Social loafing occurs when individuals put in less effort while working in a group compared to when they work alone. A common example is during group projects in school where some members contribute minimally, relying on others to complete the work. This behavior reduces overall group productivity and can negatively impact the group's final outcome. In workplace settings, social loafing often emerges in team tasks where individual performance is difficult to measure. Employees may withhold their full effort, assuming that their lack of contribution will go unnoticed. This phenomenon undermines team cohesion and can lead to unfair distribution of workload, causing frustration among more active participants.
Table of Comparison
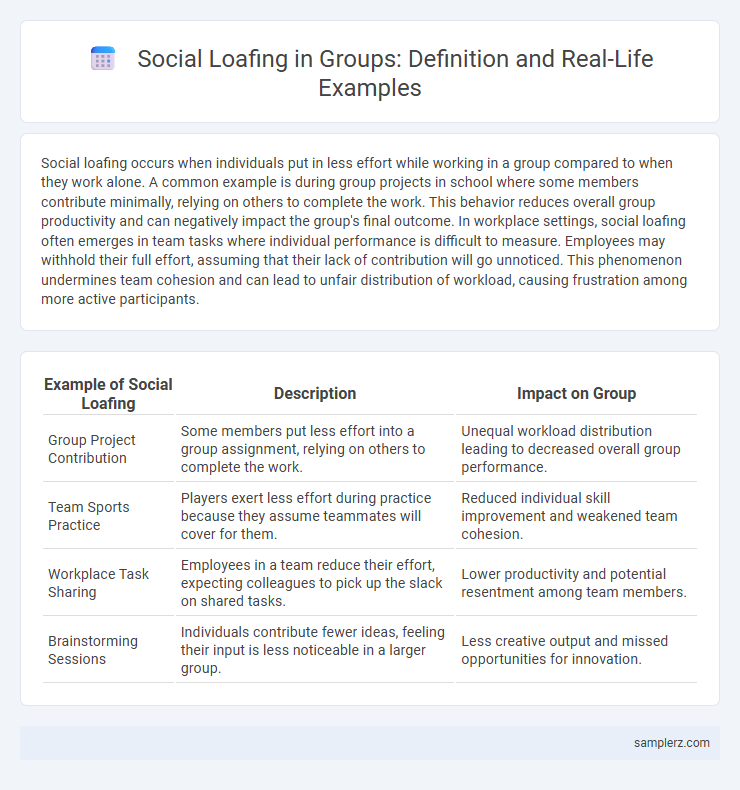
| Example of Social Loafing | Description | Impact on Group |
|---|---|---|
| Group Project Contribution | Some members put less effort into a group assignment, relying on others to complete the work. | Unequal workload distribution leading to decreased overall group performance. |
| Team Sports Practice | Players exert less effort during practice because they assume teammates will cover for them. | Reduced individual skill improvement and weakened team cohesion. |
| Workplace Task Sharing | Employees in a team reduce their effort, expecting colleagues to pick up the slack on shared tasks. | Lower productivity and potential resentment among team members. |
| Brainstorming Sessions | Individuals contribute fewer ideas, feeling their input is less noticeable in a larger group. | Less creative output and missed opportunities for innovation. |
Common Real-Life Examples of Social Loafing
In group projects at school, some members may contribute less effort, relying on others to complete the work, exemplifying social loafing. During office team meetings, employees often speak less or overlook responsibilities, expecting colleagues to fill the gaps. Sports teams also experience reduced individual effort when players assume teammates will compensate, leading to decreased overall performance.
Social Loafing in Workplace Teams
Social loafing in workplace teams occurs when individual members exert less effort because they believe others will compensate, leading to decreased productivity and morale. Research shows that in teams of five or more, individual contributions are often less visible, increasing the likelihood of social loafing. Implementing clear accountability measures and fostering team cohesion can significantly reduce the impact of social loafing in professional environments.
Group Projects in Schools: A Classic Case of Social Loafing
In group projects in schools, social loafing often manifests when some students contribute less effort, relying on others to complete the work. This behavior reduces overall group productivity and can lead to uneven workload distribution. Research shows that clearly defined roles and accountability measures help minimize social loafing in academic settings.
Volunteer Organizations and Social Loafing
In volunteer organizations, social loafing often occurs when some members reduce their effort because they believe others will compensate, leading to decreased overall productivity and engagement. For example, during community clean-up events, certain volunteers may contribute less, assuming their peers will complete the tasks, diminishing group effectiveness. Addressing social loafing requires clear role assignments and individual accountability to ensure active participation and maximize volunteer impact.
Social Loafing in Sports Teams
Social loafing in sports teams occurs when individual athletes exert less effort during training or games, relying on teammates to carry the workload. This phenomenon often leads to decreased overall team performance and reduced motivation among diligent players. Research shows that clearly defined roles and individual accountability can significantly reduce social loafing in competitive sports environments.
Online Collaboration and Social Loafing Behaviors
In online collaboration, social loafing often manifests when group members contribute less effort due to perceived anonymity and reduced accountability within digital platforms. Studies indicate that without clear role assignments and performance tracking, participants tend to rely excessively on others, leading to decreased productivity. Utilizing collaborative tools with transparent activity logs can mitigate social loafing by enhancing individual responsibility.
Social Loafing at Community Events
Social loafing frequently occurs at community events when individuals in large volunteer groups contribute less effort, assuming others will compensate. This phenomenon reduces overall productivity, as personal accountability diminishes in expansive gatherings like charity drives or neighborhood clean-ups. Studies reveal that clearly defined roles and smaller team sizes effectively mitigate social loafing at community functions.
Social Loafing in Family Group Tasks
Social loafing frequently occurs in family group tasks, such as when siblings are assigned household chores but some members contribute less effort, relying on others to complete the work. Research indicates that individual accountability decreases as group size increases, leading to reduced motivation and uneven participation. Effective strategies to counter social loafing in family settings include assigning specific roles and emphasizing personal responsibility for task completion.
Cultural Influences on Social Loafing Examples
In collectivist cultures, social loafing tends to be less prevalent as group members prioritize communal goals and social harmony. Conversely, individualistic cultures may experience higher social loafing rates due to a stronger emphasis on personal achievement and autonomy. Studies in cross-cultural psychology highlight that cultural values significantly impact the degree to which individuals reduce effort in group tasks.
Strategies to Recognize Social Loafing in Groups
Social loafing in groups becomes evident when certain members consistently contribute less effort or rely on others to complete tasks, leading to uneven workload distribution. Observing decreases in individual accountability through missed deadlines or lack of participation in discussions helps to recognize social loafing early. Implementing clear performance metrics and monitoring individual contributions in collaborative projects can effectively identify and address social loafing behaviors.
example of social loafing in group Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com