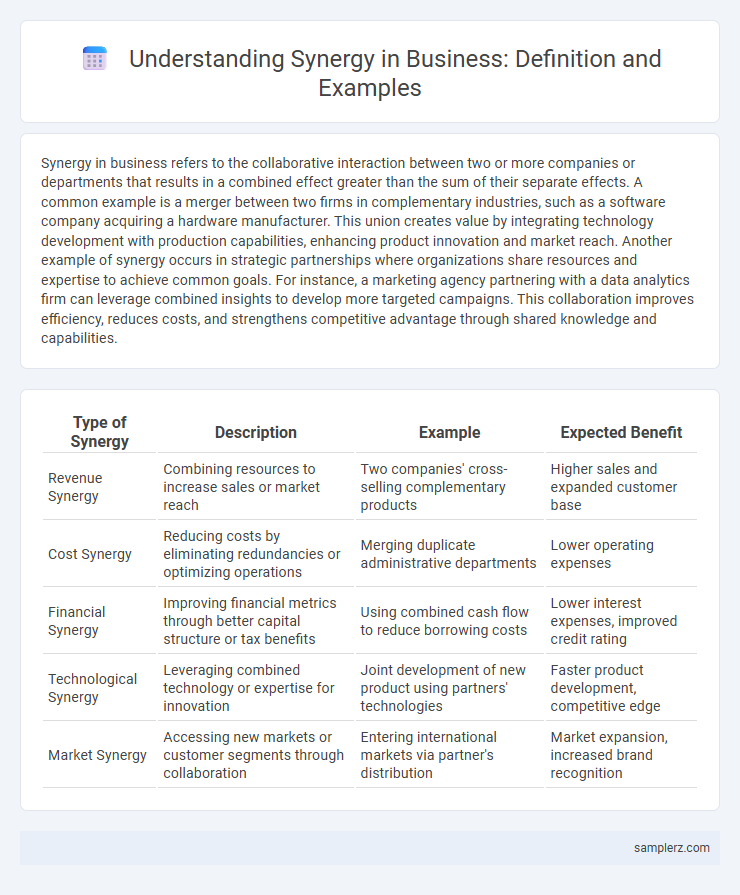
| Type of Synergy | Description | Example | Expected Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue Synergy | Combining resources to increase sales or market reach | Two companies' cross-selling complementary products | Higher sales and expanded customer base |
| Cost Synergy | Reducing costs by eliminating redundancies or optimizing operations | Merging duplicate administrative departments | Lower operating expenses |
| Financial Synergy | Improving financial metrics through better capital structure or tax benefits | Using combined cash flow to reduce borrowing costs | Lower interest expenses, improved credit rating |
| Technological Synergy | Leveraging combined technology or expertise for innovation | Joint development of new product using partners' technologies | Faster product development, competitive edge |
| Market Synergy | Accessing new markets or customer segments through collaboration | Entering international markets via partner's distribution | Market expansion, increased brand recognition |
Understanding Synergy in Business
Synergy in business occurs when the combined efforts of a merger or partnership produce greater value than the sum of their separate effects, exemplified by companies leveraging complementary strengths to enhance innovation and market reach. For instance, Google's acquisition of YouTube integrated advanced search algorithms with vast video content, driving exponential growth and user engagement. Understanding synergy enables businesses to strategically align resources, optimize operations, and achieve sustainable competitive advantages.
Key Types of Business Synergies
Mergers between companies often realize revenue synergies by cross-selling complementary products, enhancing market reach and customer base. Cost synergies emerge through economies of scale, streamlining operations, and reducing redundancies in supply chain and administrative functions. Financial synergies are achieved by combining assets, improving capital structure, and lowering borrowing costs, which enhance overall business valuation.
Mergers and Acquisitions: Real-World Examples
Mergers between Disney and Pixar showcase synergy through combining Disney's distribution strength with Pixar's innovative animation technology, resulting in blockbuster films and increased market share. The acquisition of LinkedIn by Microsoft epitomizes synergy by integrating LinkedIn's professional networking platform with Microsoft's cloud and productivity services, driving user engagement and revenue growth. Another example includes Amazon's purchase of Whole Foods, which merges Amazon's e-commerce expertise with Whole Foods' physical retail presence, enhancing omnichannel shopping experiences and operational efficiency.
Strategic Partnerships that Drive Synergy
Strategic partnerships between companies often drive synergy by combining complementary strengths to enhance innovation, market reach, and operational efficiency. For example, the alliance between Starbucks and PepsiCo leverages Starbucks' premium coffee expertise and PepsiCo's extensive distribution network to expand ready-to-drink coffee products globally. Such partnerships create shared value by optimizing resources, accelerating growth, and increasing competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Cross-Departmental Collaboration Success Stories
Cross-departmental collaboration in business drives innovation and operational efficiency by integrating diverse expertise from marketing, sales, and product development teams. For instance, Apple's collaboration between design and engineering departments resulted in the seamless functionality and aesthetic appeal of the iPhone, boosting market competitiveness. Such synergy fosters shared goals, accelerates problem-solving, and enhances overall company performance.
Technology Integration Enhancing Business Synergy
Technology integration drives business synergy by seamlessly combining disparate systems such as CRM, ERP, and supply chain management platforms, resulting in improved data flow and operational efficiency. Companies like Salesforce and Microsoft demonstrate this by integrating AI-powered analytics into their software suites, enabling better decision-making and customer insights. This technological synergy reduces costs while fostering innovation and agility across business units.
Supply Chain Synergy in Leading Companies
Leading companies like Amazon and Walmart demonstrate supply chain synergy by integrating advanced logistics, data analytics, and vendor collaboration to reduce costs and enhance delivery speed. Amazon's use of real-time inventory tracking combined with automated warehouses streamlines order fulfillment, while Walmart's robust supplier partnerships optimize inventory management and distribution efficiency. This synergy drives competitive advantage by improving customer satisfaction and operational reliability.
Synergy through Product Diversification
Synergy through product diversification occurs when a company expands its product lines to leverage existing strengths, enhance market reach, and optimize resource utilization. For example, Apple's diversification into wearables, such as the Apple Watch, complements its iPhone ecosystem, creating integrated user experiences and boosting overall brand value. This strategy drives revenue growth by capturing new customer segments while maximizing operational efficiencies across product categories.
International Expansion and Synergy Creation
Expanding internationally allows businesses to leverage local market knowledge and resources, creating synergies that enhance operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Collaborations between global subsidiaries optimize supply chains and unify brand strategies, resulting in increased market penetration and revenue growth. Cross-border partnerships integrate diverse expertise, driving innovation and accelerating product development.
Measuring the Impact of Synergy in Business
Measuring the impact of synergy in business involves analyzing financial metrics such as revenue growth, cost savings, and profit margins following mergers or partnerships. Key performance indicators (KPIs) like Return on Investment (ROI) and Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA) help quantify the additional value created through combined operations. Data-driven synergy assessments also consider market share expansion and productivity improvements to demonstrate tangible business benefits.
example of synergy in business Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com