Social loafing occurs when individuals exert less effort while working in a group compared to working alone. For example, in a team project at work, some members may rely on others to complete tasks, reducing their own contribution. Data from organizational studies show that social loafing can decrease overall team productivity by up to 30%. This phenomenon is often observed in settings like group assignments, where accountability is diffused among participants. Research highlights that social loafing tends to increase as group size grows, with individual efforts becoming less visible. Strategies to combat social loafing include assigning specific roles and increasing individual accountability within the group.
Table of Comparison
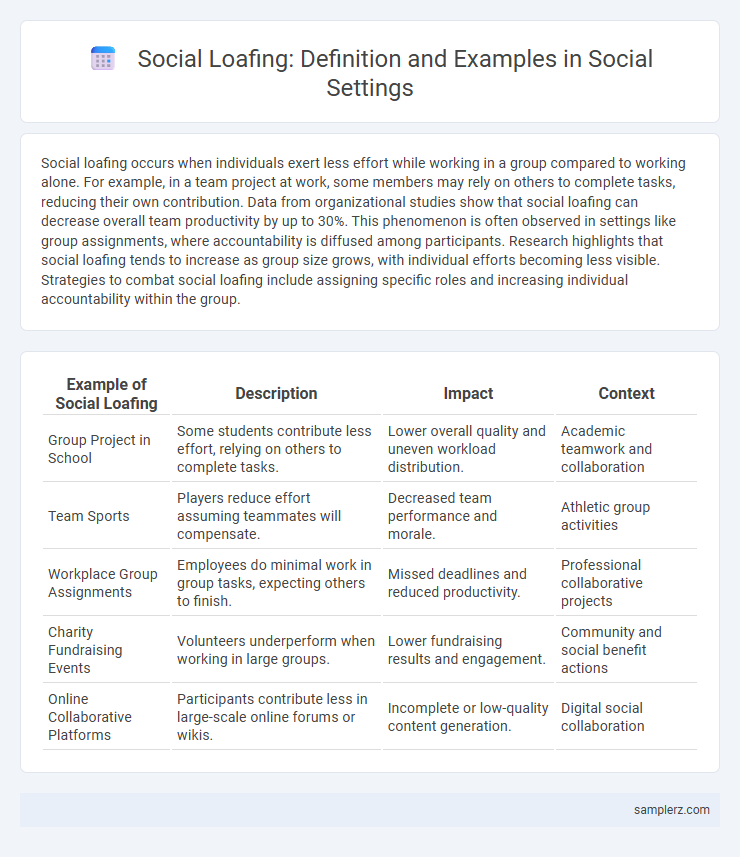
| Example of Social Loafing | Description | Impact | Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group Project in School | Some students contribute less effort, relying on others to complete tasks. | Lower overall quality and uneven workload distribution. | Academic teamwork and collaboration |
| Team Sports | Players reduce effort assuming teammates will compensate. | Decreased team performance and morale. | Athletic group activities |
| Workplace Group Assignments | Employees do minimal work in group tasks, expecting others to finish. | Missed deadlines and reduced productivity. | Professional collaborative projects |
| Charity Fundraising Events | Volunteers underperform when working in large groups. | Lower fundraising results and engagement. | Community and social benefit actions |
| Online Collaborative Platforms | Participants contribute less in large-scale online forums or wikis. | Incomplete or low-quality content generation. | Digital social collaboration |
Common Real-Life Examples of Social Loafing
In group projects, students often exhibit social loafing by relying on others to complete tasks, resulting in uneven workload distribution. Workplace teams experience reduced individual effort when employees assume their contributions are less noticeable in larger groups. During community volunteering events, some participants may contribute less, expecting others to compensate for their lower engagement.
Social Loafing in Group Projects and Teamwork
Social loafing frequently occurs in group projects and teamwork when individual members contribute less effort, assuming others will pick up the slack. This phenomenon reduces overall productivity and can lead to uneven workloads, causing frustration among more motivated team members. Effective strategies to mitigate social loafing include clearly defined roles, accountability measures, and frequent performance evaluations within the group.
Social Loafing in Volunteer Activities
Social loafing in volunteer activities occurs when individuals put in less effort because they believe others will compensate, reducing overall group productivity. Studies show that groups larger than five members tend to experience a 20-30% decrease in individual contribution, highlighting the challenge of maintaining motivation. Strategies such as assigning specific roles and setting clear accountability can effectively mitigate social loafing in volunteer organizations.
Workplace Scenarios Illustrating Social Loafing
Employees in large project teams often contribute less effort when individual accountability is unclear, leading to social loafing. In meetings, some members may rely on others to carry the workload, reducing overall productivity and engagement. This phenomenon frequently occurs in collaborative workplace settings where tasks are divided without clear responsibility.
Social Loafing in Community Events
Social loafing often occurs in community events when individuals contribute less effort, assuming others will compensate. For instance, during neighborhood cleanups, some participants may avoid active tasks like trash collection or sorting recyclables, relying on the group's collective effort. This reduction in personal accountability weakens overall event effectiveness and community engagement.
Social Loafing during School Group Assignments
Social loafing frequently occurs during school group assignments when certain students contribute less effort, relying on peers to complete the work. This phenomenon reduces overall group productivity and can hinder learning outcomes, with some members disengaging while others carry the bulk of the tasks. Research shows that clearly defined roles and individual accountability significantly mitigate social loafing in educational settings.
The Role of Social Loafing in Sports Teams
Social loafing in sports teams often manifests when individual athletes exert less effort during group training sessions compared to solo practice, reducing overall team performance. Research indicates that social loafing increases in larger teams where individual contributions are harder to identify, lowering motivation and accountability. Effective strategies to counteract social loafing include assigning specific roles, enhancing peer evaluations, and fostering strong team cohesion.
Social Loafing in Online Collaborative Communities
In online collaborative communities, social loafing occurs when individuals contribute less effort because their input is less visible or harder to evaluate, leading to decreased overall productivity. Studies show that anonymity and lack of direct accountability in platforms like Wikipedia or open-source projects often result in reduced participation from some members. Effective strategies to counteract social loafing include implementing transparent contribution tracking and fostering a strong sense of group identity among participants.
Social Loafing in Nonprofit Organizations
In nonprofit organizations, social loafing often occurs when volunteers or team members reduce their effort, assuming others will compensate for their lack of contribution. This phenomenon can lead to decreased overall productivity and hinder the achievement of fundraising and community service goals. Effective management strategies, such as clear role assignments and accountability measures, are essential to minimize social loafing in nonprofit settings.
Social Loafing in Family and Household Tasks
Social loafing commonly occurs in family and household tasks when individual family members contribute less effort to chores, assuming others will compensate. This phenomenon often results in uneven distribution of work, leading to frustration and decreased overall productivity within the household. Research indicates that clearly defined roles and accountability can significantly reduce social loafing in family settings.
example of social loafing in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com