Heteronormativity in family structures typically assumes that a family consists of a married man and woman with their biological children. This perspective often marginalizes same-sex couples and single-parent families, reinforcing traditional gender roles and expectations. Data from sociological studies show that heteronormative assumptions influence policies related to parental rights and marriage benefits. Research indicates that heteronormativity affects family dynamics by shaping societal norms around caregiving and household responsibilities. Surveys reveal that children from non-heteronormative families face social challenges due to prevailing biases. These findings highlight the need for inclusive definitions of family that recognize diverse family compositions and promote equality.
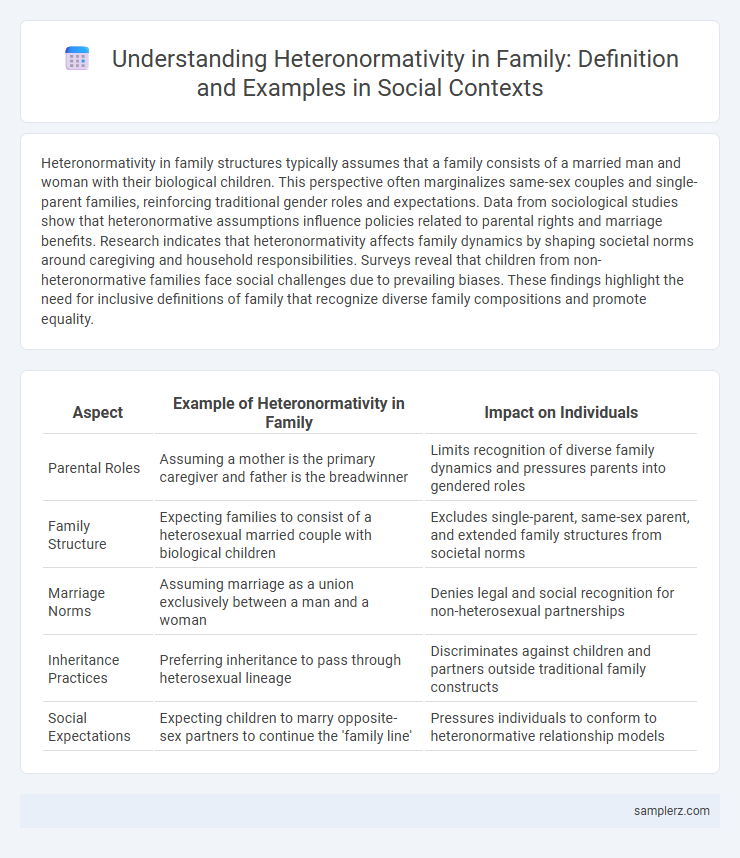
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Example of Heteronormativity in Family | Impact on Individuals |
|---|---|---|
| Parental Roles | Assuming a mother is the primary caregiver and father is the breadwinner | Limits recognition of diverse family dynamics and pressures parents into gendered roles |
| Family Structure | Expecting families to consist of a heterosexual married couple with biological children | Excludes single-parent, same-sex parent, and extended family structures from societal norms |
| Marriage Norms | Assuming marriage as a union exclusively between a man and a woman | Denies legal and social recognition for non-heterosexual partnerships |
| Inheritance Practices | Preferring inheritance to pass through heterosexual lineage | Discriminates against children and partners outside traditional family constructs |
| Social Expectations | Expecting children to marry opposite-sex partners to continue the 'family line' | Pressures individuals to conform to heteronormative relationship models |
Gender Roles in Household Chores
Traditional family structures often reinforce heteronormativity by assigning household chores based on rigid gender roles, with women predominantly responsible for cleaning, cooking, and childcare, while men are expected to handle maintenance and outdoor tasks. This division perpetuates gender inequality and limits opportunities for shared responsibilities and mutual respect within the household. Studies show that these patterns persist even in dual-income families, highlighting the deep-rooted influence of heteronormative expectations on domestic labor distribution.
Expectations Around Marriage and Children
Heteronormativity in families often enforces expectations that marriage must occur between a man and a woman and that having children is a natural or obligatory outcome. This framework marginalizes non-heterosexual relationships by promoting traditional gender roles and family structures. Research shows that these norms influence social policies and cultural attitudes, reinforcing exclusion of same-sex couples and childfree families.
Parental Reactions to LGBTQ+ Family Members
Parental reactions to LGBTQ+ family members often reflect heteronormative expectations through initial denial or attempts to change sexual orientation or gender identity. Studies show that families emphasizing traditional gender roles or heterosexual norms may experience higher conflict and psychological stress when a member comes out. Supportive environments that challenge heteronormativity improve mental health outcomes and foster acceptance within the family unit.
Heterosexual Assumptions in Family Gatherings
Heteronormativity in family gatherings often surfaces through implicit expectations that all couples are heterosexual, such as assuming a woman's partner is male or a man's partner is female. These assumptions can marginalize LGBTQ+ family members by invalidating their relationships and identities. Reinforcing traditional gender roles during celebrations further perpetuates heteronormative norms in familial contexts.
“Mom and Dad” as the Default Family Structure
The phrase "Mom and Dad" underscores heteronormativity by positioning heterosexual couples as the default family structure, marginalizing diverse family forms such as single-parent, same-sex, or non-binary parent families. This linguistic framing influences social policies and media representations, reinforcing traditional gender roles and expectations within the family unit. Consequently, the persistent use of "Mom and Dad" perpetuates a narrow definition of family, limiting social recognition and support for alternative family configurations.
Stereotypes in Family Media and Storytelling
Family media and storytelling often reinforce heteronormativity by portraying traditional nuclear families with a mother, father, and children, marginalizing diverse family structures. Stereotypes such as the caregiving mother and the breadwinning father perpetuate gender roles and exclude LGBTQ+ narratives. These portrayals shape societal expectations and influence perceptions of what constitutes a "normal" family.
Inheritance and Succession Based on Heteronormative Lines
Inheritance laws often prioritize married heterosexual couples, reinforcing heteronormative family structures by legally favoring biological or legally recognized spouses over other relations. Succession protocols typically exclude non-heteronormative partnerships, resulting in unequal distribution of assets for LGBTQ+ individuals. This legal framework perpetuates systemic disadvantages by maintaining traditional gender and relationship norms in family wealth transfer.
Pressure to Conform to Gender Norms
Families often impose strict expectations for children to conform to traditional gender roles, reinforcing heteronormativity by encouraging boys to exhibit masculinity and girls to embrace femininity. This pressure manifests in activities, clothing choices, and emotional expression, limiting individual identity exploration. Such enforcement perpetuates societal norms that prioritize heterosexual relationships and binary gender identities.
Exclusion of Non-Heteronormative Partners
Heteronormativity in families often manifests through the exclusion of non-heteronormative partners, where LGBTQ+ relationships are marginalized or deemed invalid. This exclusion limits social recognition and legal protections for same-sex or queer partnerships, reinforcing traditional gender and relationship norms. Such practices perpetuate systemic inequality by invalidating diverse family structures beyond heterosexual norms.
Religion and Heteronormativity in Family Values
Religious teachings often reinforce heteronormativity by promoting marriage exclusively between a man and a woman, shaping family values around traditional gender roles. Many faith-based communities uphold these doctrines, influencing social expectations and legitimizing nuclear family structures. Such religious frameworks contribute to the marginalization of LGBTQ+ identities within familial contexts.
example of heteronormativity in family Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com