The looking-glass self is a social psychological concept where individuals shape their self-identity based on how they believe others perceive them. For example, a teenager may develop confidence or insecurity depending on the feedback they receive from peers regarding their appearance or behavior. This continuous interaction with social mirrors enables people to adjust their self-concept in response to perceived judgments. In a workplace setting, an employee might assess their competence through the reactions and evaluations of colleagues and supervisors. Positive recognition can enhance their self-esteem, while criticism might prompt self-reflection and improvement. The looking-glass self emphasizes the role of social interactions and perceived perceptions in constructing personal identity.
Table of Comparison
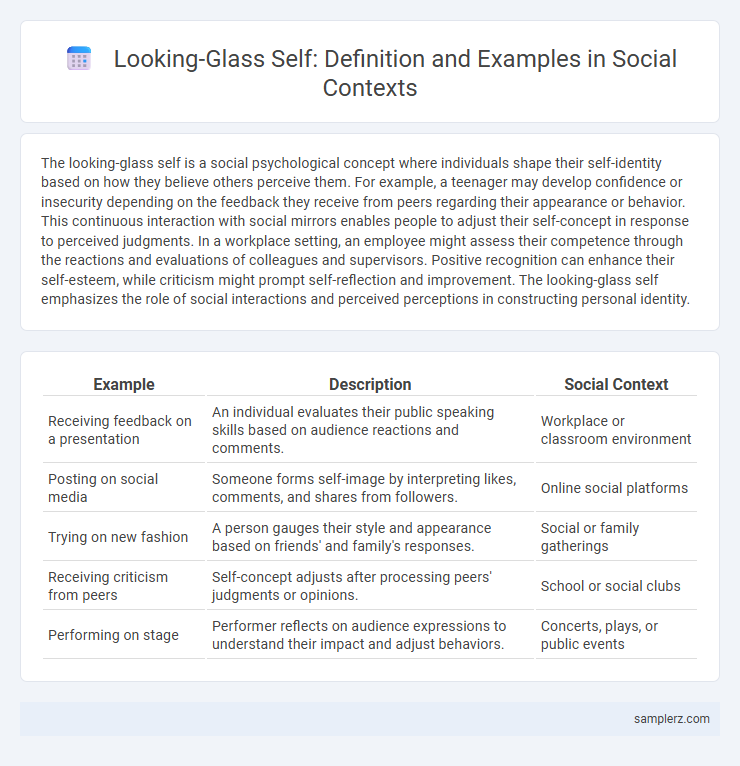
| Example | Description | Social Context |
|---|---|---|
| Receiving feedback on a presentation | An individual evaluates their public speaking skills based on audience reactions and comments. | Workplace or classroom environment |
| Posting on social media | Someone forms self-image by interpreting likes, comments, and shares from followers. | Online social platforms |
| Trying on new fashion | A person gauges their style and appearance based on friends' and family's responses. | Social or family gatherings |
| Receiving criticism from peers | Self-concept adjusts after processing peers' judgments or opinions. | School or social clubs |
| Performing on stage | Performer reflects on audience expressions to understand their impact and adjust behaviors. | Concerts, plays, or public events |
Understanding the Looking-Glass Self in Social Interactions
The looking-glass self shapes individual identity through social interactions by reflecting how others perceive and respond to us. When engaging in conversations or group activities, people interpret others' reactions as mirrors, adjusting their behavior and self-concept accordingly. This dynamic process highlights the importance of empathy and perspective-taking in forming a coherent self-image within social contexts.
Everyday Examples of the Looking-Glass Self
The looking-glass self manifests in everyday social interactions, such as when individuals adjust their behavior based on perceived reactions from friends or colleagues during conversations. For example, a person might smile more in group settings after observing others' positive responses, shaping their self-image through reflected appraisals. These ongoing feedback loops influence self-identity continuously through social contexts like workplace meetings, family gatherings, and online social media engagements.
The Role of Social Feedback in Shaping Identity
Social feedback plays a crucial role in shaping identity by reflecting back how individuals perceive themselves through others' responses. For instance, when peers praise someone's creativity, that person internalizes this perception, strengthening their self-concept as innovative and talented. This dynamic process illustrates the looking-glass self, where identity is continuously molded by social interactions and external evaluations.
Mirror Reflections: Perceiving Ourselves Through Others
Mirror reflections in social interactions illustrate the looking-glass self by showing how individuals internalize others' perceptions to shape their self-identity. Observing reactions such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body language allows people to form an image of themselves based on external feedback. This dynamic highlights the powerful role of social environments in constructing personal self-concepts through continuous social mirroring.
Social Media as a Modern Looking-Glass
Social media platforms like Instagram and Facebook serve as modern looking-glasses by reflecting users' identities through the feedback and reactions of their online networks. The constant interaction with likes, comments, and shares shapes self-perception and influences behavior, reinforcing the concept of the looking-glass self. This digital reflection intensifies social comparison and identity formation in virtual environments.
Looking-Glass Self in Group Dynamics
The looking-glass self in group dynamics illustrates how individuals develop self-identity by interpreting others' perceptions within social groups. Group feedback acts as a mirror, shaping members' self-concepts and influencing behavior to align with perceived group norms. This process reinforces social cohesion and impacts personal and collective identity formation.
Childhood Experiences and the Looking-Glass Self
Childhood experiences play a crucial role in shaping the looking-glass self by influencing how children perceive themselves through the reactions of parents, peers, and educators. Early social interactions create internalized reflections, where children imagine how others view them and adjust their self-concept accordingly. These formative social feedback loops contribute to identity development and emotional growth throughout adolescence.
The Impact of Peer Opinions on Self-Image
Peer opinions play a critical role in shaping self-image through the looking-glass self concept, where individuals interpret how others perceive them and adjust their self-concept accordingly. Social interactions with peers provide feedback that influences self-esteem and identity formation, especially during adolescence. Negative or positive peer evaluations can significantly alter one's self-perception, reinforcing or challenging internal beliefs about oneself.
Navigating Self-Concept in Multicultural Settings
In multicultural settings, the looking-glass self shapes individual self-concept through the perceived judgments of diverse social groups, influencing identity negotiation and adaptation. Interactions with varied cultural norms and values compel individuals to continuously interpret and internalize others' reactions, fostering a dynamic and fluid self-image. This process enhances cross-cultural communication skills and empathy by aligning self-perception with multicultural social feedback.
Improving Self-Awareness Through Social Reflection
The looking-glass self concept illustrates how individuals improve self-awareness by internalizing others' perceptions during social interactions. Feedback from peers in various environments, such as workplaces or social groups, enables people to adjust their behavior and self-image for better social integration. This process fosters continuous self-reflection and personal growth influenced by others' responses.
example of looking-glass self in social Infographic
 samplerz.com
samplerz.com