Deviance in peer groups often manifests through behaviors that violate social norms within the group. For example, a teenager consistently skipping school to engage in unauthorized activities represents deviant conduct among peers. Such actions disrupt the expected standards of behavior and can influence others to adopt similar patterns. Peer deviance includes acts like substance abuse, theft, or defiance of authority figures, which challenge the group's conventional rules. These behaviors can lead to social isolation or reinforce group solidarity depending on the peer dynamics. Data shows that peer influence significantly impacts the likelihood of youths engaging in deviant acts, highlighting the role of social context.
Table of Comparison
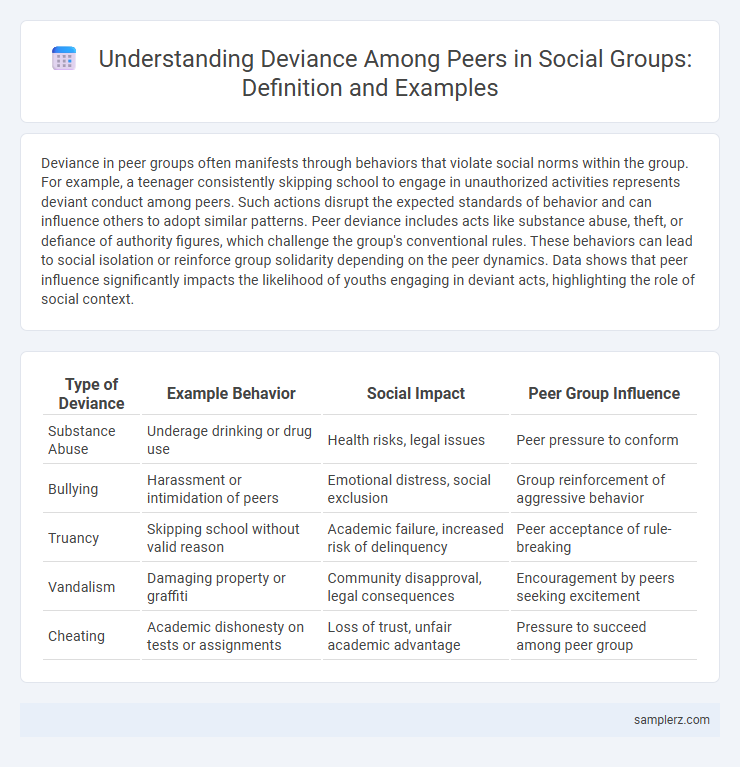
| Type of Deviance | Example Behavior | Social Impact | Peer Group Influence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Substance Abuse | Underage drinking or drug use | Health risks, legal issues | Peer pressure to conform |
| Bullying | Harassment or intimidation of peers | Emotional distress, social exclusion | Group reinforcement of aggressive behavior |
| Truancy | Skipping school without valid reason | Academic failure, increased risk of delinquency | Peer acceptance of rule-breaking |
| Vandalism | Damaging property or graffiti | Community disapproval, legal consequences | Encouragement by peers seeking excitement |
| Cheating | Academic dishonesty on tests or assignments | Loss of trust, unfair academic advantage | Pressure to succeed among peer group |
Common Forms of Peer Deviance in Social Groups
Common forms of peer deviance in social groups include substance abuse, such as alcohol and drug use, which often spreads through peer pressure and desire for acceptance. Delinquent behaviors like vandalism, theft, and truancy frequently emerge in close-knit peer networks where norms oppose societal rules. Engaging in risky sexual behavior and bullying are also prevalent, reflecting group dynamics that reinforce deviance to establish identity or status.
Real-Life Examples of Peer Group Deviant Behavior
Peer group deviant behavior often includes activities such as underage drinking, drug use, and vandalism, which are common in adolescent social settings. For example, studies show that teenagers involved in peer groups engaging in shoplifting or bullying are more likely to display antisocial traits and academic decline. Research from the National Institute on Drug Abuse highlights how peer pressure significantly contributes to early substance abuse among youth, emphasizing the social impact of deviant group norms.
How Peer Pressure Contributes to Deviance
Peer pressure significantly influences individuals, especially adolescents, to engage in deviant behaviors such as substance abuse, truancy, or delinquency by creating a compelling need for acceptance within social groups. Studies show that the desire to conform to peers' risky behaviors increases the likelihood of breaking societal norms and laws. Persistent peer-induced reinforcement strengthens deviant identities, making it challenging to revert to socially acceptable conduct.
Subtle Acts of Deviance Among Friends
Subtle acts of deviance among friends often include minor rule-breaking behaviors such as bending social norms, sharing confidential information, or engaging in small-scale dishonesty like white lies. These actions, though seemingly insignificant, gradually shift group dynamics and influence collective behavior patterns within peer networks. Research highlights that such covert deviance can undermine trust and contribute to more significant antisocial behavior over time.
Social Media and Peer Deviant Trends
Peer deviant trends on social media often include cyberbullying, where individuals use online platforms to harass or demean others, and the proliferation of risky challenges, such as dangerous stunts that gain viral attention. These behaviors reflect deviations from accepted norms, influenced by peer pressure and the desire for social validation within online communities. The anonymity and rapid information spread on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat amplify the impact and visibility of deviant peer behaviors.
Deviance in School: Peer Influence Case Studies
Deviance in school often manifests through peer influence, where students engage in behaviors such as truancy, bullying, or substance abuse to gain acceptance within social groups. Case studies reveal that peer pressure significantly increases the likelihood of students adopting deviant acts that challenge school norms and authority. Understanding these dynamics helps in developing targeted interventions to reduce negative peer-driven deviance in educational settings.
The Line Between Harmless Fun and Social Deviance
Engaging in harmless fun with peers often involves minor rule-breaking, such as harmless pranks or playful teasing, which fosters group cohesion and social bonding. However, when behaviors escalate to bullying, exclusion, or substance abuse, these actions cross the line into social deviance by violating group norms and harming relationships. Understanding this boundary is essential for maintaining healthy peer interactions and preventing long-term negative social consequences.
Groupthink and Collective Deviance in Peers
Groupthink in peer groups leads individuals to suppress dissenting opinions, resulting in irrational or dysfunctional decision-making that aligns with group consensus despite potential negative consequences. Collective deviance occurs when peers collectively engage in norm-violating behavior, reinforcing delinquent actions through mutual acceptance and social bonds. These dynamics undermine individual accountability and escalate deviant behavior within social networks.
Peer Deviance and Its Impact on Social Norms
Peer deviance, such as collective shoplifting or underage drinking among close-knit youth groups, disrupts established social norms by normalizing rule-breaking behavior within the peer context. This phenomenon alters group dynamics and can lead to wider community acceptance of deviant acts, eroding conventional standards. The reinforcement of deviant behavior through peer approval exemplifies the powerful role of social influence in shaping individual conduct.
Strategies to Address Deviant Behavior in Peer Groups
Peer groups often exhibit deviant behavior such as bullying, substance abuse, and exclusion, which can significantly impact social development. Strategies to address these behaviors include implementing peer mediation programs, fostering inclusive environments through social skills training, and encouraging positive peer influence via mentorship initiatives. Schools and community organizations play a vital role in promoting accountability and reinforcing pro-social norms among adolescents.
example of deviance in peer Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com